Question: Does the consumption of broccoli and/or other brassica vegetables as a daily
staple increase the risk of cancer?
Answer: Yes, the regular consumption of brassica vegetables as a daily staple does
indeed increase the risk of cancer, and even heart disease.
Read on to
discover the evidence and exactly why BV's (brassica vegetables) actually increase the risk of cancer in humans.
The almost
universal belief that broccoli fights cancer is simply wrong, and if anything
the opposite is true. Even The American Cancer Society is hesitant about
linking cancer prevention with broccoli:
"Broccoli
contains certain chemicals that may reduce the risk of colorectal or other
cancers, although it is not clear which individual compounds may be responsible
for the protective effects. While research in this area continues, the best
advice at this time to reduce cancer risk is to eat a wide variety of
vegetables...." Source: The American Cancer Society, cancer.org.
*
BV's are high
in a variety of glucosinolates some of which are harmful. When you eat BV's
such as broccoli or cabbage, some of their glucosinolates break down to indole-3-carbinol,
and then some of the indole-3-carbonil breaks down to diindolymethane (DIM for
short). In effect, the consumption of BV's gives you indole-3-carbinol and DIM.
In a
laboratory, indole-3-carbinol and DIM can also be synthesised for testing to
see if they fight cancer. Experiments on mice have tentatively shown that these
synthesised compounds can prevent the formation of some kinds of cancer cells.
Other studies on mice and on human lab samples have indicated that
indole-3-carbinol and DIM may have applications in reducing the incidence of
breast and cervical cancer.
But other
studies have indicated that indole-3-carbinol may actually promote cancer. Here are four such studies:
1. Oganesian,
A., et al., Potency of dietary indole-3-carbinol as a promoter of aflatoxin B1-
initiated hepatocarcinogenesis: results from a 9000 animal tumor study.
Carcinogenesis, 1999. 20(3): p. 453-458.
2. Kim, D.J.,
et al., Enhancement by indole-3-carbinol of liver and thyroid gland neoplastic
development in a rat medium-term multiorgan carcinogenesis model. Carcinogenesis,
1997. 18(2): p. 377-381.
3. Dashwood,
R.H., et al., Promotion of aflatoxin B1 carcinogenesis by the natural tumor
modulator indole-3-carbinol: influence of dose, duration, and intermittent
exposure on indole-3-carbinol promotional potency. Cancer Res, 1991. 51(9): p.
2362-2365.
4. Dashwood,
R.H., et al., Tumor dose-response studies with aflatoxin B1 and the ambivalent
modulator indole-3-carbinol: inhibitory versus promotional potency. Basic Life
Sci, 1990. 52: p. 361-365.
So what is
happening here?
"Apparently,
there's some debate over whether or not these compounds fight cancer or promote
cancer. The simple version of the story is that, taken before exposure to a
carcinogen, these agents may actually reduce the risk of cancer. However, when
taken after exposure to a carcinogen, the same agents may increase the risk for
cancer. So while most studies report inhibitory or protective effects of
indole-3-carbinol in vivo, a few provide evidence for the promotion or
enhancement of carcinogenesis, depending upon the initiator (an agent that
starts the process leading to cancer), exposure protocol, and species".
Source: Dr. Thomas Incledon, more Fool's Gold, 2000 www.t-nation.com.
So the
anti-cancer effects of indole-3-carbinol and DIM are ambivalent and research is
still ongoing. Note: when we are talking about indole-3-carbinol,
we are in effect talking about DIM which comes from indole-3-carbinol.
Indole-3-carbinol itself has little effect on the body until it is broken down
by digestion. But when it is broken down it produces DIM and other compounds
which are being investigated for their anti-cancer effects.
