The Afghan Oil Pipeline and the US-Taliban Negotiations
I always mention the TAPI Pipeline (Turkmenistna-Afghanistan-Pakistan-India), which would unlock the natural gas of Central Asia (Turkmenistan, Azerbaijan), and send it to India and the Indian Ocean.
Map 1
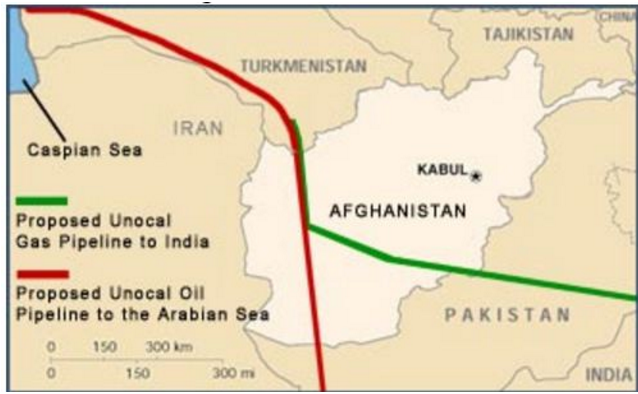
But together with the TAPI pipeline the Americans were also promoting the Afghan Oil Pipeline, which would also unlock the oil of Central Asia (Kazakhstan, Azerbaijan) and send it to the Indian Ocean oo. See Wikipedia link below.
Whether the TAPI or the Afghan Oil Pipeine was more important I do not know. Probably they were equally important for India and the Americans. Obviously TAPI is more important for Turkmenistan, and the Afghan Oil pipeline is more important for Kazakhstan, but what I am talking about is the point of view of the larger players.
When the Soviet Union collapsed in 1991, the Muslim colonies of the Soviet Union became independent communist dictatorships, under the leadership of the local communist leaders i.e. Aliyev in Azerbaijan, Karimov in Uzbekistan, Nazarbayev in Kazakhstan, and Niyazov in Turkmenistan.
For the Americans it was very important to unlock the oil and gas reserves of Central Asia.
Map 2
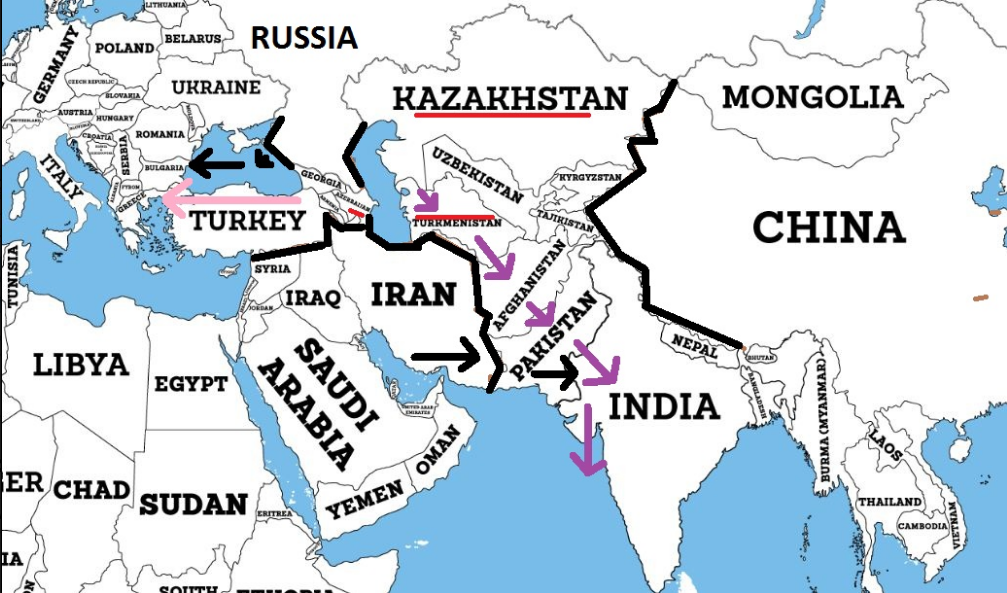
Besides the obvious reasons, by unlocking the oil and gas of Central Asia, and by sending it to India, the Americans would ensure that Central Asia would no longer being dependent on Russia, Iran and China. The best thing was that the Communist dictators of the new countries wanted exactly the same thing, even though they were afraid of Russia and Iran.
