Double wishbone suspension
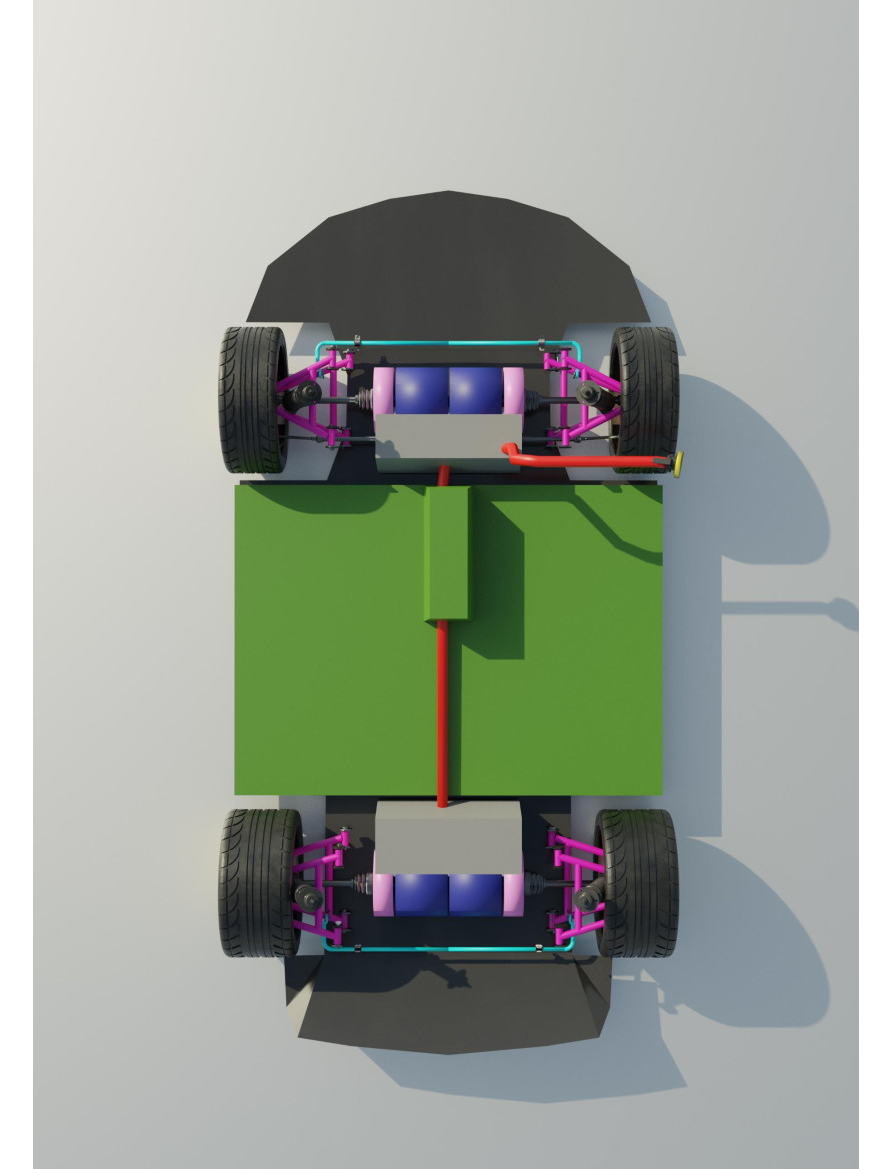
The car uses a double wishbone suspension. Unlike other types of suspension, the double wishbone design offers a more progressive geometry. The more the double wishbone suspension is compressed, the greater the negative camber due to the use of variable levers. This has a positive effect on handling at such moments when the driver is heavily into the corner and the car starts to slip off the trajectory. At these times the wishbone suspension system will maintain better tire-to-road contact. This means that the car will be more stable. An additional advantage of the double wishbone suspension is the smaller dimensions of the upper arm relative to the lower one. In this regard, during the upward movement of the wheel, the camber angle changes, as a result of which the plane of the wheel remains perpendicular to the road surface even during body rolls. In general, depending on the length and location of the A-arms themselves, the camber and toe angle can be adjusted. The suspension guiding device is the lower and upper levers, the elastic device is coiled cylindrical springs, the damping device is double-acting telescopic hydraulic shock absorbers, and the anti-roll bar is an elastic U-shaped rod.