Here is an abridged
extract from the distinguished 'Linus Pauling Institute' in the USA:
"Oral indole-3-carbinol [pure synthesised indole-3-carbinol] has been found to inhibit the
development of cancer in a variety of animal models and tissues, including
cancers of the mammary gland, uterus, stomach, colon, lung, and liver. However,
a number of studies have found that indole-3-carbinol actually promoted or
enhanced the development of existing cancer. The cancer-promoting effects of indole-3-carbinol
were first reported in a trout model of liver cancer. However, indole-3-carbinol
has also been found to promote cancer of the liver, thyroid,
colon, and uterus in rats....Although the long-term effects of indole-3-carbinol
supplementation on cancer risk in humans are not known, the contradictory
results of animal studies have led several experts to caution against the
widespread use of I3C and DIM supplements in humans until their potential risks
and benefits are better understood". Source: Victoria J. Drake, Ph.D.,
David E. Williams, Ph.D., Indole-3-Carbinol, 2008, Linus Pauling Institute, Oregon
State University, USA, http://lpi.oregonstate.edu.
A detailed
examination of indole-3-carbinol and DIM is beyond the scope of this book and
there is no intention to denigrate or dismiss the possible anti-cancer effects
of these compounds in their pure synthesised form.
The amount of
indole-3-carbinol and DIM derived from just the consumption of BV's is
negligible and not enough to affect cancer. "Direct measurements of
upward, beneficial shifts in estrogen metabolism indicate you would have to eat
at least two pounds per day of raw or lightly cooked cruciferous vegetables to
derive the same benefit as two capsules of specially formulated DIM. Benefits
for cervical dysplasia, PMS, BPH, and other conditions have not been seen with
the use of broccoli, cabbage juice, or dried powders or extracts from
vegetables". Source: Thomas Stearns Lee, DIM (Di-Indoly Methane) For
Natural Protection from Estrogen's Effects, Frequently Asked Questions,
www.naturodoc.com.
*
"Cell-culture
studies and human clinical trials have shown that indole-3-carbinol at doses of
200400 mg/day can influence estrogen metabolism and promote formation of
2-OH-estrone, and therefore may be useful in breast cancer prevention. Current
U.S. research studies are under way on indole-3-carbinol and women at increased
risk for breast cancer". Source: Dan Lukaczer, N.D., Estrogen's
Two-Way Street, the November 2001 Issue of Nutrition Science News.
With reference
to the above quote, to derive 200-400 mg of indole-3-carbinol per day you would
have to eat huge amounts of BV's daily. And if you were to do this, you would
suffer malnutrition by having to exclude other foods. You would also
significantly inhibit your thyroid and suffer health problems from the large
amounts of antinutrients that come with BV's (phytates, oxalates and insoluble
fiber).
Worst still, as
explained in a moment, by consistently consuming large amounts of BV's you
inhibit testosterone, and this greatly increases the risk of cancer plus a host
of other health problems.
As already
discussed in the previous section, most medicines are derived from plants. And
many of these plants are inedible or even poisonous, yet they give us valuable
and life-saving drugs and cures.
This is the
case with BV's. The point here is that although certain compounds in BV's may
fight cancer when purified and synthesised (and when carefully administered as
a medicine) it does not mean that the consumption of BV's themselves will help
fight cancer.
In what
follows we will look at the link between BV's and cancer under the following
four headings:
Consumption
of brassica vegetables as a staple causes underactive thyroid.
Approximately
300,000 American die each year from the proper use of
over-the-counter and prescriptions drugs made from plant-derived compounds. This
exceeds deaths due to crack, handguns, and traffic accidents combined. Many
millions more die each year worldwide from the improper use of
drugs made from plant-derived compounds (just think of deaths related to
drug-addiction).

They myth that
consumption of BV's such as cabbage and broccoli fight cancer by virtue of
having glucosinolates is just that, a myth. If anything, the research shows the
opposite. Research shows that glucosinolates in BV's inhibit the thyroid from
working properly and interfere with the synthesis of necessary thyroid
hormones. The thyroid needs iodine to function, just like a car needs fuel to
function.
