Chapter 10: Using CredSSP for multi-hop authentication
In this chapter, we will look at how CredSSP7 can be used for multi-hop authentication8 in PowerShell remoting. CredSSP and multi-hop support are not features of PowerShell 2.0 or PowerShell remoting, per se. Credential Security Service Provider (CredSSP) is a new security service provider that enables an application to delegate the user’s credentials from the client to the target server. Multi-hop support in Windows Remote Management uses CredSSP for authentication. Since PowerShell 2.0 remoting is built on top of WinRM, we can use CredSSP to perform multi-hop authentication.
Let us look at an example to understand what multi-hop authentication is. Imagine a group of computers as shown here and you establish a remoting session from computer A (client) to computer B (server) and then from computer B, you try to create a file in a file share on computer C.
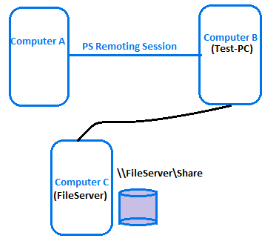
Now, within the remoting session to computer B, we want to execute a command — as below — to create test.txt on computer C.
Invoke-Command -ComputerName Test-PC.SP2010lab.com -credential SP2010LAB\Administrator ScriptBlock {[System.IO.File]::Create(\\FileServer\Share\Test.txt)}
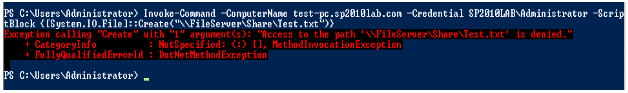
Figure 18 file share access error
This command results in an “Access Denied” error as shown above. This command fails since the remote session tries to access the file share using the machine credentials instead of the credentials used to invoke the remote session. We could have successfully created the text file if there was a way to pass or delegate credentials from the client so that we can authenticate to the file share. This is what is called multi-hop authentication and PowerShell remoting enables this using CredSSP. Note: When a domain controller (Windows Server 2008 or Windows Server 2008 R2 is used as a second hop, the credentials are always received and delegated without the need for CredSSP. Refer to https://connect.microsoft.com/PowerShell/feedback/details/630672/a-domain-controller-receives-anddelegates-credentials-even-when-credssp-is-not-configured for more information on this. The reason for this is the “Trust this computer delegation to any service (Kerberos only)” setting “Delegation Tab” of a Domain controller’s properties in AD users and computer snap-in. This is enabled by default on all domain controllers.
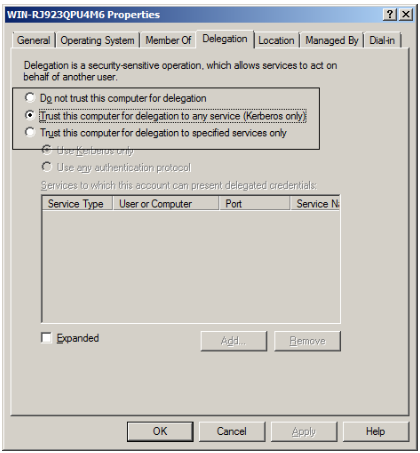
Delegating credentials
The cmdlets to create a remoting session — Invoke-Command, Enter-PSSession and New-PSSession – have a parameter to specify the authentication method as CredSSP. However, before we use this parameter, we need to enable credSSP on the computers participating in multi-hop authentication. Also, when enabling CredSSP, we need to specify the role — client or server — of a computer. A client is the computer from which the remoting session is initiated and server is the computer from which the multihop authentication is triggered. So, from the above example, we need to enable CredSSP authentication on computer A and computer B.
PowerShell 2.0 provides the following cmdlets to manage CredSSP authentication.
1. Enable-WSManCredSSP
2. Disable-WSManCredSSP
3. Get-WSManCredSSP
Let us now look at how we enable WSManCredSSP and specify client / server roles. First, let us enable CredSSP on computer A.
Note

Enable-WSManCredSSP -Role Client -DelegateComputer "*.SP2010lab.com"
As shown here, you can use Enable-WSManCredSSP cmdlet to enable CredSSP authentication and specify the computer role as client. When the computer role is defined as a client, you can also specify the DelegateComputer parameter to specify the server or servers that receive the delegated credentials from the client. The delegateComputer accepts wildcards as shown above. You can also specify “*” to specify all computers in the network.
When Enable-WSManCredSSP cmdlet is used to enable CredSSP on the client by specifying client in the role parameter. The cmdlet then performs the following:
1. The WS-Management setting <localhost|computername>\Client\Auth\CredSSP is set to true.
2. Sets the Windows CredSSP policy AllowFreshCredentials to WSMan/Delegate on the client.
Now, we will enable CredSSP on computer B and deginate that as server.
Enable-WSManCredSSP -Role Server
The above cmdlet enables CredSSP on computer B and sets the WS-Management setting <localhost|computername>\Service\Auth\CredSSP is to true. Now, we can use Invoke-Command to run the script block as shown at the beginning of this post. However, we will specify the authentication method as CredSSP and pass the credentials.
Invoke-Command -ComputerName test-pc.SP2010lab.com -Credential SP2010Lab\Administrator Authentication CredSSP -ScriptBlock {[System.IO.File]::Create(\\FileServer\Share\Test.txt)}
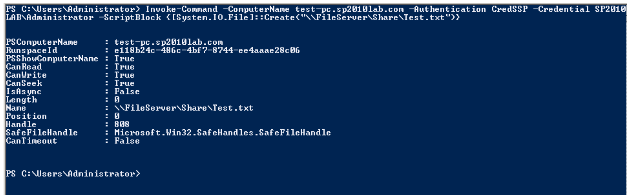
Figure 19 CredSSP authentication
As you see here, we see the output from Create() method which shows the details of the newly created file.
Caution

You can use Disable-WSManCredSSP to disable CredSSP authentication on a client or a server computer.
Disable-WSManCredSSP -Role Client
Disable-WSManCredSSP -Role Server
You can use Get-WSManCredSSP cmdlet to verify if a computer has CredSSP enabled and also the role (client/server).
Summary
Credential delegation is required when you need to access or authenticate to a second computer within a remote session. Some of the other examples also include SharePoint 2010 cmdlets. Since, every SharePoint cmdlet will have to gather data from various servers within the farm and depending on how you farm accounts are configured, you may need to use CredSSP authentication to authenticate to all the servers within the farm.
This chapter concludes this remoting guide.








