Chapter 1
Acoustics for Music Theory1
1.1 Music is Organized Sound Waves
Music is sound that's organized by people on purpose, to dance to, to tell a story, to make other people feel a certain way, or just to sound pretty or be entertaining. Music is organized on many different levels. Sounds can be arranged into melodies2, harmonies3, rhythms4, textures5 and phrases6. Beats7, measures8, cadences9, and form10 all help to keep the music organized and understandable. But the most basic way that music is organized is by arranging the actual sound waves themselves so that the sounds are interesting and pleasant and go well together.
A rhythmic, organized set of thuds and crashes is perfectly good music - think of your favorite drum solo - but many musical instruments are designed specifically to produce the regular, evenly spaced sound waves that we hear as particular pitches11. Crashes, thuds, and bangs are loud, short jumbles of lots of different wavelengths. These are the kinds of sound we often call "noise", when they're random and disorganized, but as soon as they are organized in time (rhythm12), they begin to sound like music. (When used as a scientific term, noise refers to continuous sounds that are random mixtures of different wavelengths, not shorter crashes and thuds.)
However, to get the melodic kind of sounds more often associated with music, the sound waves must themselves be organized and regular, not random mixtures. Most of the sounds we hear are brought to our ears through the air. A movement of an object causes a disturbance of the normal motion of the air molecules near the object. Those molecules in turn disturb other nearby molecules out of their normal patterns of random motion, so that the disturbance itself becomes a thing that moves through the air - a sound wave. If the movement of the object is a fast, regular vibration, then the sound waves are also very regular. We hear such regular sound waves as tones, sounds with a particular pitch13. It is this kind of sound that we most often associate with music, and that many musical instruments are designed to make.
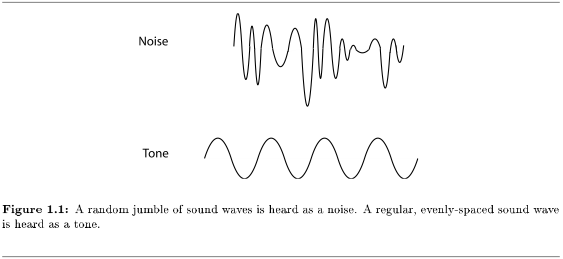
Musicians have terms that they use to describe tones. (Musicians also have other meanings for the word "tone", but this course will stick to the "a sound with pitch" meaning.) This kind of (regular, evenly spaced) wave is useful for things other than music, however, so scientists and engineers also have terms that describe pitched sound waves. As we talk about where music theory comes from, it will be very useful to know both the scientific and the musical terms and how they are related to each other.
For example, the closer together those evenly-spaced waves are, the higher the note sounds. Musicians talk about the pitch14 of the sound, or name specific notes15, or talk about tuning (Chapter 5). Scientists and engineers, on the other hand, talk about the frequency (p. 5) and the wavelength (p. 5) of the sound. They are all essentially talking about the same things, but talking about them in slightly different ways, and using the scientific ideas of wavelength and frequency can help clarify some of the main ideas underlying music theory.
1.2 Longitudinal and Transverse Waves
So what are we talking about when we speak of sound waves? Waves are disturbances; they are changes in something - the surface of the ocean, the air, electromagnetic fields. Normally, these changes are traveling (except for standing waves (Chapter 2)); the disturbance is moving away from whatever created it, in a kind of domino effect.
Most kinds of waves are transverse waves. In a transverse wave, as the wave is moving in one direction, it is creating a disturbance in a different direction. The most familiar example of this is waves on the surface of water. As the wave travels in one direction - say south - it is creating an up-and-down (not north-and-south) motion on the water's surface. This kind of wave is fairly easy to draw; a line going from left-to-right has up-and-down wiggles. (See Figure 1.2 (Transverse and Longitudinal Waves).)
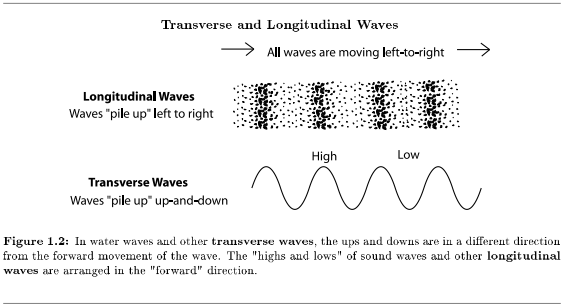
But sound waves are not transverse. Sound waves are longitudinal waves. If sound waves are moving south, the disturbance that they are creating is giving the air molecules extra north-and-south (not east-and-west, or up-and-down) motion. If the disturbance is from a regular vibration, the result is that the molecules end up squeezed together into evenly-spaced waves. This is very difficult to show clearly in a diagram, so most diagrams, even diagrams of sound waves, show transverse waves.