Russia and Iran are competing with these countries in the oil and gas markets, and China has almost monopsony power over them and can get their oil and gas at lower than normal prices, since they Turkmenistan and Kazakhstan have no real alternatives.
Iran and Russia block Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan and Turkmenistan when they try to send their oil and gas to Europe through Turkey. Especially they block Turkmenistan and Kazakstan by not permitting the under-water Trans-Caspian Pipeline, which would connect Azerbaijan and Turkmenistan. From the south the Islamist militants who are supported by Iran and the Arabs of the Gulf are blocking in Afghanistan the countries of Central Asia from reaching India.
When the Taliban took control of Afghanistan in 1996, only Pakistan, Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates recognized their government. The Americans were asking from the Taliban to allow the construction of the pipelines, and in return the Americans were willing to recognize their government.
Iran, together with the Arabs of the Gulf, was trying to sabotage the negotiations, but at the same time Iran was almost at war with the Taliban, due to their close relationship with Pakistan and the Arabs of the Persian Gulf. The Taliban had ignored the Islamists of Afghanistan who were supported by the Iranians, mainly the Shias of Afghanistan, who are 20% of the population, and who had formed an alliance with some Tajics and Uzbeks of Northern Afghanistan, the so called Northern Alliance. The Northern Alliance was also supported by Russia and India, while the Taliban were supported by Pakistan and the Arabs of the Persian Gulf.
Map 3
While the Americans were negotiating with the Talibans, Al Qaeda, an ally of the Taliban, was trying to sabotage their negotiations. Al Qaeda was providing financial and military assistance to the Taliban, and in 1998 Al Qaeda attacked the American embassies in Tanzania and Kenya. Two hundred people lost their lives, and another four thousands were injured.
From that moment the negotiations between the Americans and the Taliban took another turn, and the Bill Clinton administration started pushing the Taliban to hand them Osama bin Laden, and to denounce Al Qaeda. But that was very difficult given that Al Qaeda was supporting financially and militarily the Taliban.
The fact is that the attacks on the American embassies had exactly the result that Al Qaeda wanted, which was to undermine the negotiations between United States and various Taliban factions. At the same time due to the Arab money the corrupt Taliban leaderships were not willing to allow the construction of the pipelines, which would be good for all the countries, except of course for Iran and the Arab countries of the Persian Gulf.
As I said after the attacks on the American embassies the negotiations between the Clinton administration and the Taliban went very badly, but when George Bush came to power in January 2001 he started fresh negotiations with the Taliban. But Al Qaeda came back with the attack at the Twin Towers (9/11), and the negotiations were over.
The Americans attacked Afghanistan in 2001, and they overturned the Taliban government, by supporting the Northern Alliance, which was Iran’s ally. Even though Iran, together with Iraq (Saddam) and Sudan, had supported the Saudi terrorists who carried out the attack on the Twin Towers too. But the attack on the Twin Towers was mainly a Saudi assault, even if the Saudi King was not involved.
The United States and Iran managed to form a government in Afghanistan, under the leadership of Karzai, even though the Iranians preferred the Tajik Rabbani to return to power. Karzai was a Pashtun, but a Durrani Pashtun, and Pakistan does not have good relations with Durrani Pasthuns of Western Afghanistan. The Pakistanis mainly support the Ghilzais Pashtuns of Eastern Afghanistan.
It is very difficult for the United States to find a reliable ally in Afghanistan, because like the Arabs, the Iranians are not willing to allow them to unlock the reserves of Central Asia. Only China could be a reliable ally for the Americans in Afghanistan, because China wants peace in Afghanistan too, but for other reasons of course (i.e. new silk roads, peace in Xin Jiang etc).
