y
( t )
2
= t
y
( t ) = 2cos( t )
x ( t ) = 2sin( t )
x ( t ) = 2 + t
x ( t ) = 2
− − 2 t
4.
5.
6.
y
( t ) = 4cos( t )
y
( t ) = 3 − 2 t
y
( t ) = 3 + t
A
B
C
D
E
F
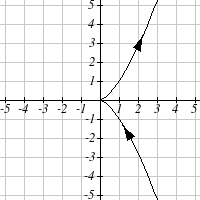
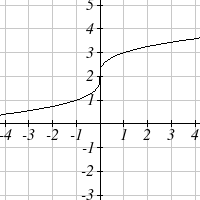
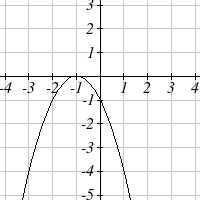
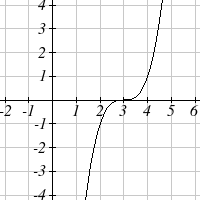
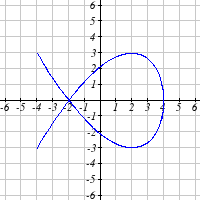
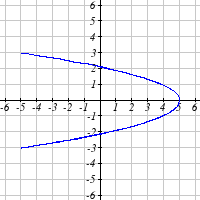
From each pair of graphs in the t-x and t-y planes shown, sketch a graph in the x-y plane.
7.
8.
Section 8.5 Parametric Equations 515
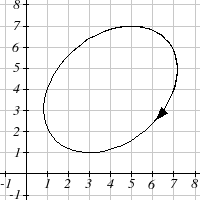
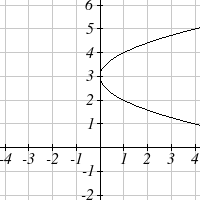
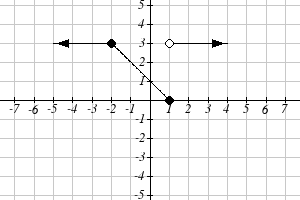
From each graph in the x-y plane shown, sketch a graph of the parameter functions in the
t-x and t-y planes.
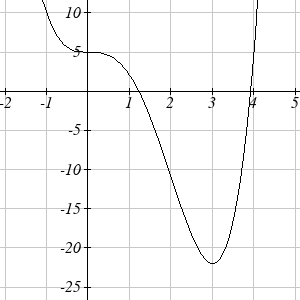
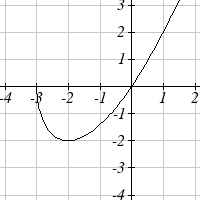
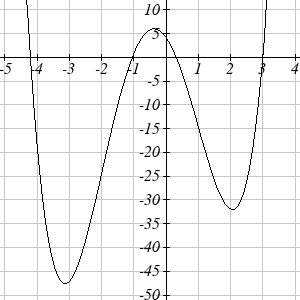
9.
10.
Sketch the parametric equations for 2−≤ t ≤2.
x ( t ) =1+ 2 t
x ( t ) = 2 t − 2
11.
12.
y
( t )
2
= t
y
( t )
3
= t
Eliminate the parameter t to rewrite the parametric equation as a Cartesian equation
x ( t ) = 5− t
x ( t ) = 6 −3 t
13.
14.
y
( t ) = 8 − 2 t
y
( t ) = 10 − t
x ( t ) = 2 t +
1
x ( t ) = 3 t −1
15.
16.
y
( t ) = 3 t
y
( t )
2
= 2 t
( ) = 2 t
x t
e
x ( t ) = 4log( t )
17.
18.
y
( t ) = 1− 5 t
y
( t ) = 3 + 2 t
x ( t ) 3
= t − t
x ( t )
4
= t − t
19.
20.
y
( t ) = 2 t
y
( t ) = t + 2
x ( t )
2 t
= e
x ( t ) 5
= t
21.
22.
y
10
( t )
6 t
= e
y
( t ) = t
x ( t ) = 4cos( t )
x ( t ) = 3sin( t )
23.
