Problems
Mechanical Problems (dysphagia to solids first and liquids later)
Intermittent problem
Esophageal ring (a.k.a Steakhouse Syndrome)
Clue in history: Patient has difficulty swallowing while
chewing foods like bread or steak.
Long standing history of GERD
Barrett’s esophagus (squamous to columnar metaplasia) or
stricture formation.
Dysphagia to solids with significant weight loss
If long standing smoking history, Squamous cell carcinoma
more likely
If long standing history of uncontrolled GERD,
Adenocarcinoma more likely
Eosinophilic esophagitis
Dense eosinophilic infiltrate in the squamous epithelium
Mainstay of treatment is viscous budesonide, fluticasone,
or proton pump inhibitors (PPIs)
Motility Problems (dysphagia to both solids and liquids concurrently)
Intermittent and associated with chest pain, especially after drinking
carbonated drinks
Diffuse Esophageal Spasm (DES)
Associated with connective tissue disease or heartburn
Scleroderma
Associated with cough/regurgitation with improvement of dysphagia with
raising hand above the head
Achalasia (which can in the context of Chagas Disease)
Before treating with surgical myotomy or pneumatic dilatation,
EGD must be done first to rule out secondary achalasia from
lymphoma or cancer.
14 | P a g e
K N O W M E D G E
Achalasia will have increased LES tone on manometry studies.
GERD, on the other hand, will have decreased LES tone.
