5.5.1 ) Principles of MLPA Assay
MLPA is a multiplex PCR assay that utilizes up to 40 probes, each specific for a different DNA sequence (mainly exons of a specific gene of interest), to evaluate the relative copy number of each DNA sequence. Each probe is composed of two half-probes (5' and 3' half-probes), consisting of a target-specific sequence and a universal primer sequence allowing the simultaneous multiplex PCR amplification of all probes.
The MLPA reaction can be divided into five steps:
(1) DNA denaturation and Probes hybridization;
(2) Ligation reaction;
(3) PCR amplification;
(4) Separation of amplification products by electrophoresis;
(5) Data analysis.
DNA sequences and to detect copy number variation of specific genes, including small intragenic rearrangements. So far, over 300 probe sets are commercially available from MRC Holland, specific for a very large range of common and rare genetic disorders. MLPA assay has become in a few years a widely used technique in laboratories performing genetic testing for the molecular diagnosis of several diseases.
5.5.2 ) Procedure:
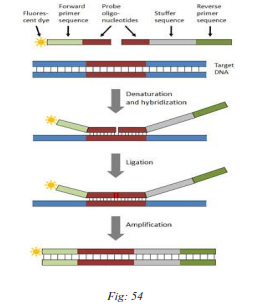
Fig: Principle of MLPA.
The DNA is denatured and incubated with a mixture of MLPA probes. The two half probes are able to recognize contiguous target-specific sequences, and only in the presence of a perfect match without a single gap, after hybridization, can the two half-probes be ligated and amplified. PCR amplification is performed using only one PCR primers pair, one of which is fluorescently labelled. Because only ligated probes will be amplified during the subsequent PCR reaction, the number of probe ligation products is a measure of the number of target sequences in the sample. PCR products are then separated by size using Capillary Electrophoresis under denaturing conditions. The height or area of the PCR derived fluorescence peaks is measured, quantifying the amount of PCR product after normalization and comparing it with control DNA samples, thus indicating the relative amount of target DNA sequence in the input DNA sample.
5.5.3 Application of MLPA)
Originally MLPA was designed as a copy number analysis tool for detecting disease-causing genomic mutations and has been successfully applied in the testing and identification of hundreds of genomic mutations in numerous genes. MLPA has a potential major role in the analysis of common copy number variation in genome-wide association analyses, which may be enhanced by future improvements to increase throughput and lower costs, such as array-MLPA.