A peaceful Afghanistan could cost China her monopsony power over the Central Asian countries, but I believe that China would be willing to accept a bit higher prices in order to have a peaceful Afghanistan.
The United States and China have put a lot of pressure on Pakistan, in order to use its influence over the Taliban for peace to be achieved. Under the US and Chinese pressure the Pakistanis had to try, and that gave Iran the opportunity to form a limited alliance with the Taliban in Afghanistan. Iran is supporting opposing sides in Afghanistan. Now the Russias said that they want to cooperate with their old enemy the Taliban.
A great article about the American-Taliban negotiations during the Clinton and Bush administrations, and the Al Qaeda efforts to undermine these negotiations is “Al-Qaida monitored U.S. negotiations with Taliban over oil pipeline”, June 2002. Salon is a very big American website, and the author, Jean Charles Brizard, is a well known French expert on international terrorism.
PS CentGas
CentGas was the consortium that was trying in the 90s to send the natural gas of Turkmenistan to Pakistan. It was made up of Unocal (US), Gazprom (Russia), Delta (Saudi Arabia), two Japanese energy companies, one South Korean, and one Pakistani company.
Do not confuse the private Saudi company Delta with the state owned Saudi Aramco, which is the queen of Saudi Arabia.
As you can see the Americans had managed to include the Russians in the project, because Russia was not exporting natural gas to South Asia. Japan and South Korea, two US allies, were also included, because they do not have access to natural gas from pipelines, and they buy expensive LNG. Japan and South Korea, with their huge economies, are the two largest LNG importers in the world.
See “CentGas”
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CentGas
PS 2 The Unocal Announcement for the 9/11 Attack
After the 9/11 attack leftist conspiracy theorists who were paid by the Islamists and the Communist dictators of Latin America were saying that it was the Americans who carried out the attack, and not Saudi terrorists with the support of Iran, Sudan, Iraq and Pakistan.
The American energy company Unocal had to publicly announce that it had stopped negotiations with the Taliban after the bombings of the American embassies in Kenya and Tanzania in 1998. And that’s true. Both Unocal and Gazprom withdrew from the consortium after the bombings of the American embassies in 1998.
“Company not Supporting the Taliban in Any Way”
https://www.chevron.com/stories/unocal-statement-company-not-supporting-taliban-in-any-way
Articles
“Al-Qaida monitored U.S. negotiations with Taliban over oil pipeline”, June 2002
A 1998 memo written by al-Qaida military chief Mohammed Atef reveals that Osama bin Laden’s group had detailed knowledge of negotiations that were taking place between Afghanistan’s ruling Taliban and American government and business leaders over plans for a U.S. oil and gas pipeline across that Central Asian country.
The e-mail memo was found in 1998 on a computer seized by the FBI during its investigation into the 1998 African embassy bombings, which were sponsored by al-Qaida. Atef’s memo was discovered by FBI counter-terrorism expert John O’Neill, who left the bureau in 2001, complaining that U.S. oil interests were hindering his investigation into al-Qaida. O’Neill, who became security chief at the World Trade Center, died in the Sept. 11 attack.
Atef’s memo shines new light on what al-Qaida knew about U.S. efforts to normalize relations with the Taliban in exchange for the fundamentalist government’s supporting the construction of an oil and gas pipeline across Afghanistan. As documented in the book I coauthored with Guillaume Dasquie, “Bin Laden: The Forbidden Truth,” the Clinton and Bush administrations negotiated with the Taliban, both to get the repressive regime to widen its government as well as look favorably on U.S. companies’ attempts to construct an oil pipeline. The Bush White House stepped up negotiations with the Taliban in 2001. When those talks stalled in July, a Bush administration representative threatened the Taliban with military reprisals if the government did not go along with American demands.
