Part 3
Identify which statements refer to a hearing aid, which refer to a cochlear implant, or both.
a. It works as a transducer, converting vibrational energy to electrical (electrochemical and electromechanical) energy. Cochlear implant
b. It helps people whose hearing loss is caused by problems in the outer or middle ear. Hearing aid
c. It increases the vibrational energy entering the ear. Hearing aid d. It helps sounds bypass injured or absent hair cells. Cochlear implant
e. It helps people whose hearing loss is caused by problems in the inner ear. Cochlear implant
f. It can help profoundly deaf people communicate using sound.
Cochlear implant
Content Standard C:
4. Conclude the activity by reviewing students’ answers to the tasks posed on Master 4.5. During the discussion, supplement the infor-Disease is a break-
mation students have already been given about the hearing path-down in structure or
way as appropriate.
function of an organ-
ism.
For example, students may be interested to learn that hair cells are unparalleled in their ability to detect the minute levels of vibrational energy in sound waves, and that they respond 1,000 times faster to stimulation than do visual-receptor cells.
103
Student Lesson 4
How Your Brain Understands What Your Ear Hears
Lesson 4 Organizer: Web Version
Activity 1: The Mysterious Black Box
What the Teacher Does
Procedure Reference
Introduce the concept of transduction as it relates to human Page 95
hearing and explain that they will complete a Web-based
Steps 1 and 2
activity about the hearing pathway.
Have students log onto Web site and click on “Lesson 4—A
Pages 95–96
Black Box problem: How Do I Hear?”
Step 3
• Instruct students to follow the directions and place the images of the hearing pathway in their proper sequence.
Activity 2: Understanding Form and Function
What the Teacher Does
Procedure Reference
Review the concept of transduction.
Pages 100–101
Step 1
Write the terms “vibration,” “pressure wave,” and “electrical Page 101
impulse” on the board and have the class apply them to each Step 2
part of the hearing pathway.
Have students complete the tasks on Master 4.5, Under-Pages 101–103
standing Form and Function.
Step 3
Review and discuss student responses to the tasks posed on Page 103
Master 4.5.
Step 4
= Involves using the Internet.
= Involves copying a master.
104
Lesson 4 Organizer: Print Version
Activity 1: The Mysterious Black Box
What the Teacher Does
Procedure Reference
Turn on a lamp and ask how the light bulb produces light.
Page 96
Step 1
Write “transduction” on the board.
Page 96
• Explain that it refers to the process by which energy is Step 2
converted from one form to another.
• Ask students if they can name other examples of
transducers.
Display a transparency of Master 4.1, The Mysterious Black Pages 97–98
Box.
Step 3
• Ask students to identify the question it raises.
Display a transparency of Master 4.2, A Few Questions.
Page 98
• Ask students to answer the questions.
Step 4
Explain that students will use Black Box Cards to construct a Page 98
flow chart of the hearing pathway.
Step 5
Distribute Black Box Cards (from Master 4.3) to each stu-
Page 99
dent team and instruct them to put the cards into the cor-Step 6
rect sequence.
Test each student team’s card sequence.
Page 99
• Have each team explain their sequence.
Step 7
• If the sequence is correct ring the bell.
= Involves using a transparency.
= Involves copying a master.
105
Student Lesson 4
How Your Brain Understands What Your Ear Hears
Write the names of the hearing-pathway components on the
Pages 99–100
board.
Step 8
• Have students match the names with the images on
their cards.
Construct the hearing pathway on the board.
Page 100
Step 9
Activity 2: Understanding Form and Function
What the Teacher Does
Procedure Reference
Review the concept of transduction.
Pages 100–101
Step 1
Write the terms “vibration,” “pressure wave,” and “electrical Page 101
impulse” on the board and have the class apply them to
Step 2
each part of the hearing pathway.
Have students complete the tasks on Master 4.5, Under-Pages 101–103
standing Form and Function.
Step 3
Review and discuss student responses to the tasks posed on Page 103
Master 4.5.
Step 4
106

The Mysterious Black Box
Master 4.1
A Few Questions
1. What do the lines between the bell and the ear indicate?
2. What is a sound wave?
3. Do vibrations reach all the way into the brain to let us hear sound?
Master 4.2
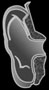





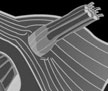
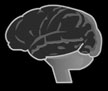
Black Box Cards
Focuses sound waves; helps in determining
Conducts sound waves to the eardrum.
the direction from which sound waves arrive.
System of bones that works as a lever system
Vibrates in response to arriving sound waves.
to transmit vibrations deeper into the ear and
to increase the vibrations’ force.
Tiny hairlike extensions on the cells in this
structure move in response to pressure waves
Liquid inside this structure transmits pres-
in surrounding liquid, causing cells to make
sure waves in response to vibrations.
generate electrical impulses that vary accord-
ing to the waves’ amplitude and frequency.
Interprets electrical impulses as sounds of
Carries electrical impulses to the brain.
varying pitch, loudness, and timing.
Master 4.3
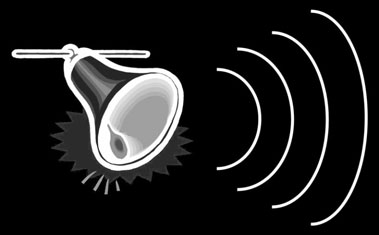
The Bell Card
Master 4.4
Understanding Form and Function
Name(s)_________________________________________
Date____________________________













