FOREX TRADING TERMINOLOGY
The Forex market comes with its very own set of terms and jargon. So, before you go any deeper into learning how to trade the Fx market, it’s important you understand some of the basic Forex terminology that you will encounter on your trading journey…
• Basic Forex terms:Cross rate - The currency exchange rate between two currencies, both of which are not the official currencies of the country in which the exchange rate quote is given in. This phrase is also sometimes used to refer to currency quotes which do not involve the U.S. dollar, regardless of which country the quote is provided in.
For example, if an exchange rate between the British pound and the Japanese yen was quoted in an American newspaper, this would be considered a cross rate in this context, because neither the pound or the yen is the standard currency of the U.S. However, if the exchange rate between the pound and the U.S. dollar were quoted in that same newspaper, it would not be considered a cross rate because the quote involves the U.S. official currency.
Exchange Rate - The value of one currency expressed in terms of another. For example, if EUR/USD is 1.3200, 1 Euro is worth US$1.3200.
Pip – The smallest increment of price movement a currency can make. Also called point or points. For example, 1 pip for the EUR/USD = 0.0001 and 1 pip for the USD/JPY = 0.01.
Leverage - Leverage is the ability to gear your account into a position greater than your total account margin. For instance, if a trader has $1,000 of margin in his account and he opens a $100,000 position, he leverages his account by 100 times, or 100:1. If he opens a $200,000 position with $1,000 of margin in his account, his leverage is 200 times, or 200:1. Increasing your leverage magnifies both gains and losses.
To calculate the leverage used, divide the total value of your open positions by the total margin balance in your account. For example, if you have $10,000 of margin in your account and you open one standard lot of USD/JPY (100,000 units of the base currency) for $100,000, your leverage ratio is 10:1 ($100,000 / $10,000). If you open one standard lot of EUR/USD for $150,000 (100,000 x EURUSD 1.5000) your leverage ratio is 15:1 ($150,000 / $10,000).
Margin - The deposit required to open or maintain a position. Margin can be either “free” or “used”. Used margin is that amount which is being used to maintain an open position, whereas free margin is the amount available to open new positions.
With a $1,000 margin balance in your account and a 1% margin requirement to open a position, you can buy or sell a position worth up to a notional $100,000. This allows a trader to leverage his account by up to 100 times or a leverage ratio of 100:1.
If a trader’s account falls below the minimum amount required to maintain an open position, he will receive a “margin call” requiring him to either add more money into his or her account or to close the open position.
Most brokers will automatically close a trade when the margin balance falls below the amount required to keep it open. The amount required to maintain an open position is dependent on the broker and could be 50% of the original margin required to open the trade.
Spread - The difference between the sell quote and the buy quote or the bid and offer price. For example, if EUR/USD quotes read 1.3200/03, the spread is the difference between 1.3200 and 1.3203, or 3 pips. In order to break even on a trade, a position must move in the direction of the trade by an amount equal to the spread.
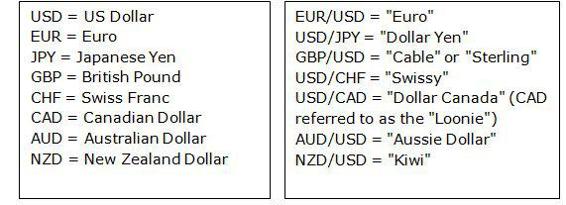
• The major Forex pairs and their nicknames:
• Understanding Forex currency pair quotes:
You will need to understand how to properly read a currency pair quote before you start trading them. So, let’s get started with this:The exchange rate of two currencies is quoted in a pair, such as the EURUSD or the USDJPY. The reason for this is because in any foreign exchange transaction you are simultaneously buying one currency and selling another.
If you were to buy the EURUSD and the euro strengthened against the dollar, you would then be in a profitable trade. Here’s an example of a Forex quote for the euro vs. the U.S. dollar:
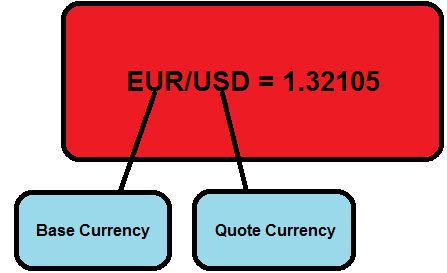
The first currency in the pair that is located to the left of the slash mark is called the base currency, and the second currency of the pair that’s located to the right of the slash market is called the counter or quote currency.
If you buy the EUR/USD (or any other currency pair), the exchange rate tells you how much you need to pay in terms of the quote currency to buy one unit of the base currency. In other words, in the example above, you have to pay 1.32105 U.S. dollars to buy 1 euro.
If you sell the EUR/USD (or any other currency pair), the exchange rate tells you how much of the quote currency you receive for selling one unit of the base currency. In other words, in the example above, you will receive 1.32105 U.S. dollars if you sell 1 euro.
An easy way to think about it is like this: the BASE currency is the BASIS for the trade. So, if you buy the EURUSD you are buying euro’s (base currency) and selling dollars (quote currency), if you sell the EURUSD you are selling euro’s (base currency) and buying dollars (quote currency). So, whether you buy or sell a currency pair, it is always based upon the first currency in the pair; the base currency.
The basic point of Forex trading is to buy a currency pair if you think its base currency will appreciate (increase in value) relative to the quote currency. If you think the base currency will depreciate (lose value) relative to the quote currency you would sell the pair.
• Bid and Ask price
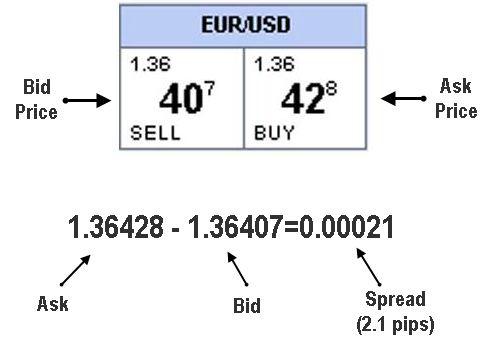
Bid Price – The bid is the price at which the market (or your broker) will buy a specific currency pair from you. Thus, at the bid price, a trader can sell the base currency to their broker.
Ask Price – The ask price is the price at which the market (or your broker) will sell a specific currency pair to you. Thus, at the ask price you can buy the base currency from your broker.
Bid/Ask Spread – The spread of a currency pair varies between brokers and it is the difference between the bid and ask the price.
Article by Nial Fuller and sourced from learntotradethemarket.com






