treatment is essential
Unlike asthma, COPD is an irreversible condition. Administering the bronchodilator albuterol
will not increase FEV1.
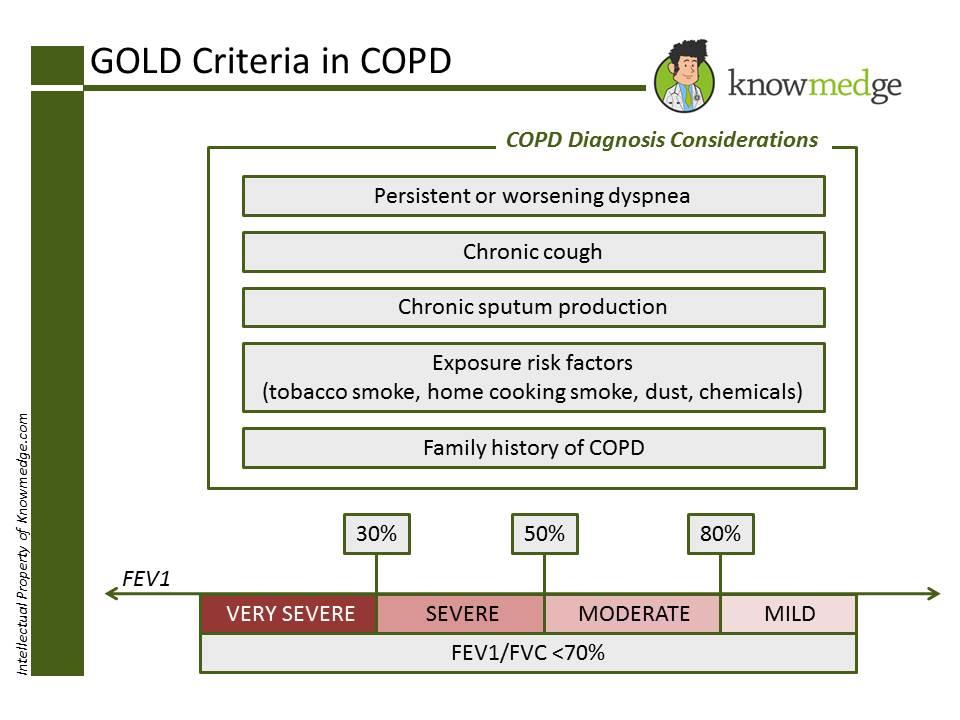
GOLD (Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease) criteria is the primary method
used to diagnose and identify the severity of COPD. A diagnosis of COPD should be
considered for any patient over the age of 40 who has any of the following conditions:
Dyspnea that is persistent, worsens over time and gets worse with exercise
Chronic cough
Chronic sputum production
63 | P a g e
K N O W M E D G E
History of exposure to risk factors (Tobacco smoke, smoke from home cooking,
occupational dust, chemicals)
Family history of COPD
FEV1/FVC ratio less than 70% is an indication that there is an airflow limitation and, thus,
COPD. The spirometric criteria for a diagnosis of COPD is a post-bronchodilator FEV1/FVC
ratio less than 70%.
FEV1 will tell us the intensity of the COPD which can be characterized into four stages:
Stage I (Mild): FEV1 > 80% of predicted value; Rx: Short acting Bronchodilator as
needed with or without Ipratropium
Stage II (Moderate): 50% ≤ FEV1 < 80% of predicted value; Rx: Short acting
Bronchodilator as needed with long acting bronchodilator around the clock with or
without pulmonary rehab
Stage III (Severe): 30% ≤ FEV1 < 50% of predicted value; Rx: As above for moderate
COPD plus Inhaled steroids
Stage IV (Very severe): FEV1 < 30% of predicted value (or FEV1 < 50% of predicted
value plus chronic respiratory failure); Rx: As above for severe COPD plus Long-term
oxygen therapy for at least 15 hours daily. Surgical intervention should be considered.
The slide below reveals the cut-off criteria for the different stages.
64 | P a g e
K N O W M E D G E
Other indications for Oxygen therapy in COPD patients are:
PaO2 less than 55 mm Hg or Oxygen saturation less than 88% OR
PaO2 less than 59 mm Hg or Oxygen saturation greater than 88% with evidence of Cor
pulmonale (Right ventricular dysfunction) or secondary erythrocytosis (hematocrit
greater than 55%)
Pearl # 6: IgE and Eosinophil levels help us distinguish ABPA, Hypersensitivity
pneumonitis, and Churg-Strauss syndrome
ABPA → Increased IgE levels and increased peripheral eosinophils >10% → Rx with steroids
65 | P a g e
K N O W M E D G E
HYPERSENSITIVITY PNEUMONITIS → IgE levels and peripheral eosinophils are normal →
Remove offending agent
CHURG-STRAUSS SYNDROME → IgE levels are normal, peripheral eosinophils >10% →
(Clue: asthmatic patient with increase peripheral eosinophils and a foot drop) → Management
with steroids
Pearl # 7: Light’s criteria will guide you to correctly identifying Pleural Effusions as