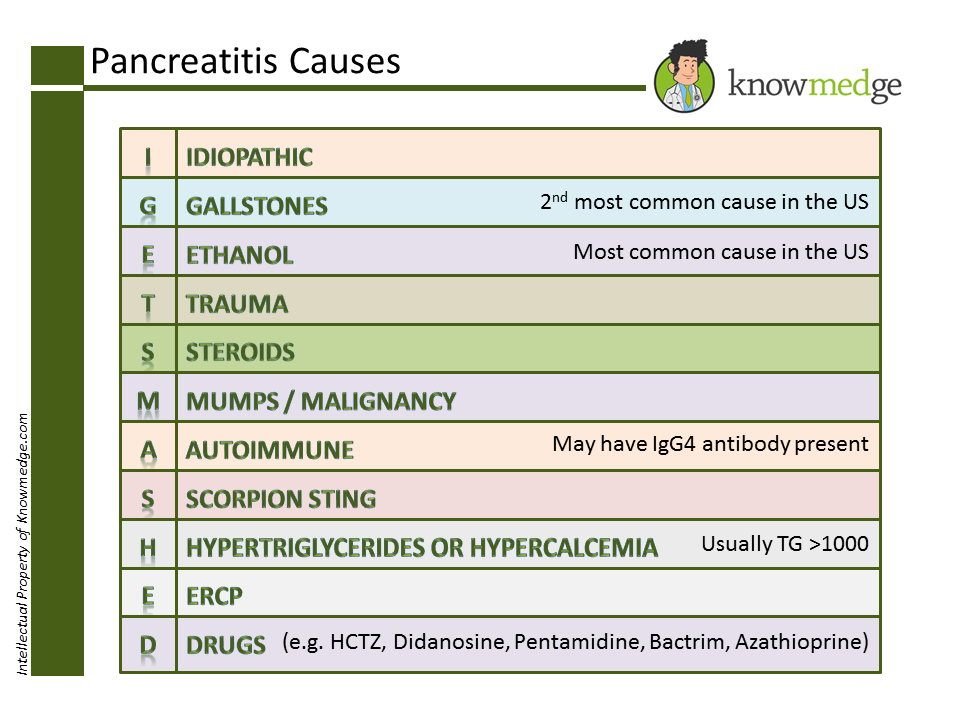
Pearl # 3: Remember the main causes of Pancreatitis by the mnemonic “I GET
SMASHED”
Pearl # 4: Alcoholics aren’t the only folks to develop cirrhosis
To the lay public, cirrhosis is to alcohol as lung cancer is to smoking. However, we
know that it’s not such a simple association. Smokers aren’t the only patients to develop
lung cancer and those who don’t drink alcohol can still become cirrhotic. Let’s review
some of the non-alcohol related causes of liver failure with two easy-to-digest slides:
15 | P a g e
K N O W M E D G E
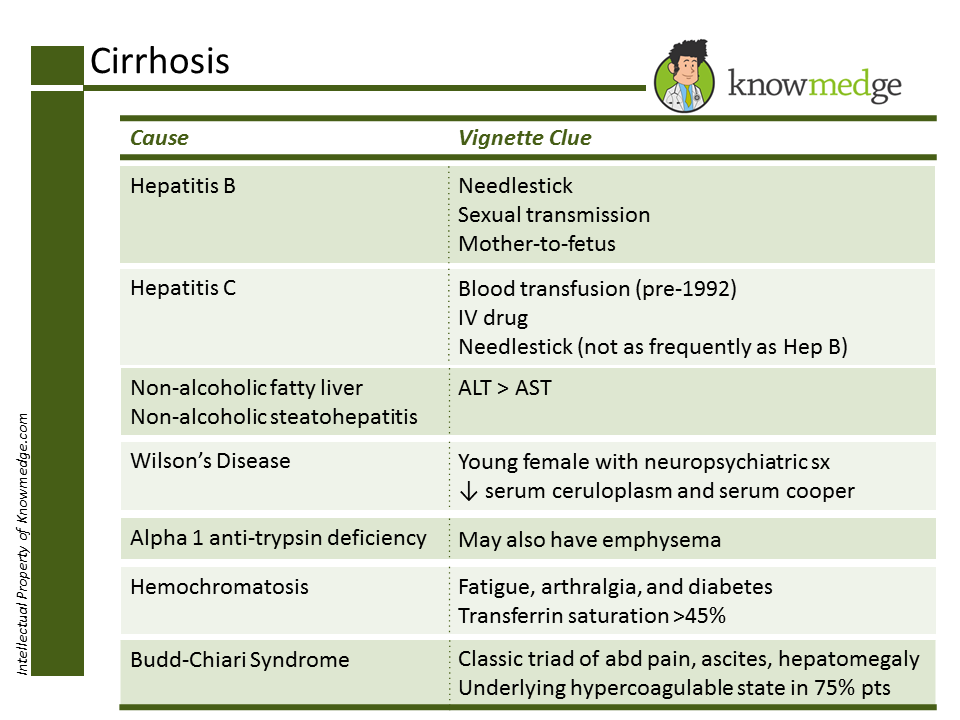
First, we review Viral Hepatitis, Fatty Liver/Steatohepatitis, Wilson’s, Alpha 1 Anti-
Trypsin Deficiency, Hemochromatosis and Budd-Chiari along with helpful clinical clues
that may appear in the question vignette:
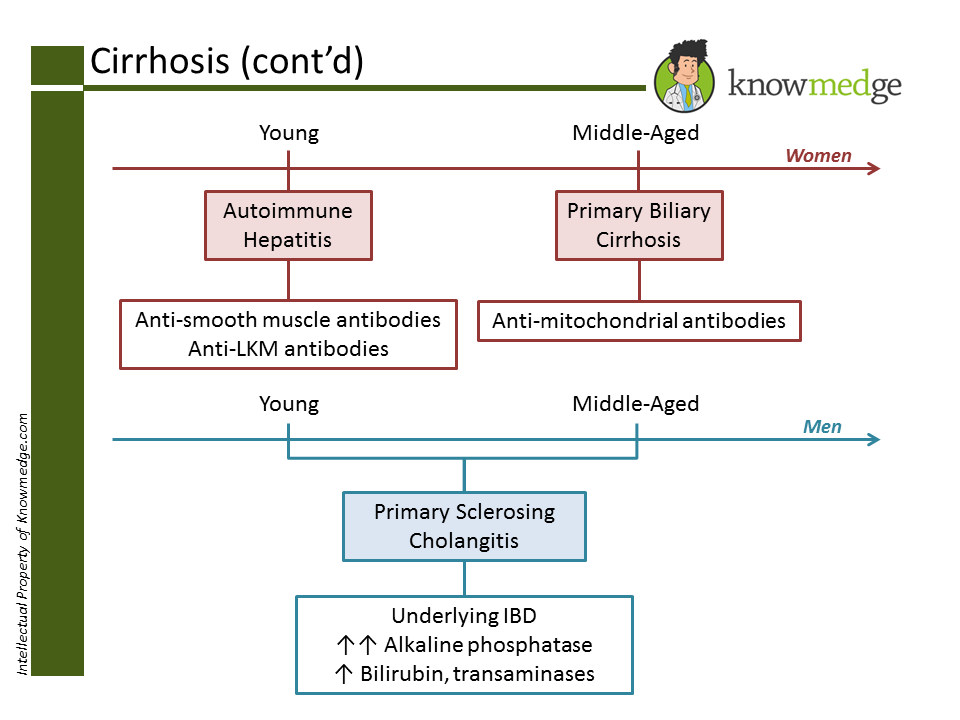
Of course, we can’t forget Autoimmune Hepatitis, Primary Biliary Cirrhosis, and Primary
Sclerosing Cholangitis. Many medical students and residents find it confusing to match up the
gender, age, and serologies with the correct condition. While these are not hard-and-fast rules,
for exam purposes, in general we can use the following colorful schematic to make it tough to
ever forget again.
16 | P a g e
K N O W M E D G E
Pearl # 5: They may both be considered IBD, but know how to distinguish Ulcerative
Colitis and Crohn’s Disease