Here is a
technical explanation from the distinguished 'Linus Pauling Institute' in the
USA:
"Two
mechanisms have been identified to explain [the goitrogenic effect of
glucosinolates]. The hydrolysis of some glucosinolates found in cruciferous
vegetables (e.g., progoitrin) may yield a compound known as goitrin, which has
been found to interfere with thyroid hormone synthesis. The hydrolysis of
another class of glucosinolates, known as indole glucosinolates, results in the
release of thiocyanate ions, which can compete with iodine for uptake by the
thyroid gland. Increased exposure to thiocyanate ions from cruciferous
vegetable consumption or, more commonly, from cigarette smoking, does not
appear to increase the risk of hypothyroidism unless accompanied by iodine
deficiency". Source: Jane Higdon, Ph.D., Victoria J. Drake, Ph.D.,
Linus Pauling Institute, 2008, Oregon State University, USA.
There are no
long term human trials showing whether BV consumption causes an underactive
thyroid in people with no iodine deficiency. Unfortunately, iodine deficiency
and an underactive thyroid is very common throughout the world (more about this
in a moment), and for such people it makes sense to not risk exacerbating one's
state of health by consuming BV's.
An underactive
thyroid can cause serious health problems such as stunted body growth, muscle
loss, weight gain, memory loss and many other health problems. It is sad to see
parents often berating their children for not eating their cabbage or broccoli,
when in fact such consumption may well inhibit good body growth.
The scary
thing about an underactive thyroid is that it is very insidious - you don't
notice it until the harm is done because the effects are gradual. Regular
consumption of BV's may not shut down the thyroid or cause full hypothyroidism.
But such consumption can make the thyroid slow down enough to cause on-going
health problems that may not be apparent to the person affected.
Many people
who regularly consume BV's as a staple go for years putting on weight, losing
muscle, feeling under-par and weak, and generally suffering poor health. They
wonder why they are like this since they 'eat well', don't smoke and lead an
active life. The cause is often a regular diet high in BV's that keeps their
thyroid from working properly.
Note for
women wanting to conceive: a mild or subclinical underactive thyroid
has been associated with impaired fertility and an increased risk of
miscarriage.
The following
image shows the serious health problems caused by an underactive thyroid or by hypothyroidism
(the symptoms are similar) and it strikes both genders although it is less
common in men:
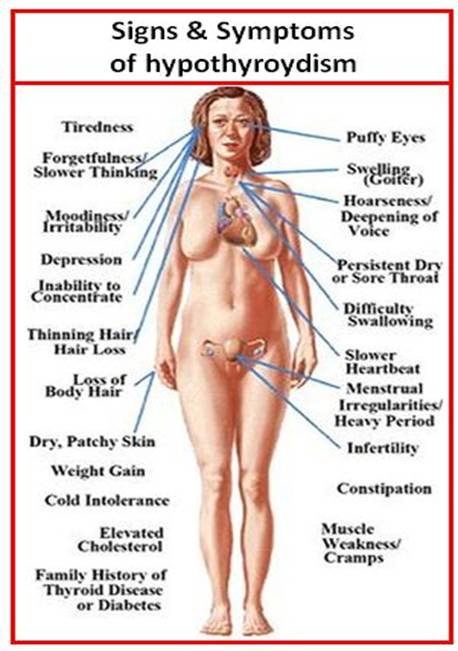
Ask yourself whether you may be suffering from any of these symptoms
and reflect on your diet. Do you eat BV's several times a week?
Some may argue that the goitrogenic effect of BV's is too mild to
affect people, and that in any event there is no shortage of iodine in the
human diet. But you would be wrong to think this. Whether or not your diet
gives you enough iodine, the consumption of BV's as a staple will cause an
on-going effect on your thyroid because glucosinolate compounds in BV's will inhibit
the thyroid from using what little iodine you receive from the diet. Without
sufficient iodine, the thyroid cannot function properly and you're into
hypothyroidism territory.