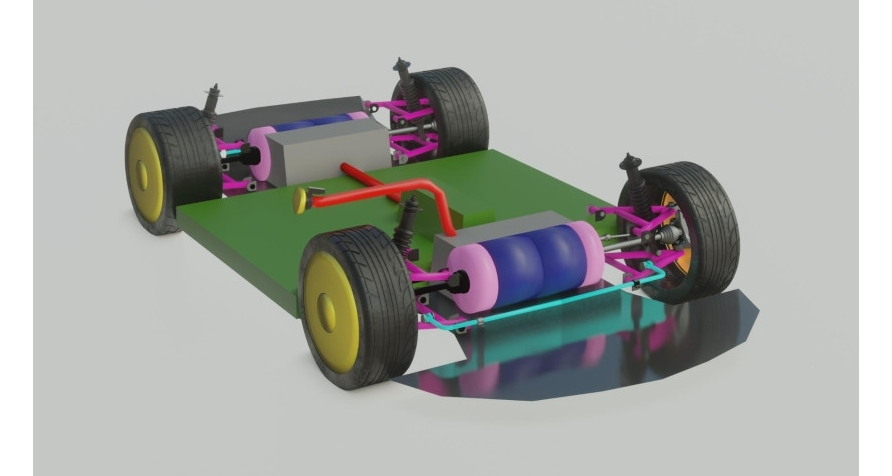
The upper and lower suspension arms are installed across the vehicle and have longitudinal rolling axes. The axle of the lower arm and upper arm are attached to a bracket in the body. The inner ends of the upper and lower arms are connected to the axles by rubber-metal hinges. The upper and lower rubbermetal hinges have the same device and differ only in their size. The use of rubber-metal joints ensures quiet operation of the suspension and eliminates the need to lubricate the joints. Outer ends of the upper and the lower suspension arms are connected to the steering knuckle by ball joints. Ball joints are nonseparable, have the same device, are interchangeable and do not require lubrication during operation. The suspension spring is installed between the lower support cup attached to the lower arm and the upper support cup connected to the support, which is connected to the suspension cross member between the ends of the spring and the support cups, vibration-insulating pads are installed. The bottom end of the shock absorber is attached to the support cup bracket by means of a rubber-metal hinge.
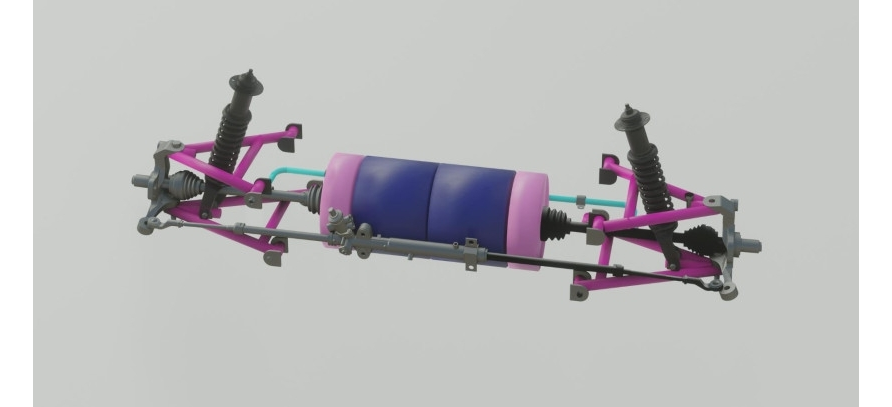

Double wishbone front suspension.
The upper end of the shock absorber is attached to the bracket via rubber pads. The upward travel of the wheel is limited by a compression buffer, which is fixed to a support installed inside the suspension spring. Under static loading, the compression buffer touches the lower spring seat for continuous operation. The stop limits the compression of the buffer. The downward travel of the wheel is limited by a recoil buffer, which is installed in a bracket connected to the cross member and support. Wheel travel downward, the recoil buffer rests against the special support area of the upper arm. The anti-roll bar is a torsiontype resilient device installed across the vehicle. The stabilizer bar is U-shaped and has a circular cross-section. It is made of spring steel. The middle part of the stabilizer bar and its ends are attached in rubber supports with clips to the car body and to the brackets of the support cups of the lower arms.






