Performance Analysis of 2.5 Gbps GPON
S.Srinath
B.Tech , Department of ECE, Vellore Institute Of Technology, Vellore, Tamilnadu, India
ABSTRACT: The ITU-T G.984 is Gigabit-capable Passive Optical Networks (GPON) standard. In this paper, 2.5 Gb/s GPON link is presented. The quality or performance of a digital communication system is specified by its BER or Q value with respect to other parameters such as receiver sensitivity . The system performance is presented through various parameters such as Q factor, eye diagram. The proposed models have the nominal bit rate 2.5 Gbit/s with required bandwidth. It implemented using Opti-System 7.0.
KEYWORDS: GPON, Bit Error Rate(BER), Q Factor, Eye Diagram.
I.INTRODUCTION
Fiber optics uses light signals to transmit data. As this data moves across a fiber, there needs to be a way to separate it so that it gets to the proper destination. A passive optical network does not include electrically powered switching equipment and instead uses optical splitters to separate and collect optical signals as they move through the network. A passive optical network shares fiber optic strands for portions of the network. Powered equipment is required only at the source and receiving ends of the signal. GPON (Gigabit Passive Optical Network) network consists of three important units ie Optical Line Terminal (OLT), Optical Network Unit (ONU) and Optical Splitters. The data is transmitted from the central office to a single optical fibre which runs from the central office to the optical splitters. This splitter then divides the power into N separate paths that goes to different subscribers. The number of splitting paths can vary from 2 to 64.Optical Line Terminal is a device that serves as the service provider endpoint of a passive optical network. It has two main functions: To perform conversion between the electrical signals used by the service provider’s equipment and the fiber optic signals used by the passive optical network. To coordinate the multiplexing between the conversion devices on the other end of that network (called Optical Network Units).Optical Network Unit is used in combination with an Optical Line Terminal (OLT). It is a device that terminates any one of the endpoints of a fiber to the premises network. It transforms incoming optical signals into electronics at a customer's premises. Optical Splitters are used to divide the incoming light beam from a single fiber into two or more fiber channels.GPON offers many advantages:It supports triple play service. It is a term for the provisioning of two bandwidth intensive service- high speed internet access and television and a less bandwidth demanding service, telephone over a single broadband connection.It has a high bandwidth transmission and long reach service coverage (20 km).Since PON uses the same fiber for upstream as well as downstream transmission, it utilizes WDM (Wave Division Multiplexing) for bidirectional transmission. It adopts two multiplexing techniques. In the downstream direction the data packets are transmitted in a broadcast manner. 1,490 nm wavelength is used for downstream traffic while in the upstream direction the packets are transmitted in a TDMA manner. The wavelength used for upstream traffic is 1310 nm. 1550 nm is reserved for overlay services, typically RF video (analog).
In this paper different characteristics like jitter, minimum Bit Error Rate (BER), Q factor and optical power for different wavelengths are compared. We will also see the variation of these factors when there is a change in the fiber attenuation.
II.RELATED WORK
While previous survey and research papers focussed on the downstream performance of a GPON system for data rates less than 2Gbps, this paper focuses on both the upstream and downstream performance of a GPON for data rate above 2Gbps ie 2.5Gbps(ITU-T G.984.1 standard).Higher data rate simulation is performed in this paper as high speed GPON network are the need of the hour. The performance measure of a GPON system presented in this paper analyses how the BER , Q-Factor and Optical power changes as wavelength and attenuation changes and how effective these factors are for better communication. The downstream performance analysis of GPON system is analysed for ‘single user’ case and ‘multiple user’ case. The upstream performance analysis of GPON system is analysed for ‘multiple user’ case. For analysing the performance of multiple user GPON system ‘Bi-Directional Optical Fibres’, ‘Bi-Directional Circulators’ and ‘Bi-Directional Splitters’ available in Optisystem 7.0 software were used.
III. THEORY
Bit Error Rate (BER) is defined as the number of bit errors is the number of received bits of a data stream over a communication channel that has been altered due to noise, interference, and distortion or bit synchronization errors. BER is the number of bit errors divided by the total number of transferred bits during a studied time interval i.e. 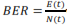 where E(t) is the number of bits received in error over time t, and N(t) is the total number of bits transmitted in time t. BER is a unit less performance measure, often expressed as a percentage.Q Factor describes how under damped an oscillator or resonator is. Higher Q factor indicates a lower loss of energy.Higher Q indicates a lower rate of energy loss relative to the stored energy of the resonator. A high-Q tuned circuit in a radio receiver would have more selectivity and hence better job of filtering out
where E(t) is the number of bits received in error over time t, and N(t) is the total number of bits transmitted in time t. BER is a unit less performance measure, often expressed as a percentage.Q Factor describes how under damped an oscillator or resonator is. Higher Q factor indicates a lower loss of energy.Higher Q indicates a lower rate of energy loss relative to the stored energy of the resonator. A high-Q tuned circuit in a radio receiver would have more selectivity and hence better job of filtering out