Part 1: On-page Optimization - the Basics
On-page optimization is the fundamental part of the overall marketing strategy which every website owner should put first. Proper website architecture not only provides the opportunity to rank well in search engines, but it also increases the readability of your website for visitors.
Search engines are getting more and more intelligent and smarter every day. The times when on-page optimization referred purely to keyword placement, and search engines just wanted to see keywords in definite locations of the website’s HTML code, has gone. Now the algorithms that search engines use to evaluate and rank pages have become massively more complex. Today’s SEO requires a better understanding of your audience. It starts not with keywords but with the User and an understanding what he/she really needs.
The aim of foundational website optimization is not to “game” Google or Bing, but to interact with search engines in the best way and, what is the most important, to create a great experience to the users.
There is no one absolutely right way to optimize a web page, but there are concrete objectives that you can accomplish so that each page of your website would provide a truly unique kind of value that will finally lead to:
1. High rankings in search engines;
2. Traffic from social networks like Facebook, Google+, Twitter, etc.;
3. Natural external links to your website’s pages;
4. Your brand’s high reputation and trust that will finally lead to conversion.
Ok, here we go:
-
You have your website or you have a good website template ready for customization and optimization;
-
You’re strongly geared up for becoming popular, gaining in success online and making money;
-
You have this guide telling you how to do that.
So, you have enough for a good start to make your website well optimized and user-friendly. Ready? Let it roll!
What Does Matter in Today’s SEO?
A search engine’s algorithm has always been a complex mixture of factors that evaluate a page’s relevancy for a query. Despite the progress of SEO and Google’s updates like Hummingbird (the algorithm which brought improvements in semantic search), the primary point of a search engine’s algorithm hasn’t changed. So, if you’re progressing with the natural SEO, you’re on the right way, and there is nothing to worry about.
Now you might be thinking: “It’s easy just to say “make it naturally”, but what are the concrete things to do?” Here we will try our best to tell you in detail what you can do with your website to make it well on-page optimized.
So, the general things that do continue matter for search algorithms are:
-
Quality Content and Use of Keywords continue to stay of a great value despite hot debates and some doubt around the necessity of focusing on keywords. However, keywords are not going away completely. If they didn’t matter, what would we be typing into our queries?
-
Mobile Optimization – that’s going to stay critical, because more and more searches are accessing content from mobile devices.
-
Google’s Social Network (G+) identifies your brand, ties it with the definite concepts what sends a signal to Google.
-
Backlinks – despite Google’s warnings about using links that pass PageRank, links still remain of a great value and send the info about your page’s credibility to search engines.
-
Structured Data Markup/Rich Snippets – by marking your content, you increase your chances for better click-through rates and help search engines to present search results for the customers better.
The essential point of website optimization that you need to comprehend and always keep in mind is that you’re making your website for the user, your user. When you understand what your audience really wants, it’s half the battle.
Now let’s get straight to the point – our first and biggest task is Keyword Research.
Keyword Research (Keywords)
It all starts with words that a user types into a search box. Making keyword research means make research of the market. When done right, it provides you with the true language which people are using when they’re searching for the product or service you offer.
“Right” keywords mean “right” kind of visitors. It’s useless to wait for the revenue from your website if you use “wrong” keywords…

Brainstorming
Now it's time to brainstorming a bit. Write down every word and phrase you can think of that people might use in their queries while searching for your product or service. You can also get some ideas from your colleagues, family and friends - you can discover a bunch of unexpected phrases and words for your list. Also, a good idea is to use Thesaurus to look for synonyms.
When considering variations, keep in mind that the user’s age, place of living, profession, interests, etc., may matter. We often have more than two ways of saying the same thing. For example: cell phone - mobile phone - digital phone.
Create an Excel spreadsheet to set your keyword research up - that’s really convenient.
What About Helpful Web Tools?
After you have your starting list of about 30-40 keywords ready, it makes sense to browse through the web and see what people actually search for when they are interested in similar products or services. There are some web resources that can help you find more keywords:
There are different types of keyword research tools available, among which the most popular are Google Keyword Planner and Bing Keyword Research Tool.
In Google Keyword Planner the process starts with entering a keyword of your choice that you feel matches with the theme of your website. The Keyword Planner tool will then come up with a list of related keywords.
