What is a gene?
A gene is the basic physical and functional unit of heredity. Genes, which are made up of DNA, act as instructions to make molecules called proteins. In humans, genes vary in size from a few hundred DNA bases to more than 2 million bases. The Human Genome Project has estimated that humans have between 20,000 and 25,000 genes.
Every person has two copies of each gene, one inherited from each parent. Most genes are the same in all people, but a small number of genes (less than 1 percent of the total) are slightly different between people. Alleles are forms of the same gene with small differences in their sequence of DNA bases. These small differences contribute to each person's unique physical features.
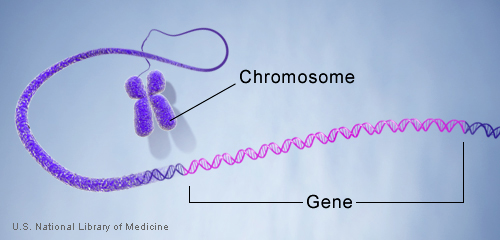
Genes are made up of DNA. Each chromosome contains many genes.
For more information about genes:
Genetics Home Reference provides consumer-friendly gene summaries (http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/BrowseGenes) that include an explanation of each gene's normal function and how mutations in the gene cause particular genetic conditions.
The Centre for Genetics Education offers a fact sheet that introduces genes and chromosomes (http://www.genetics.edu.au/Information/Genetics-Fact-Sheets/ Genes-and-Chromosomes-FS1).
For more information about genes, refer to the chapter titled What is a Genome? (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/About/primer/genetics_genome.html) in the NCBI Science Primer.




