7.4 Repeaters
Unfortunately, long distance line of sight isn't always possible. Sometimes, you will encounter an obstacle that you simply can't go over (or through). Or you might need to stretch a link to go farther than your available radios and antennas permit. Maybe you are just on the edge of range of a good AP but need to provide access to a room full of people (and they don't all have high-gain antennas). A repeater may help in your application.
A radio repeater is a piece of equipment with two complete radios in it. Any traffic heard on the first radio is repeated to the second, and vice versa. If directional antennas are used, a weak signal reaching one of the transmitters is then rebroadcast over the other channel, as if it had originated from that point. Figure 7-4 shows the use of this technique to extend range or get around obstacles.
Figure 7-4. A repeater does just that: repeat everything it hears to someone else down the line
While a classic radio repeater might work fine with 802.11b, I unfortunately don't have access to radio gear capable of broadcasting a 25MHz wide signal at 2.4GHz. But I do have the next best thing: a couple of 802.11b PCMCIA cards.
The following sections describe two repeater-like configurations that I've used successfully.
7.4.1 Two Cards in One PC
If you have a PC with two PCMCIA slots, you can configure Linux to use both interfaces, and pass packets between them. Insert two wireless cards, and you have the hardware needed for a repeater application. While many client cards specifically disable Ethernet bridging, you can still use masquerading between the interfaces to bring two networks together.
One intriguing portable device that works well as a repeater is the Fujitsu Stylistic 1000. It is an old 486/100 tablet PC that comes with a monochrome LCD screen, stylus, 200MB PCMCIA hard drive, no keyboard, all of the usual PC ports, a lithium ion battery, and two extra PCMCIA slots. You can pick them up through used parts suppliers for around $100. (Thanks to the BAWUG crew for finding these nifty little devices!)
Take a look at Chapter 5 for details on how to get Linux installed and configured for masquerading. Once the software is configured, the only remaining issue is this: how do you squeeze one card on top of the other? Most wireless cards have a slight protruding bulge to make room for their internal antenna and won't fit in a stacked PCMCIA bay.
There are a couple of ways around this problem. Obviously, if you're using a card like the Cisco LMC35x for the bottom card, there is no bulge and therefore no problem. If you're using a card like the D-Link DWL-650,[2] the bulge is small enough that you can just squeeze two cards in at the same time. If you're using an Orinoco card on the bottom, your only recourse is to pop the plastic cover off and remove the two silver internal antenna tabs. This makes the card more or less useless without an external antenna, but it can be worth it if you're pressed for time (or cash) and have a card that you're willing to dedicate to long distance work. Remember to connect an external antenna to both radios when using two in one machine, or else the transmitters will be operating right next to each other, and cause a tremendous amount of interference.
See http://kevlar.burdell.org/~will/antenna/for one quick way to add an external antenna to the DWL-650.
This technique, shown in Figure 7-5, is very inexpensive, but it has the serious drawback that the two networks aren't actually bridged but are connected through a NAT box. While this may suit your purposes, it won't help much if both networks need to contact each other directly. If you need bridging between networks, look into higher-end equipment, such as the Cisco Ethernet Bridge or Orinoco AP-1000. Alternatively, you might try the method described in the following section.
Figure 7-5. Two Orinoco cards in one
 7.4.2 Two APs Back-to-Back
7.4.2 Two APs Back-to-Back
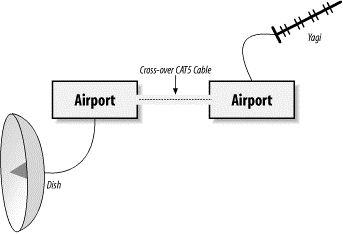
Many access points are capable of bridging the wireless network directly to the wire. What happens if you connect two APs in bridging mode back-to-back over a crossover CAT5 cable? Naturally, you have a bridging repeater.
I have only tried this with two Apple AirPorts, shown in Figure 7-6, but theoretically any AP capable of bridge mode should work fine. In this configuration, anyone within range of access point A will have their traffic repeated verbatim to access point B, and vice versa. As the Apple AirPorts actually use Orinoco Silver radio cards, the necessary external antenna connectors are already present inside the UFO. In fact, by removing the outer shell, it is possible to mount both AirPorts in a single, small, weatherproof box, with each connected to its own directional antenna. Each AirPort can even be configured with its own channel and security settings, if necessary. Performance won't be as optimal as with a straight shot (because you have doubled your chances of a data collision), but it can make a connection possible where one might otherwise not be.
Figure 7-6. Two Apple AirPorts in bridge mode, connected with a crossover cable, can act as an 802.11b repeater