The seven-page memo was signed “Abu Hafs,” which is the military name of Atef, who was the military chief of al-Qaida and is believed to have been killed in November 2001 during U.S. operations in Afghanistan. It shows al-Qaida’s keen interest in the U.S.-Taliban negotiations and raises new questions as to whether the U.S. military threat to the Taliban in July 2001 could have prompted al-Qaida’s Sept. 11 attack.
Atef’s memo is not about the pipeline alone, though it mentions the project several times. It is an analysis of the political situation facing the Taliban. It documents the movement’s rise, its leadership, the geopolitical importance of Afghanistan, the Taliban’s relationship with Pakistan, as well as the movement’s relationship with the Arab mujahedin. The document’s intended readership is unclear. But it reveals that the pipeline was seen as a strategic offering toward the West, in order to make the Taliban government acceptable to the United States and Pakistan, as well as to reduce military and investigative pressure on the country to rein in or even extradite bin Laden.
Atef explains that the United States wants “to take control of any region which has huge quantities of oil reserves,” and “the American government is keen on laying the oil and gas pipelines from Turkmenistan through Afghanistan to Pakistan.” Atef concludes that al-Qaida’s “duty toward the movement [Taliban] is to stand behind it, support it materially and morally, especially because its regional and international enemies are working night and day to put an end to it and make it fail.”
It seems clear the military chief didn’t expect the pipeline negotiations to bear fruit. Referring to Pakistanis as “nonbelievers,” and noting that the pipeline “will be under American control … and it also goes through the territories of Pakistan which are allied to America,” Atef implies that the Taliban has no intention of ultimately cooperating with the project, but is trying to string along the Americans and Pakistanis to win some breathing room for its unpopular government.
The Atef memo is the latest piece of evidence documenting a murky chapter in recent American history — the overtures of the last two American administrations to the repressive Taliban regime. Several U.S. oil companies, most notably Unocal, had been advocates of diplomatic overtures to the Taliban, in order to facilitate the building of a pipeline from the Caspian Sea region to Pakistan and the Persian Gulf through Afghanistan. In 1996, Unocal vice president Chris Taggart described the fall of Kabul to the Taliban regime as a “very positive step” and urged the U.S. to extend recognition to the new rulers in Kabul and thus “lead the way to international lending agencies coming in.”
Just 10 days after the Taliban seized power in Kabul, Zalmay Khalilzad, former National Security Council official and Unocal consultant who was appointed special envoy to Afghanistan by President George W. Bush at the end of 2001, argued in a Washington Post opinion article that the U.S. should try to work with the mullahs and form a broad-based government that included other factions. “The Taliban does not practice the anti-U.S. style of fundamentalism practiced by Iran — it is closer to the Saudi model …” Khalilzad contended, concluding that “we should use as a positive incentive the benefits that will accrue to Afghanistan from the construction of oil and gas pipelines across its territory … These projects will only go forward if Afghanistan has a single authoritative government.”
Soon after, the State Department spokesman Glyn Davies told the New York Times he had hope that “the new authorities in Kabul will move quickly to restore order and security and to form a representative interim government that can begin the process of reconciliation nationwide.” Davies also said the United States “wanted to send diplomats to Afghanistan to meet with the Taliban and held out the possibility of re-establishing full diplomatic ties with the country,” according to the Times.
In November 1997 Unocal invited a Taliban delegation to Texas and, in early December, the company opened a training center at the University of Nebraska, to instruct 137 Afghans in pipeline construction technology. The company also donated to the university’s Center for Afghanistan Studies. Unocal CEO John Imle estimated that the company spent between $15 and $20 million on its Central Asia oil pipeline (CentGas) project — on preliminary feasibility studies, humanitarian projects and other efforts to lobby the Taliban (Unocal equipped the regime with satellite phones, for instance.)