If you are healthy and you have enough iodine in your diet, the
goitrogenic effect of eating BV's as a staple will be insidious and not
obviously perceptible. Even a medical test may show your thyroid to be OK. But
the continuous, albeit mild, goitrogenic effect will have an adverse effect on
just about every aspect of your health, giving you an under-par quality of
life.
But if you are at all iodine deficient it is particularly important
to avoid BV's. The reality is that iodine deficiency is rampant throughout the
world.
"Iodine deficiency resulting in goiter occurs in 187 million
people globally as of 2010 (2.7% of the world population)". Source: Global, regional, and national age-sex specific
all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990-2013: a
systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013, Lancet 385:
117–171.
*
"[In the USA] low thyroid
function affects approximately 20-25 percent of the female population and about
10 percent of males. An additional 30 percent of persons over the age of 35 may
also have sub-clinical or mild hypothyroidism whereby their thyroid stimulating
hormone is within normal range, but they have many of the symptoms of low
thyroid. The thyroid secretes two hormones - T3 and T4 - that are crucial for
controlling our metabolism. Because thyroid hormones affect every cell in the
body, a deficiency will result in many symptoms". Source: Lorna
Vanderhaeghe, Thyroid (Hypothyroidism), Women helping Women,
www.healthyimmunity.com.
*
"In the US, it’s estimated that one in seven women suffers from
iodine deficiency". Source: Caldwell KL, et
al, Urinary iodine concentration: United States National Health and Nutrition
Examination Survey 2001-2002, Thyroid, 2005 Jul; 15(7):692-9.
*
"Approximately 40% of the
world’s population remains at risk for iodine deficiency". Source:
Iodine Deficiency, American Thyroid Association, 2012, www.thyroid.org.
*
"In the developed world, iodine deficiency has increased more
than fourfold over the past 40 years. Nearly 74% of normal, 'healthy' adults
may no longer consume enough iodine". Sources:
1. Gunton JE, et al, Iodine deficiency in ambulatory participants at a Sydney
teaching hospital: is Australia truly iodine replete? Med J Aust., 1999 Nov 1; 171(9):467-70.
2. Hoption Cann SA., Hypothesis: dietary iodine intake in the etiology of
cardiovascular disease. J Am Coll Nutr. 2006 Fe 25(1):1-11.
*
An underactive thyroid is one of the most common chronic disorders
throughout the world. In the United States alone roughly 11 million American
adults and children have underactive thyroids. It is most common in older women;
at least 10 percent of older women in the USA are affected by an underactive
thyroid or by hypothyroidism.
Put simply, many millions of people have iodine deficiency or
underactive thyroids, or some combination of both without even knowing it. It
is therefore disingenuous to argue that a fit and healthy body can withstand
any goitrogenic effect from such food. Why take the risk?
People who eat BV's as a staple, whether raw or cooked, are likely
to be much more health-conscious compared to the population at large. This is
so because a person who consciously eats unpalatable food (i.e. BV's) in the
belief that it is healthy is more likely to be adopting healthy lifestyles such
as not smoking, being physically and following a highly nutritious diet.
When you hear of fit and healthy people who regularly eat BV's, they
are fit and healthy in spite of eating BV's; they are fit and healthy because
of other healthy lifestyle factors, not because of BV consumption.
*
Broccoli is often lauded as a good vegetable to eat if you want to
lose weight because it is claimed to fill you up 'without being fattening'. But
nothing could be further from the truth. By causing an underactive thyroid,
this results in less thyroid hormones being produced. This in turn impacts on
the adrenal glands.
"Thyroid function influences and is influenced by the
pituitary, adrenals, parathyroid, and sex glands, all of which work
together". Source: Hoption Cann SA.,
Hypothesis: dietary iodine intake in the etiology of cardiovascular disease. J
Am Coll Nutr. 2006 Feb; 25(1):1-11.
The strong link between an underactive thyroid and weight gain is
well established. Basically, an underactive thyroid inhibits the adrenal glands
from producing certain hormones that switch on 'lipolysis'.