Don’t target all of them otherwise you risk to lose focus on the most important and relevant set of keywords. Besides, not all of them are suitable for your website. Remember that all these keywords research tools will only give you some suggestions but it is up to you to choose the final set of keywords that you feel are good for driving targeted traffic to your website.
A keyword with high search volume may be tempting, but we should not ignore the fact that getting high rankings with those keywords will be extremely tough because too many people are competing for them. So, it makes sense to go for keywords with medium search volume because fewer people are targeting them and, therefore, the chances of ranking high will be much better.
Google Trends is a great tool to foresee potential traffic from your targeted keywords. You can get keyword info for a definite period of time (e.g. a month, a year, etc.); the data are divided into region, language, city, time range and category.
Our interest is the "Related Terms" box, where we can find some ideas for our keyword research.

What is especially cool about this tool is that we can analyze fresh keywords which have not many searches and cannot be analyzed via AdWords Keyword Tool.
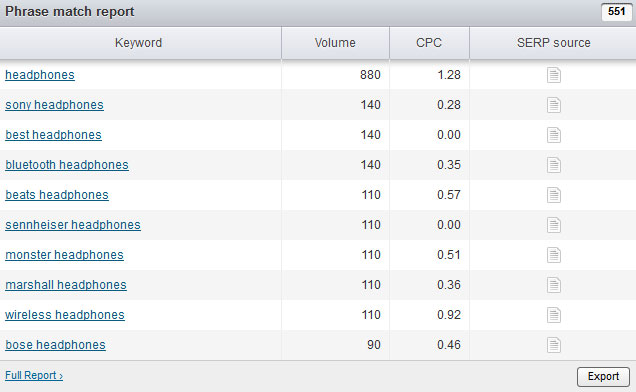
SemRush is a useful tool which can help you with related keywords via its "Phrase match report"; you can also get the list of domains for those terms.

Long Tail Keywords
By selecting ‘Long Tail Keywords’, you can help drive huge amount of traffic to your website. Long Tail Keywords are basically search queries that usually include more than 4 to 5 words. For example, if a keyword is – ‘Web Design’, a long tail keyword may look like this – ‘the best web design company in [City Name]’. These are basically search queries used by people to gather information from different search engines. The best way to find them is by scoping out long key phrases from any of the keywords research tools we have mentioned earlier.
There is an alternative option available though. Just make a search in Google or Bing with any keyword of your choice and then it will come up with a list of related keywords [at the bottom of the SERP].

Semantic Search and Keywords Research
Semantic Search is entirely different from keywords based search because it’s about understanding the intention of the searcher. Before Google’s Hummingbird update, its computational power was not that strong to understand the relation between a search query and the intent of the searcher.
For example, when you search with the term – ‘who is the director of Transformers 4,' Google now knows exactly what you are looking for and shows a picture of the smiling face of Michael Bay along with his name in the SERP rather than showing ‘10 blue links’.

It’s quite clear that search engines are no longer keyword centric. They have evolved, and if you are too dependent on keywords to build content around them, you are simply doing it wrong.
Brainstorm ideas, find words and phrases which people are using when searching for your product or service. It’s not necessary these words and phrases to be keywords. To make your website more search engine friendly and to make the most of semantic search and Google Hummingbird update, you need to do brainstorming to be able to come up with those phrases that people actually use in real life.
URL Optimization
Google uses around 200 various metrics to rank pages, and URL structure is one of the biggest factors for a website to rank well. A URL needs to be relevant, brief and descriptive as far as possible.
If your website has several levels of navigation and folders, the URL structure needs to reflect that too. URL needs to make it abundantly clear about the location of the web page and should be descriptive at the same time without becoming overly lengthy.
Bad example:
http://www.abc.com/index.php?product=215&sort=color&price=1
The above URL does not give you a single clue about what the page is about and more important, it doesn't even include the keyword that you are supposedly targeting.
Good example:
http://www.abc.com/headphone/Sony-Headphones/Sony-ZX110A-Wired- Headphones
This URL has a proper folder structure, has a clearly defined path, includes the keyword [which is the product name actually] and at the same time, it is short.