In February 1998, Unocal’s vice president for international relations, John Maresca, told a House subcommittee hearing on U.S. interests in the Central Asian Republics that an oil pipeline “would benefit Afghanistan, which would receive revenues from transport tariffs, and would promote stability and encourage trade and economic development.” Emphasizing that “the proposed Central Asia Oil Pipeline (CentGas) cannot begin construction until an internationally recognized Afghanistan government is in place,” he urged the administration and the Congress “to give strong support to the United Nations-led peace process in Afghanistan.”
Until the 1998 al-Qaida embassy bombings, the Clinton administration’s approach toward the Taliban was much the same as Unocal’s: All parties agreed that the political stabilization of Afghanistan was crucial to the region, and was also a way to gain access to oil reserves of the Caspian Sea region. Though bin Laden had been in the country since 1996, the U.S. had not pressured the Taliban to hand him over.
The embassy bombings in August 1998 changed everything. The Clinton administration denounced the regime and Secretary of State Madeleine Albright turned up the heat on Taliban human rights abuses. The United Nations imposed sanctions, freezing Afghanistan’s foreign assets and limiting its citizens’ travel. The U.S. continued to talk to the Taliban, but the emphasis was on extraditing bin Laden in exchange for international recognition; the pipeline was off the table. Unocal, which had been close to finalizing its pipeline deal before the embassy bombings, cancelled it.
When George W. Bush took office in 2001, his administration made new overtures to the Taliban, and the pipeline deal gained renewed support, as an incentive to get the Taliban to make political concessions and form a broader government. U.S. representatives met with Afghanistan’s former King Shah, to see if he might be included in a new government. And American companies began exploring the failed 1998 pipeline project. A report by an Afghan-born Enron manager in July 2001, for instance, illustrates that company’s deep interest in some sort of pipeline deal. Enron had begun funding the same sorts of humanitarian projects as Unocal had three years earlier.
In March 2001, several Taliban officials, including Sayed Rahmattulah Hashimi, Mullah Omar’s personal advisor, were invited to Washington by their U.S. lobbyist, Leila Helms, the niece of former CIA Director Richard Helms. The agenda included discussions of extraditing bin Laden as well as facilitating American companies’ access to oil reserves in central Asia. The delegation met with representatives of the Directorate of Central Intelligence (DCI) and the Bureau of Intelligence and Research of the State Department.
This visit provoked concern and criticism in Washington over how Hashimi obtained a visa, a plane ticket, security clearance and access to American institutions — including the State Department and the National Security Council — despite travel restrictions on Taliban leadership imposed by U.N. sanctions (the official answer was that Hashimi fell below the rank of senior official covered by the sanctions.)
Four months later, American diplomats met with Taliban emissaries as well as representatives from Pakistan, Iran and Russia for four days of talks in Berlin in mid-July. Again, the message was that if the Taliban would extradite bin Laden and form a broad-based national government, it could win international recognition and reap extensive economic subsidies from the construction of a pipeline. The meeting was one of several convened by Francesco Vendrell, a Spanish diplomat who serves as the U.N.’s chief representative on Afghanistan. The delegates at the July meeting included Robert Oakley, former U.S. ambassador and Unocal lobbyist; Karl “Rick” Inderfurth, former assistant secretary of state for South Asian affairs; Lee Coldren, head of the Office of Pakistan, Afghan and Bangladesh Affairs in the State Department until 1997; Tom Simons, former U.S. ambassador to Pakistan and the most recent official negotiator with the Taliban; Niaz Naik, former Foreign Minister of Pakistan; Nikolai Kozyrev, a former Russian special envoy to Afghanistan; and Saeed Rajai Khorassani, formerly the Iranian representative to the U.N. The Taliban ambassador to Pakistan, Abdul Salam Zaeef, attended several sessions with some of the delegates in Berlin, according to Naif Naik, though officially the Taliban had not been invited. Naik was expected to carry the U.S. message to the Taliban.
According to Naik, the point of the meeting was that “we would try to convey to them that if they did certain things, then, gradually, they could win the jackpot, get something in return from the international community.” It might, Naik said, “be possible to persuade the Taliban that once a broader-based government was in place and the oil pipeline under way, there would be billions of dollars in commission, and the Taliban would have their own resources.”