Longitudinal waves may also be a little difficult to imagine, because there aren't any examples that we can see in everyday life (unless you like to play with toy slinkies). A mathematical description might be that in longitudinal waves, the waves (the disturbances) are along the same axis as the direction of motion of the wave; transverse waves are at right angles to the direction of motion of the wave. If this doesn't help, try imagining yourself as one of the particles that the wave is disturbing (a water drop on the surface of the ocean, or an air molecule). As it comes from behind you, a transverse waves lifts you up and then drops down; a longitudinal wave coming from behind pushes you forward and pulls you back. You can view here animations of longitudinal and transverse waves16, single particles being disturbed by a transverse wave or by a longitudinal wave17, and particles being disturbed by transverse and longitudinal waves18.
The result of these "forward and backward" waves is that the "high point" of a sound wave is where the air molecules are bunched together, and the "low point" is where there are fewer air molecules. In a pitched sound, these areas of bunched molecules are very evenly spaced. In fact, they are so even, that there are some very useful things we can measure and say about them. In order to clearly show you what they are, most of the diagrams in this course will show sound waves as if they are transverse waves.
1.3 Wave Amplitude and Loudness
Both transverse and longitudinal waves cause a displacement of something: air molecules, for example, or the surface of the ocean. The amount of displacement at any particular spot changes as the wave passes. If there is no wave, or if the spot is in the same state it would be in if there was no wave, there is no displacement. Displacement is biggest (furthest from "normal") at the highest and lowest points of the wave. In a sound wave, then, there is no displacement wherever the air molecules are at a normal density. The most displacement occurs wherever the molecules are the most crowded or least crowded.
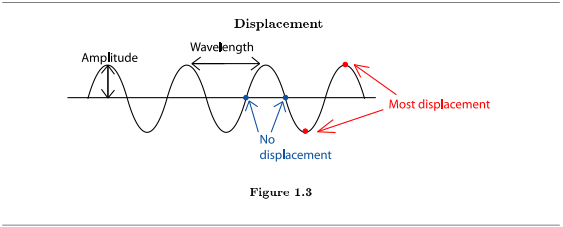
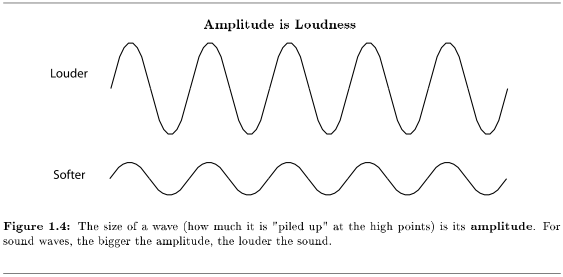
The amplitude of the wave is a measure of the displacement: how big is the change from no displacement to the peak of a wave? Are the waves on the lake two inches high or two feet? Are the air molecules bunched very tightly together, with very empty spaces between the waves, or are they barely more organized than they would be in their normal course of bouncing off of each other? Scientists measure the amplitude of sound waves in decibels. Leaves rustling in the wind are about 10 decibels; a jet engine is about 120 decibels.
Musicians call the loudness of a note its dynamic level. Forte (pronounced "FOR-tay") is a loud dynamic level; piano is soft. Dynamic levels don't correspond to a measured decibel level. An orchestra playing "fortissimo" (which basically means "even louder than forte") is going to be quite a bit louder than a string quartet playing "fortissimo". (See Dynamics19 for more of the terms that musicians use to talk about loudness.) Dynamics are more of a performance issue than a music theory issue, so amplitude doesn't need much discussion here.
1.4 Wavelength, Frequency, and Pitch
The aspect of evenly-spaced sound waves that really affects music theory is the spacing between the waves, the distance between, for example, one high point and the next high point. This is the wavelength, and it affects the pitch20 of the sound; the closer together the waves are, the higher the tone sounds.