Here are some other URL best practices:
-
Try not to use underscore, random words and spaces in the URL. Use hyphens to separate words. But the number of hyphens in a URL should be kept to a logical limit.
-
Try not to cross 2,048 characters while creating a URL because longer URLs will not be able to render itself on browsers like Internet Explorer.
-
Parameters are not necessarily bad but you should restrict their use as far as possible.
-
Include keywords in the URL but make it reader-friendly. When you add keywords to the URL, make sure it gives you a clear idea of what the page is about for both readers and search engines.
Metadata Optimization
Once you are done with keyword research, the next important step is writing Metadata for pages. Each website page should have its unique set of Metadata and they should include keywords but that should be done naturally.
Here are three most important components of Metadata:
Title
This is the most important element of a page which is often used with Meta description element. Try to limit the title tag length within 65 characters otherwise it will get truncated in the SERP. The Title tag sits between <head></head> in the HTML code:
<title>The Title of the Page, Keep it within 65 Characters</title>
Meta Description
As the name suggests, this tag contains a synopsis of the page. In simple English, it tells search engines what the page is about. Try to limit the length of the Meta Description tag within 150 characters. Use keywords judiciously in this section.
<meta name="description" content="Add short description of the page." />
Meta Keywords
This tag is fast becoming obsolete and almost all search engines have made it clear that they no longer take this tag into account when it comes to determining quality of a website.
<meta name="keywords" content="keyword 1, keyword 2, keyword 3">
Meta Robots
This Meta tag allows us to control whether to allow or deny search engines to index your web pages. This “robots” tag is obeyed by almost all major search engines; however, if you want to give directives to some specific search engines, you need to specify the name of the bot in the Meta robots section.
The default value of Meta Robots tag is <meta name="robots" content="index, follow" />
Here are some other directives:
-
Noindex – prevents search engines from indexing the page;
-
Nofollow - prevents Googlebot from passing link juice to the link and also it directs search engines not to follow the links.
-
Noarchive - prevents Google to show cache version of a web page.
-
None – equivalent to noindex, nofollow tag. This will prevent search engines from indexing the page and also prevent it from following the links in the web page.
Page Content Optimization
Just a few years ago, the concept of page content optimization was limited to the idea of stuffing as many keywords in the body copy as possible. However, after the Panda and other subsequent updates, the concept has undergone a massive change.
Page content optimization largely involves those tactics that aim at making the web page content more visitors and search engine friendly.
Here are few things that you should be taking care of while writing content for a web page:
-
Theme - the content should be built around the theme of the web page. If the page is about, let's say, climate change, it makes sense to create a closely neat content around the topic using synonyms naturally.
-
Headings - page content needs to have proper headings. Ideally, headings need to have keywords included but no need to force the keywords in them. Use not more than one H1 tag per page. Try to include the keywords naturally if possible otherwise just make sure the headings are good enough to capture the attention of the audience.
-
Unique and Informative – under no circumstances you shouldn't copy and paste content from other external sources on your web page. You should try your level best to ensure the fact that your web page content is 100% unique. You can use CopyScape [a paid tool] to determine whether the content is unique or has been copied from external sources.
-
Be Aware of Thin Content – just making the content unique is not enough anymore; it has to be engaging and informative as well. The Panda update not only targets web pages with duplicate content, but it also targets web pages with ‘thin’ content. ‘Thin’ content or ‘filler’ content is basically “the content with little or no added value”. Make the content unique and also make sure that the content adds value to users’ experience.
Use of Keywords – they should be blended naturally within the body copy. Don’t worry about keywords density at all. No need to emphasize the keywords by using bold fonts because Search Engines have got smart enough to figure out what the page is about.
Internal Links
The importance of a page in a website is determined by the number of internal links are pointing to it. The links send a signal to search engines about the relative importance of the page in a website and therefore, internal linking should be done carefully.
Here are some pro tips to make your website’s internal linking structure rock:
-
Make Navigation Friendly – try to use plain and simple HTML while adding links of internal web pages in the navigation so that search engines can find those pages and index them easily.
-
Know the Limit – don’t add a large number of internal links from a web page. The majority of search engines cannot crawl more than 150 links in a given page, so try to limit the number of internal links to this point.