When lipolysis is inhibited, fat cells cannot lose fat, and weight
gain is inevitable. For optimum health you want to be in a state of lipolysis
as often as possible. The regular consumption of BV's will indirectly inhibit
lipolysis, thus promoting weight gain. Lipolysis is the body's own powerful weight
loss weapon; once you understand how to switch on and exploit lipolysis you
will be able to lose weight easily and maintain a healthy slim body. For more
information about lipolysis, see our sister book 'The Lipo diet' (DeliveredOnline.com).
"[When] these goitrogenic compounds [brassica vegetables] are consumed, the
glycosinolates are hydrolyzed to isothiocyanates in the gut, and they can have
powerful anti-thyroid effects and interfere with the synthesis of necessary thyroid
hormones....They inhibit thyroid function by blocking the incorporation of
iodine into thyroxine precursors and by suppressing thyroxine secretion from
the thyroid." Source: Glucosinolates (Goitrogenic Glycosides),
Department of Animal Science - Plants Poisonous to Livestock, Cornell
University College of Agriculture and Life Sciences.
*
"Following these nutritional tips may help reduce
symptoms of hypothyroidism: Avoid foods that interfere with thyroid function,
including broccoli, cabbage, Brussels sprouts, cauliflower, kale, spinach...."
Source: Hypothyroidism, University of Maryland Medical Center
http://umm.edu/health.
*
"Some
glucosinolates have been shown to have toxic effects, mainly as goitrogens"
(Wikipedia).
*
"Very
high intakes of cruciferous vegetables, such as cabbage and turnips, have been
found to cause hypothyroidism (insufficient thyroid hormone) in animals".
Source: Fenwick GR, et al, Glucosinolates and their breakdown products in food
and food plants, Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 1983; 18(2):123-201.
*
Do not think
that by just taking an iodine supplement you can neutralize the anti-iodine
effect of BV's, thus giving you license to consume such vegetables. This won't
work for two reasons:
1. Certain
glucosinolates in BV's (known as goitrogens) inhibit the thyroid from producing
thyroid hormones. For the technically minded, these goitrogens actually block
the incorporation of iodine into thyroxine precursors thus preventing the thyroid
from working properly, so ingesting more iodine won't help. Put another way,
goitrogens in food interfere with thyroid peroxidise (TPO), the enzyme
responsible for adding iodine during production of thyroid hormones.
Clearly, if the
hypothyroidism is caused by an acute lack of dietary iodine (a common form of
hypothyroidism in some parts of the world), then taking more iodine will indeed
help mitigate hypothyroidism. But if an underactive thyroid is caused by
consuming goitrogens, then iodine supplements won't help; the solution is to
give up ingesting such goitrogens.
2. A person
consuming BV's may not be lacking in dietary iodine from other food sources. So
taking iodine supplements may risk overdosing the body with iodine. To recover
from an underactive thyroid deficiency is not a quick fix. The road to recovery
will be slow and gradual over a period of several weeks once you give up BV's.
You should be very cautious about taking iodine supplements so as to not risk
overdosing with iodine and causing hyperthyroidism; this is as bad as hypothyroidism,
but for other reasons.

Underactive
thyroid inhibits testosterone.
As mentioned,
BV's contain many glucosinolates, some of which convert to indole-3-carbinol
and DIM (diindolylmethane) once digested. Those who make or sell supplements
that include indole-3-carbinol or DIM try hard to proclaim that such compounds increase testosterone. Their argument goes something like this:
"Most
testosterone circulates in the blood, bound to SHBG (Sex hormone-binding
globulin). Such testosterone cannot be freely used by the body. DIM breaks up
some of the SHBG, thus freeing some of the testosterone which can then be used
by the body".
