Quantum Communications
Quantum information science combines two of the great scientific and technological revolutions of the 20th century: quantum mechanics on the one hand, and computer-based information science on the other. One of the fundamentally important research areas involved in quantum information science is quantum communications, which deals with the exchange of information encoded in quantum states of matter or quantum bits (known as qubits) between both nearby and distant quantum systems.
In July 2016, the National Science and Technology Council of the Executive Office of the President, in a report titled "Advancing Quantum Information Science: National Challenges and Opportunities", described Quantum Information Science (QIS) is “a foundational science,” with “currently envisioned applications (that) include sensing and metrology, communications, simulation, and high-performance computing”. The report also pointed out specifically that “Quantum communication, the ability to transmit information encoded in quantum states of light or matter, … is currently an active area of development”. The report also states that “In the longer term, quantum networks will connect distributed quantum sensors… to allow long-distance transmission of quantum information”. It further stated that solutions “could, with consistent attention and support, appear within 5 to 10 years.”
In support of this initiative, the Quantum Communication Project in ITL performs fundamental research on the creation, transmission, interfacing, storage, processing and measurement of optical qubits – the quantum states of photons. Particular attention is paid to applying this research to future quantum information technologies.
Our accomplishments include
- high-speed quantum key distribution (QKD) systems for secure communications;
- narrow linewidth single photon sources for atomic interfacing;
- single-photon frequency conversion technologies to interface stationary qubits in the visible band with flying qubits in the telecommunication bands;
- efficient single photon detectors and ultra-high sensitivity spectrometers for the telecom wavelengths based on up-conversion technologies.
Our current research program is focused on the development and implementation of quantum repeaters. A quantum repeater enables quantum information exchange between two distant quantum systems. Quantum repeaters can be used to extend the operating distance for secure communications as well as to form future quantum networks. Our ongoing research aims to develop and implement and characterize the essential building blocks for quantum repeaters including single photon pair sources, quantum memories and quantum interfaces that can be practical and scalable when integrated into a quantum communication system. The figure shows our project roadmap.
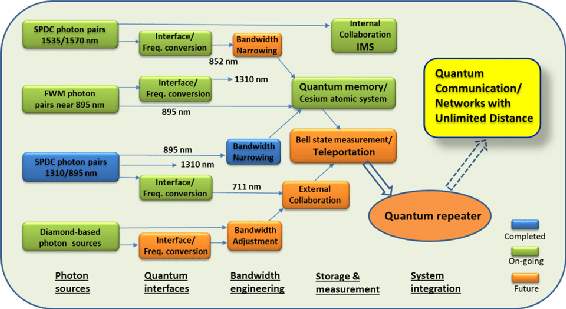
The figure shows our project roadmap.
In summary, we perform research and development (R&D) on quantum repeaters and supporting measurement technologies. Our mission is to bridge the gap between fundamental quantum research and practical applications in industries and commercialization. Our R&D is aimed to promote US innovation, industrial competitiveness and enhance the nation's security. For more information, contact project leader Dr. Xiao Tang. For more information concerning the ITL Quantum Information program, please select link 'ITL Quantum Information Program'.
Journal papers:
- O. Slattery, L. Ma, P. Kuo, and X. Tang. “Narrow-linewidth source of greatly non-degenerate photon pairs for quantum repeaters from a short singly resonant cavity,” Applied Physics B., 121, 413–419 (2015).
- Yong-Su Kim, Oliver Slattery, Paulina S. Kuo, and Xiao Tang, “Two-photon interference with continuous-wave multi-mode coherent light,” Optics Express, Vol. 22, Issue 3, pp. 3611-3620 (2014).
- O. Slattery, L. Ma, P. Kuo, Y. Kim and X. Tang, “Frequency correlated biphoton spectroscopy using tunable upconversion detector,” Laser Phys. Lett. 10, 075201(2013).
- Yong-Su Kim, Oliver Slattery, Paulina S. Kuo, and Xiao Tang, “Conditions for two-photon interference with coherent pulses,” Physical Review A 87, 063843 (2013).
- Paulina S. Kuo, Jason S. Pelc, Oliver Slattery, Yong-Su Kim, M. M. Fejer, and Xiao Tang, “Reducing noise in single-photon frequency conversion,” Optics Letters Vol.38, No. 8, 1310 (April 15 2013).
- Paulina S. Kuo, Oliver Slattery, Yong-Su Kim, Jason S. Pelc, Martin M. Fejer, and Xiao Tang, “Spectral response of an upconversion detector and spectrometer,” Optics Express, Vol. 21, Issue 19, pp. 22523 (2013).
- L. Ma, O. Slattery and X. Tang, “Single photon frequency up-conversion and its applications,” Physics Reports, Vol. 521 (2) 69-94, (2012).