-
Follow a Structural Approach – identify the most important pages of your website. Once you have got the idea, link those pages to other relevant sections of your website.
For example, if your website is eCommerce and you find that a product, let’s say, the “Sony Headphones” item, is selling like a hotcake, you can get it linked from all other pages that are somewhat related to headphones.
-
Use Proper Anchor Text – people now use texts like Click Here, Click Now, etc. for internal linking in order not get flagged by search engines for keywords spamming. However, we would rather recommend you to use descriptive texts as anchor texts while internal linking. Just don’t stuff the pages with keywords and you will be fine.
For example, if you are selling Mac books and you want to link this page from another page, you can use texts like – ‘to buy Mac Book, visit this page’ or ‘visit our Mac Book section’. It makes sense to both search engines and users.
Relevant and trustworthy external links add great user experience. But there are some rules of a thumb to be followed while adding external links from your website:
-
Use Nofollow – in case you are not sure how authentic the source is, you should be using nofollow tag against it. It will stop Page Rank juice flowing through your website. Check the example below:
< a href="http://www.anexternallink.com" rel="nofollow">External Link</a>
-
Open the Link in New Tab – if a visitor clicks on an external link that you have inserted in a web page, they will leave your website and will land on an external website. Losing a visitor is certainly not the objective of a website. To make sure that the visitors stay on your website even when they click on an external link, you need to make those external links open in new tabs when clicked. This can be done by using target="_blank" attribute in the following way:
<a href="http://www.example.com" target="_blank">Visit External.com</a>
Images and Alt
Google has no idea what your images are unless you specify in the ALT tags. All Google robots see is code, but not your beautiful picture.
Images if optimized properly can drive tons of traffic to your website. A good thing is image optimization is comparatively less complicated. Here is how you can do it:
-
Use Alt tags – since most search engines can’t read what the image is about or unable to parse it, we need to use Alt Tag [alternative texts] to make it easier for search engines to understand what the image is about. Alt tag does not need to be keywords centric all the time. Alt tag should be used to describe the image.
-
File Size – page loading time does matter, so you should not let the browser re-size a large image to make it look smaller. Use small images instead, depending on your requirements. You need to cut down the image size without making any kind of compromise on the quality fronts.
-
File Name – bird.jpg / abcd.jpg – tells us which image name is more meaningful. Of course, the first one. So, while naming the images, it's better use proper and meaningful name rather than using some random words or combinations.
Multi-channel Optimization
Since people are using multiple devices to stay connected and to perform different tasks, the importance of Multi-Channel optimization has skyrocketed.
So, if your website is struggling to render itself properly on small screen devices, your marketing activities are already in a mess. First you need to embrace responsive design if possible.. at least you should try to make sure that your website gets loaded fast on mobile devices. There are few other things that you should be taking into account while trying to make your website multi-device friendly.
-
Use Small Images – small devices do not have great computational power, so you need to make sure that your website is not using an excessive number of graphics and images. Take a minimalist approach instead.
-
Use Big Buttons – since people will be using their fingertips to navigate your website, you need to make sure that the navigational buttons are big to make room for it. Try to trim down on the use of contextual navigation for mobile friendly version of your website.
-
Don’t Use an Excessive Amount of Content – mobile devices are not great for reading, so there is no sense in adding lengthy content in the mobile version of your website. Use catchy, compact and conversion oriented content.
Crawler Access
We have already discussed the use of Meta Robots tags. Here we are going to discuss how we can use robots.txt file to control what pages we want search engines to index and what pages we don’t want them to index.
Robots.txt file is basically a simple txt file and it should be uploaded to the root folder of a website.
http://www.example.com/robots.txt
If you don’t want to block any pages from search engines, you just need to add the following tags in the robots.txt file:
User-agent: *
Disallow:
In case you want to block a certain page, for example, this one – http://www.example.com/blockpage.php - you will need to add the following tag in the robots.txt file:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /blockpage.php
To block a folder – http://www.example.com/folderexample/ - you need to add the following tags:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /folderexample/
To block the whole website, use the following tags:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /
Don't forget to indicate the sitemap in the robots.txt file:
Sitemap: http://www.yoursite.com/sitemap.xml