All sound waves are travelling at about the same speed - the speed of sound. So waves with a shorter wavelength arrive (at your ear, for example) more often (frequently) than longer waves. This aspect of a sound - how often a peak of a wave goes by, is called frequency by scientists and engineers. They measure it in hertz, which is how many peaks go by per second. People can hear sounds that range from about 20 to about 17,000 hertz.
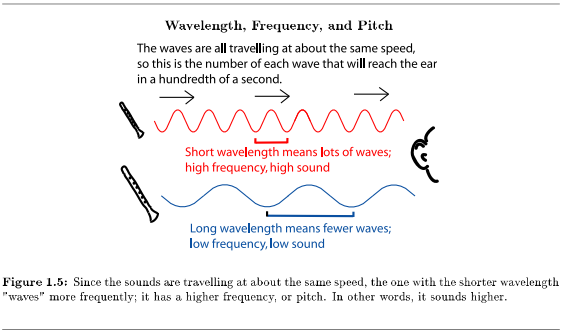
The word that musicians use for frequency is pitch. The shorter the wavelength, the higher the frequency, and the higher the pitch, of the sound. In other words, short waves sound high; long waves sound low. Instead of measuring frequencies, musicians name the pitches21 that they use most often. They might call a note "middle C" or "second line G" or "the F sharp in the bass clef". (See Octaves and Diatonic Music (Chapter 4) and Tuning Systems (Chapter 5) for more on naming specific frequencies.) These notes have frequencies (Have you heard of the "A 440" that is used as a tuning note?), but the actual frequency of a middle C can vary a little from one orchestra, piano, or performance, to another, so musicians usually find it more useful to talk about note names.
Most musicians cannot name the frequencies of any notes other than the tuning A (440 hertz). The human ear can easily distinguish two pitches that are only one hertz apart when it hears them both, but it is the very rare musician who can hear specifically that a note is 442 hertz rather than 440. So why should we bother talking about frequency, when musicians usually don't? As we will see, the physics of sound waves - and especially frequency - affects the most basic aspects of music, including pitch22, tuning (Chapter 5), consonance and dissonance23, harmony24, and timbre25.
NOTES:
1 This content is available online at <http://cnx.org/content/m13246/1.13/>.
2"Melody" <http://cnx.org/content/m11647/latest/>
3"Harmony" <http://cnx.org/content/m11654/latest/>
4"Rhythm" <http://cnx.org/content/m11646/latest/>
5"The Textures of Music" <http://cnx.org/content/m11645/latest/>
6"Melody": Section Melodic Phrases <http://cnx.org/content/m11647/latest/#s2>
7"Time Signature": Section Beats and Measures <http://cnx.org/content/m10956/latest/#s1>
8"The Staff": Section The Staff <http://cnx.org/content/m10880/latest/#s1>
9"Cadence in Music" <http://cnx.org/content/m12402/latest/>
10"Form in Music" <http://cnx.org/content/m10842/latest/>
11"Pitch: Sharp, Flat, and Natural Notes" <http://cnx.org/content/m10943/latest/>
12"Rhythm" <http://cnx.org/content/m11646/latest/>
13"Pitch: Sharp, Flat, and Natural Notes" <http://cnx.org/content/m10943/latest/>
14"Pitch: Sharp, Flat, and Natural Notes" <http://cnx.org/content/m10943/latest/>
15"Clef" <http://cnx.org/content/m10941/latest/>
16 See the file at <http://cnx.org/content/m13246/latest/Waves.swf>
17 See the file at <http://cnx.org/content/m13246/latest/Pulses.swf>
18 See the file at <http://cnx.org/content/m13246/latest/Translong.swf>
19"Dynamics and Accents in Music" <http://cnx.org/content/m11649/latest/>
20"Pitch: Sharp, Flat, and Natural Notes" <http://cnx.org/content/m10943/latest/>
21"Clef" <http://cnx.org/content/m10941/latest/>
22"Pitch: Sharp, Flat, and Natural Notes" <http://cnx.org/content/m10943/latest/>
23"Consonance and Dissonance" <http://cnx.org/content/m11953/latest/>
24"Harmony" <http://cnx.org/content/m11654/latest/>
25"Timbre: The Color of Music" <http://cnx.org/content/m11059/latest/>