- J. Pelc, P. Kuo, O. Slattery, L. Ma, X. Tang, “Dual-channel, single-photon upconversion detector at 1.3 microns”, Optics Express, Vol. 20 (17), 19075 (2012)
- J. Pelc, L. Ma, C. Phillips, C. Langrock, Q. Zhang, O. Slattery, X. Tang, M. Fejer, “Long-wavelength-pumped upconversion single-photon detector at 1550 nm: performance and noise analysis,” Optics Express, Vol. 19(22), 21445–21456 (2011)
- M. Rakher, L. Ma, O. Slattery, X. Tang, and K. Srinivasan, “Simultaneous wave-length translation and amplitude modulation of single photons from a quantum dot,” Physical Review Letter, Vol. 107, 083602 (2011)
- L. Ma, M. Rakher, M. Stevens, O. Slattery, K. Srinivasan and X. Tang, “Temporal correlation of photons following frequency up-conversion,” Optics Express, Vol. 19 10501-10510 (2011)
- L. Ma, J. Bienfang, O. Slattery and X. Tang, “Up-conversion single-photon detector using multi-wavelength sampling techniques,” Optics Express, Vol. 19 (6), 5470-5479 (2011)
- M. Rakher, L. Ma (co-first author), O. Slattery, X. Tang, and K. Srinivasan, “Quantum transduction of telecommunications-band single photons from a quantum dot by frequency upconversion,” Nature Photonics, Vol. 4, 786–791, doi:10.1038/nphoton.2010.221 (2010).
- L. Ma, O. Slattery and X. Tang, “Single photon level spectrum measurement at fiber communication band using frequency up-conversion technology,” Laser Physics, Vol. 20 (7),1216-1617 (2010).
- L. Yan, L. Ma and X. Tang, “Bragg-Grating Enhanced Narrow-Band Spontaneous Parametric Down Conversion,” Optics Express, Vol. 18 (6), 2556-2559 (2010)
- L. Ma, O. Slattery and X. Tang, “Detection and spectral measurement of single photons in communication bands using up-conversion technology,” Laser Physics, Vol. 20 (5), 1244-1250 (2010)
- L. Ma, O. Slattery, T. Chang and X. Tang, “Non-degenerated sequential time-bin entanglement generation using periodically poled KTP waveguide,” Optics Express, Vol. 17(18), 15799–15807 (2009)
- L. Ma, O. Slattery and X. Tang, “Experimental study of high sensitivity infrared spectrometer with waveguide-based up-conversion detector,” Optics Express, Vol. 17(16), 14395–14404 (2009)
- L. Ma, A. Mink and X. Tang, “High Speed Quantum Key Distribution over Optical Fiber Network System,” Journal of research of the National Institute of Standards and Technology, Vol. 114 (3), 149-177, (2009)
- L. Ma, S. Nam, H. Xu, B Baek, T. Chang, O. Slattery, A. Mink and X. Tang, “1310 nm differential phase shift QKD system using superconducting single photon detectors,” New Journal of Physics, Vol. 11, 054020, (2009)
- A Mink, J Bienfang, R Carpenter, L. Ma, B Hershman, A Restelli and X. Tang, “Programmable Instrumentation & GHz signaling for quantum communication systems,” New Journal of Physics, Vol. 11, 054016, (2009)
- L. Ma, T. Chang, A. Mink, O. Slattery, B. Hershman and X. Tang “Experimental Demonstration of a Detection-time-bin-shift Polarization Encoding Quantum Key Distribution System”, IEEE Communications Letters, Vol. 12(6), 459~461 (2008).
- L. Ma, A. Mink, H. Xu, O. Slattery and X. Tang, “Experimental Demonstration of an Active Quantum Key Distribution Network with Over Gbps Clock Synchronization”, IEEE Communication Letters, Vol 11(12), 1019~1021 (2007)
- H. Xu, L. Ma, A. Mink, B. Hershman, and X. Tang, “1310-nm quantum key distribution system with up-conversion pump wavelength at 1550 nm”, Optics Express, Vol 15(12), 7247~ 7260 (2007)
- X. Tang, L. Ma, A. Mink, A. Nakassis, H. Xu, B. Hershman, J. Bienfang, D. Su, R. Boisvert, C. Clark, and C. Williams, “Experimental study of high speed polarization-coding quantum key distribution with sifted-key rates over Mbit/s”, Optics Express, Vol. 14 (6), 2062-2070 (2006)
Conference Papers:
- L. Ma, O. Slattery, P. Kuo and X. Tang, "EIT Quantum Memory with Cs Atomic Vapor for Quantum Communication", Proc. of SPIE, Vol. 9615, 96150D-1, SPIE Quantum Communications and Quantum Imaging, (2015).