This is mostly
conjecture and the evidence is equivocal. There are no significant trials (i.e.
long-term, peer-reviewed studies) to prove whether DIM does in fact increase
the amount of free testosterone in the human body. Animal trials show that it
depends on the species. For example, after treatment with indole-3-carbinol or
DIM, rat liver enzymes respond differently than monkey liver
enzymes. Source: Wortelboer, H.M., et al, Acid reaction products of
indole-3-carbinol and their effects on cytochrome P450, and phase II enzymes in
rat and monkey hepatocytes. Biochem Pharmacol, 1992. 43(7): p. 1439-1447.
Furthermore,
even if it turns out that synthesised DIM does indeed help increase the amount
of free testosterone in the blood, this is not the end of the story as far as
BV's are concerned. Unlike pure synthesised DIM, BV's come with a host of
unhealthy ingredients some of which inhibit testosterone.
Pure synthesised
indole-3-carbinol and DIM do not contain goitrogens and do not cause an
underactive thyroid. Hence, such medications will not inhibit free testosterone
in the blood, although it is debatable (the research is not clear) whether they
actually increase free testosterone.
But as
mentioned, BV's contain goitrogens that can and do cause an underactive
thyroid. And it is now well established that an underactive thyroid can inhibit
testosterone, quite apart from the other health problems it causes.
"Testosterone
is made in the testes and adrenal glands in a male, and in a woman, the ovaries
and adrenal glands. Testosterone is very important for metabolism. It has been
shown that a low thyroid results in low testosterone levels. When the thyroid
gland returns to optimal function in individuals with challenged thyroids,
their testosterone levels also return to normal". Source: Dr. Nikolas
Hedberg, D.C., D.A.B.C.I., Hormone-Thyroid Connection, 2011,
http://drhedberg.com.
*
"Thyroid
hormone deficiency affects all tissues of the body....Free testosterone
concentrations are reduced in men with primary hypothyroidism and thyroid
hormone replacement normalizes free testosterone concentrations". Source: Meikle AW, The interrelationships between thyroid dysfunction and
hypogonadism in men and boys, Thyroid. 2004; 14 Suppl 1:S17-25.
*
"The interest in iodine comes from the fact that hypothyroid
patients have been found to have significantly lower testosterone - perhaps by
as much as 36%". Source: J Androl, et al, Serum
levels of total testosterone and sex hormone binding globulin in hypothyroid
patients and normal subjects treated with incremental doses of L-T4 or L-T3, J
Androl. 1988 May-Jun; 9(3):215-9.
*
To summarize this point, an underactive thyroid affects the adrenal
glands, thus inhibiting the adrenals from producing hormones. One of these
hormones is testosterone. So an underactive thyroid indirectly inhibits the body's
production of testosterone, and this can have a harmful feminizing effect on
the body as explained in the following pages.
"The adrenal glands produce….sex hormones, or androgens….which
are converted to more potent androgens such as testosterone and DHT or to
estrogens (female sex hormones) in the gonads" (Wikipedia.org).

Less
testosterone causes harmful feminizing effect.
We have seen
that the regular consumption of BV's as a staple can inhibit iodine uptake by
the thyroid, causing an underactive thyroid. We have also seen that an
underactive thyroid inhibits testosterone, causing less free testosterone to be
available to the body.
Does a
reduction in free testosterone in the blood have a harmful feminizing effect on
the body?
Absolutely!
Many studies show that adequate levels of testosterone in both men and women
are essential for good overall health. When testosterone is inhibited, all
sorts of health problems ensue, ranging from cancer, infertility and stunted body
growth to osteoporosis, dementia and heart disease.
More
specifically, when it comes to women, the feminising effect of consuming BV's
does not make a woman 'more feminine'. Rather, it has a devastating effect on a
woman's health. Women need testosterone as much as men, albeit at a lower
level. A healthy level of testosterone in women ensures good body growth and
normal height, greater emotional stability and general well-being, healthy sex
drive, better stamina, more energy, regular periods, a slim feminine body, firm
muscles and much more. Testosterone does not make a woman more masculine;
rather, testosterone makes a woman more feminine with all the curves in the
right places!

Men also
need healthy levels of te









