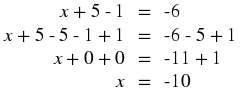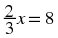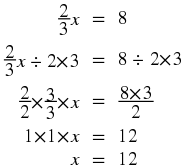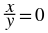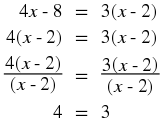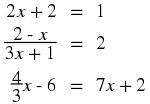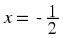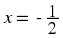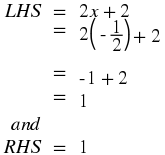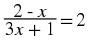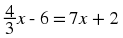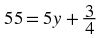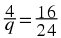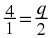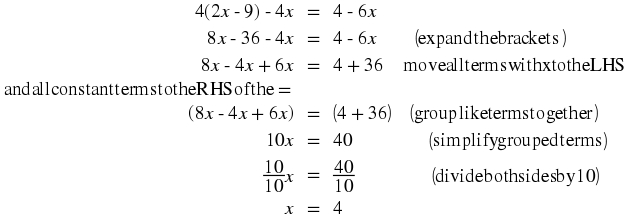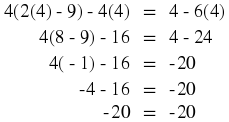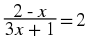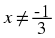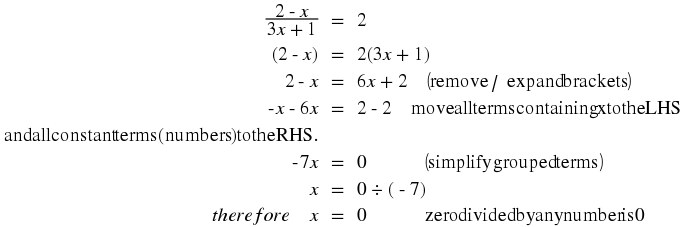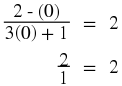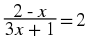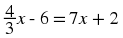Strategy for Solving Equations
Method: Rearranging Equations
You can add, subtract, multiply or divide both sides of an equation by any number you want, as long as you always do it to both sides.
For example, in the equation
x + 5 – 1 = – 6, we want to get
x
alone on the left hand side of the equation. This means we need to subtract 5 and add 1 on the left hand side. However, because we need to keep the equation balanced, we also need to subtract 5 and add 1 on the right hand side.
In another example, 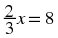 , we must divide by 2 and multiply by 3 on the left hand side in order to get
x
alone. However, in order to keep the equation balanced, we must also divide by 2 and multiply by 3 on the right hand side.
, we must divide by 2 and multiply by 3 on the left hand side in order to get
x
alone. However, in order to keep the equation balanced, we must also divide by 2 and multiply by 3 on the right hand side.
These are the basic rules to apply when simplifying any equation. In most cases, these rules have to be applied more than once, before we have the unknown variable on the left hand side of the equation.
Note
The following must also be kept in mind:
Division by 0 is undefined.
If 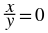 , then
x = 0 and
y ≠ 0, because division by 0 is
undefined.
, then
x = 0 and
y ≠ 0, because division by 0 is
undefined.
We are now ready to solve some equations!
Investigation : Strategy for Solving Equations
In the following,
identify what is wrong.