- O. Slattery, L. Ma, P. Kuo and X. Tang, "Comparing the Linewidths from Single-Pass SPDC and Singly-Resonant Cavity SPDC", Proc. of SPIE, Vol. 9615, 961507-1, SPIE Quantum Communications and Quantum Imaging (2015).
- Paulina S. Kuo, Jason S. Pelc, Oliver Slattery, Lijun Ma and Xiao Tang, "Domain-engineered PPLN for entangled photon generation and other quantum information applications," Proc. SPIE, 9136, 913403, (2014).
- A. Mink, and A. Nakassis, “LDPC Error Correction for Gbit/s QKD”, Proc. SPIE, Vol. 9123, pp 912304-1 to 912304-13, SPIE Defense Security & Sensing, (2014).
- O. Slattery, L. Ma, P. Kuo, Y Kim, and X. Tang “Tunable up-conversion detector for single photon and bi-photon infrared spectroscopic applications,” Proc. SPIE, Vol. 8726, 87260Y-87260Y-9, SPIE Defense, Security, and Sensing (2013).
- Paulina S. Kuo, Jason S. Pelc, Oliver Slattery, Yong-Su Kim and Xiao Tang, “Entangled photon generation in a phase-modulated, quasi-phase matched crystal”, Proc. of SPIE Vol. 8875 887508-1, SPIE Optics and Photonics (2013).
- Paulina S. Kuo, Jason S. Pelc, Oliver Slattery, Yong-Su Kim, M. M. Fejer, and Xiao Tang, “Efficient, low-noise, single-photon frequency conversion”, OSA Technical Digest, paper JTh2A.86, CLEO 2013 (2013).
- Paulina S. Kuo, Jason S. Pelc, Oliver Slattery, Yong-Su Kim and Xiao Tang, “Entangled photon generation in a phase-modulated, quasi-phase matched crystal,” Proc. of SPIE Vol. 8875 887508-1. SPIE Optics and Photonics (2013).
- O. Slattery, P. Kuo, Y Kim, L. Ma and X. Tang, "Narrowed Bandwidth SPDC Correlated Photon Source using Volume Bragg Grating", IX, Proceedings of SPIE 8518, 85180Y1-10, SPIE Quantum Communications and Quantum Imaging (2012).
- P. S. Kuo, J. S. Pelc, O. Slattery, M. M. Fejer, and X. Tang, “Dual-channel, single-photon upconversion detector near 1300 nm,” Proceedings of SPIE 8518, 85180U1-12 (2012).
- P. S. Kuo, J. S. Pelc, O. Slattery, L. Ma, M. M. Fejer, and X. Tang, “Dual-channel, single-photon upconversion detector at 1300 nm,” Presented in Nonlinear Photonics, OSA Technical Digest, paper NM3C.6. Optical Society of America (2012).
- L. Ma, J. Bienfang, O. Slattery and X. Tang, “Frequency up-conversion single-photon detectors for quantum communication systems”, Proc. SPIE, Vol. 8033, 803306-1~ 803306-9, SPIE Advanced Photon Counting Techniques V, (2011).
- L. Ma, O. Slattery and X. Tang, “Study on noise reduction in up-conversion single photon detectors,”, Proc. SPIE, Vol.7815, 781508-1~781508-8, SPIE Quantum Communications and Quantum Imaging VIII, (2010).
- L. Yan, L. Ma, and X. Tang, “Narrow-Band Photon Pairs Generated from Spontaneous Parametric Down Conversion in a Bragg-Grating Enhanced Waveguide,” Proc. SPIE, Vol.7815, 781511-1~781508-7, SPIE Quantum Communications and Quantum Imaging VIII, (2010).
- L. Ma, O. Slattery and X. Tang, “Ultra-sensitive NIR-spectrometer based on frequency up-conversion detector,” Proc. SPIE, Vol. 7680, 76800P-1-~76800P-10, SPIE Next-Generation Spectroscopic Technologies III. (2010).
- O. Slattery, L. Ma and X. Tang, “Correlated Photon Pair Generation by a Single Dual-Element PPKTP Waveguide at over GHz Repetition Rate”, Proc. SPIE, Vol.7465, 74650K-1~74650K-7, SPIE Quantum Communications and Quantum Imaging VII, (2009).
- L. Ma, O. Slattery, A. Mink and X. Tang, “Low noise up-conversion single photon detector and its applications in quantum information systems”, Proc. SPIE, Vol. 7465, 74650W-1~74650W-13, SPIE Quantum Communications and Quantum Imaging VII, (2009).
- B. Baek, L. Ma, A. Mink, X. Tang and S. Nam, “Detector performance in long-distance quantum key distribution using superconducting nanowire single-photon detectors,” Proc. SPIE, Vol. 7320 73200D-1~73200D-8, SPIE Defense, Security and Sensing 09, (2009).