24.
y
( t ) = 5sin ( t )
y
( t ) = 6cos( t )
516 Chapter 8
Parameterize (write a parametric equation for) each Cartesian equation
25. y ( x )
2
= 3 x + 3
26. y ( x ) = 2sin ( x ) +1
27. x ( y ) = 3log( y ) + y
28. x ( y ) = y + 2 y
2
2
2
2
29. x
y
+
= 1
30. x
y
+
= 1
4
9
16 36
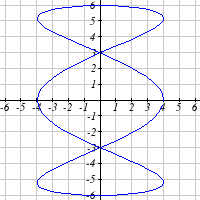
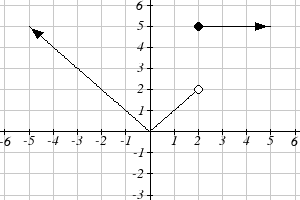
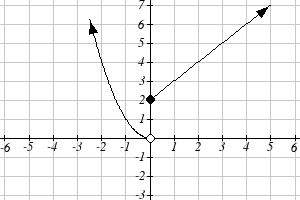
Parameterize the graphs shown.
31.
32.
33.
34.
35. Parameterize the line from ( 1,−5) to (2,3) so that the line is at ( 1,−5) at t = 0, and at
(2, 3) at t = 1.
36. Parameterize the line from (4,1) to (6, 2
− ) so that the line is at (4,1) at t = 0, and at
(6, 2)
− at t = 1.
Section 8.5 Parametric Equations 517
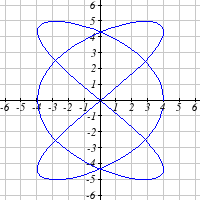
x ( t ) = a cos( bt )
The graphs below are created by parameteric equations of the form
.
y
( t ) = c sin ( dt )
Find the values of a, b, c, and d to achieve each graph.
37.
38.
39.
40.
41. An object is thrown in the air with vertical velocity 20 ft/s and horizontal velocity 15
ft/s. The object’s height can be described by the equation y ( t )
2
= 16
− t + 20 t , while
the object moves horizontally with constant velocity 15 ft/s. Write parametric
equations for the object’s position, then eliminate time to write height as a function of
horizontal position.
42. A skateboarder riding on a level surface at a constant speed of 9 ft/s throws a ball in
the air, the height of which can be described by the equation y ( t )
2
= 16
− t +10 t + 5.
Write parametric equations for the ball’s position, then eliminate time to write height
as a function of horizontal position.
518 Chapter 8
43. A carnival ride has a large rotating arm with
diameter 40 feet centered 35 feet off the ground.
At each end of the large arm are two smaller
rotating arms with diameter 16 feet each. The
larger arm rotates once every 5 seconds, while the
P
smaller arms rotate once every 2 seconds. If you
board the ride when the point P is closest to the
ground, find parametric equations for your
position over time.
44. A hypocycloid is a shape generated by tracking a fixed
point on a small circle as it rolls around the inside of a
larger circle. If the smaller circle has radius 1 and the
large circle has radius 6, find parametric equations for
P
the position of the point P as the smaller wheel rolls in
the direction indicated.
519
Solutions to Selected Exercises
Chapter 1
Section 1.1
1. a. f (40) =13
b. 2 Tons of garbage per week is produced by a city with a population of 5,000.
3. a. In 1995 there are 30 ducks in the lake
b. In 2000 there are 40 ducks in the late
5. a ,b, d, e
7. a, b
9. a, b, d
11. b
13. b, c, e, f
15. f ( )
1 =1, f (3) =1
17. g (2) = 4, g ( 3
− ) = 2
19. f (3) = 53, f (2) =1
f ( 2
− )
f (− )
1
f (0)
f ( )
1
f (2)
21.
8
6
4
2
0
23.
49
18
3
4
21
25.
4
-1
0
1
-4
27.
4
4.414
4.732
5
5.236
29.
-4
-6
-6
-4
0
31.
5
DNE
-3
-1
-1/3
33.
1/4
1/2
1
2
4
35. a. -6
b.-16
37. a. 5
b. 5
−
3
39. a. iii
b. viii c. I
d. ii e. vi f. iv g. v h. vii
41. a. iv
b. ii c. v d. I
e. vi f. iii
43. ( x − )
3 2 + ( y + 9)2 = 36
45. (a)
(b)
(c)
ad
he
tage
ight
of
he
pos
ighthe
age
time
weight
47a. t
b. a
c. r
d. L: (c, t) and K: (a, p)
520
Section 1.2
1. D: [-5, 3)
R: [0,2]
3. D: 2 < t ≤ 8
R: 6 ≤ g ( t ) < 8
5. D: [0,4]
R: [-3, 0]
7. [ ,
2 ∞)
9. (−∞ ]
3
,
11. (−∞ )
6
, ( ∞)
∪ ,6
13.