It was at the July meeting, according to Naik, that Tom Simons suggested that Afghanistan could face an open-ended military operation from bases in Uzbekistan and Tajikistan if it didn’t accede to U.S. demands. “Ambassador Simons stated that if the Taliban wouldn’t agree with the plan, and if Pakistan was unable to persuade them, the United States might use an overt action against Afghanistan,” Naik says. The words used by Simons were “a military operation,” according to Naik. Another participant reportedly said the Taliban’s choice was clear: either accept a “carpet of gold” riches from the pipeline or “a carpet of bombs,” meaning a military strike.
Lee Coldren, a member of the U.S. delegation, also confirmed to the British newspaper the Guardian the American position at the Berlin meeting. “I think there was some discussion of the fact that the United States was so disgusted with the Taliban that they might be considering some military action.”
In statements to newspapers, Simons has offered ambiguous explanations of his statements at the July meeting. In September, he told the British Guardian: “I’ve known Naik and considered him a friend for years. He’s an honorable diplomat. I didn’t say anything like that and didn’t hear anyone else say anything like that. We were clear that feeling in Washington was strong, and that military action was one of the options down the road. But details, I don’t know where they came from.”
Yet in a November interview with Le Monde, Simons seemed to confirm that there had been some talk of U.S. military action. “It is true that the Taliban was asked to deliver bin Laden and form a [broader] government,” Simons told Le Monde. “We said in July that we were investigating the attack against the USS Cole in Yemen, and that if there were solid evidence of the implication of bin Laden, one had to expect a military answer. One can always inflate such a declaration to see a global threat against the Taliban. But the American declaration related only to the response to the USS-Cole.
“As for the ‘carpet of gold and the carpet of bombs,’ we actually discussed the need for a plan for rebuilding for Afghanistan, which would follow a political agreement,” he said, adding that “It’s possible that a mischievous American participant, after several drinks, may have thought it smart to evoke gold carpets and carpet bombs. Even Americans can’t resist the temptation to be mischievous.”
The last known meeting between U.S. and Taliban representatives took place in August, five weeks before the Sept. 11 attacks, when U.S. Assistant Secretary of State for Central Asian affairs Christina Rocca met with the Taliban’s ambassador to Pakistan Abdul Salam Zaeef.
It would be unfair to suggest that the U.S. threat in July led to the al-Qaida strike. But while Simons doesn’t admit that he personally threatened the Taliban with reprisal, he confirms that only a few weeks before Sept. 11, American diplomats warned of military action against Afghanistan if its leaders did not meet U.S. economic and political demands. It is worth asking whether, had this threat been widely known, U.S. intelligence agencies might have analyzed the information they were receiving about bin Laden’s plots against the U.S. differently.
Now the newly discovered Atef memo makes clear that in 1998, at least, al-Qaida was well informed about negotiations between the Taliban and the U.S. on the oil pipeline and other American concerns. The memo also shows that those negotiations were the Taliban’s gambit to extend its power; Mullah Omar’s government never had any intention of allowing U.S. firms to construct an oil pipeline, or letting the U.S. dictate the members of its ruling body. Given the inside knowledge al-Qaida had about U.S.-Taliban negotiations, it’s reasonable to suspect bin Laden’s group also received and understood the U.S. threat of military action delivered in late July as a threat of war.
In the end, though, the U.S. got its way. Interim Afghan leader Hamid Karzai decided on May 30 to revive the pipeline project with Pakistan and Turkmenistan, signing an agreement under which the three governments agree to implement a pipeline from Turkmenistan to Pakistan through Afghanistan. Would that U.S. intelligence agencies’ investigations into al-Qaida activities in the months before Sept. 11 had such a productive ending.
http://www.salon.com/2002/06/05/memo_11/
“Afghanistan Oil Pipeline”
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Afghanistan_Oil_Pipeline