- X. Tang, L. Ma, A. Mink, T. Chang, H. Xu, O. Slattery, A. Nakassis, B. Hershman, D. Su, and R. F. Boisvert, “High-Speed Quantum Key Distribution System for Optical Fiber networks in campus and metro areas”, Proc. SPIE, Vol. 7092, 70920I-1~70920I-15, SPIE Quantum Communications and Quantum Imaging VI, (2008).
- L. Ma, T. Chang, A. Mink, O. Slattery, B. Hershman and X. Tang, “Detection-time-bin-shift Schemes for Polarization Encoding Quantum Key Distribution System,” (invited paper), Proc. SPIE, Vol. 7092, 709206-1~709206-10, SPIE Quantum Communications and Quantum Imaging VI, (2008).
- H Xu, L. Ma, X. Tang, “Low noise PPLN-based single photon detector”, Proc. SPIE. 6780, 67800U-1, SPIE Optics East 07, (2007).
- J. C. Bienfang, A. Restelli, D. Rogers, A. Mink, B. j. Hershman, T. Nakassis, X. Tang, L. Ma, H. Xu, D. H. Su, C. W. Clark, C. J. Williams, “High-repetition rate quantum key distribution”, Proc. SPIE. 6780, 67800C-1, SPIE Optics East 07, (2007).
- D. Rogers, J. Bienfang, A. Mink, B. Hershman, A. Nakassis, X. Tang, L. Ma, D. Su, C. Williams, and C. Clark, “High-speed photon counting techniques for broadband quantum key distribution,” Proc. SPIE, Vol. 6372, 637211 SPIE Optics East 06, (2006).
- L. Ma, H. Xu, X. Tang, “Polarization recovery and auto-compensation in quantum key distribution network”, SPIE Quantum Communications and Quantum Imaging IV, Proc. SPIE 6305, 630513-1~ 630513-6, (2006).
- X. Tang, L. Ma, A. Mink, A. Nakassis, H. Xu, B. Hershman, J. Bienfang, D. Su, R. Boisvert, C. Clark, and C. Williams, “Demonstration of active quantum key distribution network.”, Proc. SPIE 6305, 630506-1~ 630506-6, SPIE Quantum Communications and Quantum Imaging IV, (2006).
- D. Rogers, J. Bienfang, A. Mink, B. Hershman, A. Nakassis, X. Tang, L. Ma, D. Su, C. Williams, and C. Clark, “Free-space quantum cryptography in the H-alpha Fraunhofer window.”, Proc. SPIE 6304, 630417-1~ 630417-10, SPIE Optics and Photonics 06, (2006).
- X. Tang, L. Ma, A. Mink, A. Nakassis, H. Xu, B. Hershman, J. Bienfang, D. Su, R. Boisvert, C. Clark, and C. Williams, “Quantum Key Distribution system operating at sifted key-rate over 4Mbit/s”, Proc. SPIE 6244, 62440P-1~ 62440P-8, SPIE Defense and Security 06, (2006).
- A. Mink, X. Tang, L. Ma, A. Nakassis, B. Hershman, J. Bienfang, D. Su, R. F. Boisvert, C. Clark, and C. Williams, “High Speed Quantum Key Distribution System Supports One-Time Pad Encryption of Real-Time Video”, Proc. SPIE 6244, 62440M-1~62440M-7, SPIE Defense and Security 06, (2006).
- X. Tang, L. Ma, A. Mink, A. Nakassis, B. Hershman, J. Bienfang, R. Boisvert, C. Clark, and C. Williams, “High Speed Fiber-Based Quantum Key Distribution using Polarization Encoding,” Proc. SPIE, Vol. 5893: 1A-1~1A-9, SPIE Quantum Communications and Quantum Imaging III, (2005).
Book Chapters:
- L. Ma, O. Slattery and X. Tang, “Single photon detection using frequency up-conversion with pulse pumping,” Chapter 4 in Photodiodes - Communications, Bio-Sensings, Measurements and High-Energy Physics, InTech, ISBN 978-953-307-277-7, (2011).
- A. Mink, L. Ma, B. Hershman and X. Tang, “An application of quantum networks for secure video surveillance”, Chapter 6 in Video Surveillance, In-Tech, ISBN: 978-953-307-436-8, (2011).
- L. Ma, O. Slattery and X. Tang “NIR Single photon detectors with up-conversion technology and its applications in quantum communication systems” Chapter 15 in Advances in Lasers and Electro optics, N. Costa and A. Cartaxo ed. In-Tech, ISBN: 978-953-307-088-9, (2010).
Dates
Started: January, 2004
Created November 22, 2016, Updated November 16, 2017
Source: https://www.nist.gov/programs-projects/quantum-communications