1
1
(−∞,− )∪
− ,∞
2
2
15. [ 4,
− 4) ( 4,∞
∪
)
17. (−∞,− )
11 ( − ,
11 2) ( ,
2 ∞)
∪
∪
f (− )
1
f (0)
f (2)
f (4)
19.
-4
6
20
34
21.
-1
-2
7
5
23.
-5
3
3
16
2
if − 6 ≤ x ≤− 1
3 if x ≤ 0
25. f ( x )
= − 2 if
−1 < x ≤ 2
27. f ( x ) =
2
x if x > 0
− 4 if
2 < x ≤ 4
2 x +
3 if
−
3 ≤ x < −1
29. f ( x )
= x −
1
if
−
1 ≤ x ≤ 2
− 2 if
2
< x ≤ 5
31.
33.
35.
521
Section 1.3
1. a) 6 million dollars per year b) 2 million dollars per year
−
3. 4 5
1
= −
5. 6
4 −1
3
7. 27
9. 352
27
11. 4 b +4
13. 3
15.
1
−
17.
2
9 + 9 h + 3 h
13 h +169
19. 4 x + 2 h
21. Increasing: (− ,
5
.
1 2). Decreasing: (− ∞,− 5
.
1 )∪ ( ,
2 ∞)
23. Increasing: (− ∞ )
1, ∪ ( ,
3 4). Decreasing: ( )
3
,1 ∪ ( ,
4 ∞)
25. Increasing, concave up
27. Decreasing, concave down
29. Decreasing, concave up
31. Increasing, concave down
33. Concave up (− ∞ )
1, . Concave down ( ,1∞). Inflection point at (1, 2)
35. Concave down (− ∞ )
3
, ∪ ( ,
3 ∞)
37. Local minimum at (3, -22). Inflection at (2, -11).
Increasing on ( ,
3 ∞). Decreasing (− ∞ )
3
,
Concave up (− ∞ 0
, )∪ ( ,
2 ∞). Concave down ( ,
0 2)
39. Local minimum at (-2, -2)
Decreasing (− ,
3 2
− )
Increasing (− ,
2 ∞)
Concave up (− ,
3 ∞)
41. Local minimums at (-3.152, -47.626)
and (2.041, -32.041)
Local maximum at (-0.389, 5.979)
Inflection points at (-2, -24) and (1, -15)
Increasing (−
,
152
.
3
− 389
.
0
)∪ (
,
041
.
2
∞)
Decreasing (− ∞,− 152
.
3
)∪ (−
,
389
.
0
)
041
.
2
Concave up (− ∞,−2)∪ ( ,1∞)
Concave down (− )
1,
2
522
Section 1.4
1. f ( g ( ))
0 = 36 . g ( f ( ))
0 = 57
−
3. f ( g ( ))
0 = 4 . g ( f ( ))
0 = 4
5. 4 7. 9 9. 4 11. 7 13. 0 15. 4 17. 3 19. 2
21. ( ( )) x
f g x =
g ( f ( x )) = 7 x −36
7
23. f ( g ( x ) = x + 3
g ( f ( x ))
2
= x + 3
25. f ( g ( x )) = 5 x +1
g ( f ( x )) = 5 x +1
27. f ( g ( h ( x ))) = ( x − )4
6 + 6
29a. ( ,
0 2)∪ ( ,
2 ∞)
b. (− ∞,−2)∪ ( ,
2 ∞)
c. ( ,
0 ∞)
3 10 + 20 t
31. b
33a. r ( V ( t ))
(
)
3
=
b. 208.94
4π
35. g ( x ) = x + f ( x )
2
2,
= x
37. f ( x ) 3
= , g ( x )
= x − 5
Page 1 Page 2 Page 3 Page 4 Page 5 Page 6 Page 7 Page 8 Page 9 Page 10 Page 11 Page 12 Page 13 Page 14 Page 15 Page 16 Page 17 Page 18 Page 19 Page 20 Page 21 Page 22 Page 23 Page 24 Page 25 Page 26 Page 27 Page 28 Page 29 Page 30 Page 31 Page 32 Page 33