CHAPTER 3
FLAG SIGNALS FOR ARMORED AND MECHANIZED UNITS
3-1. GENERAL
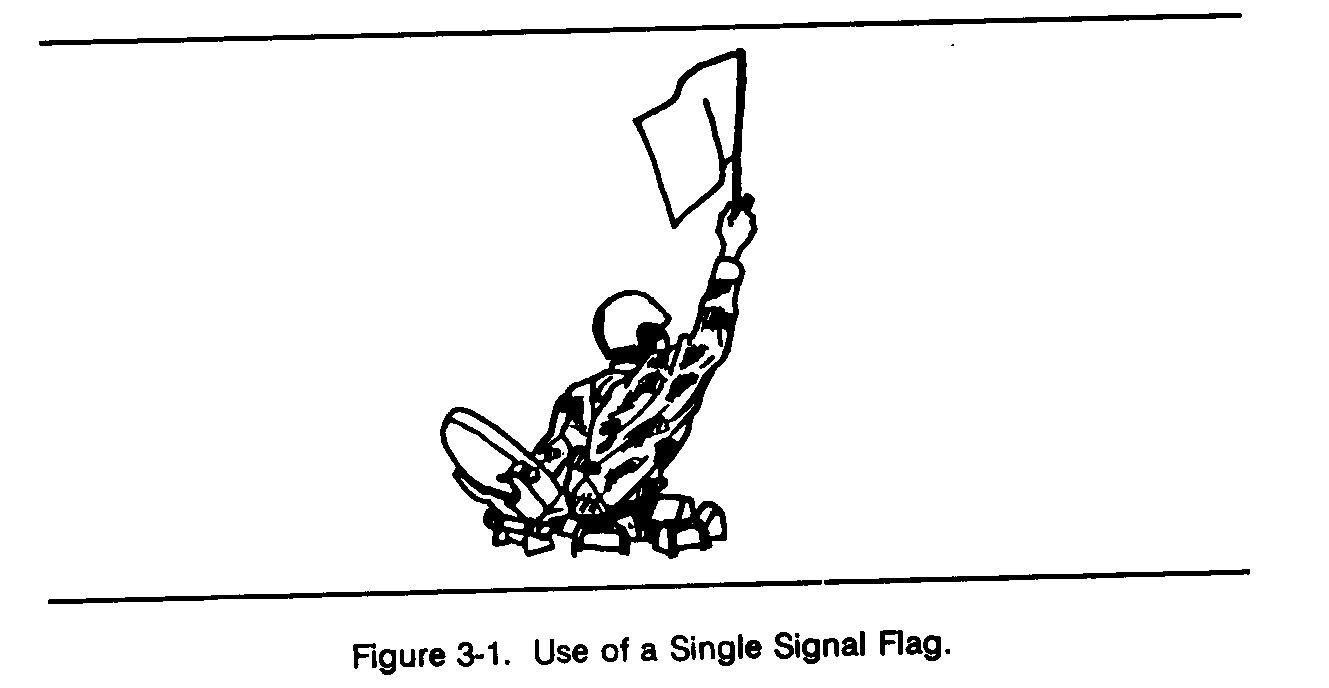
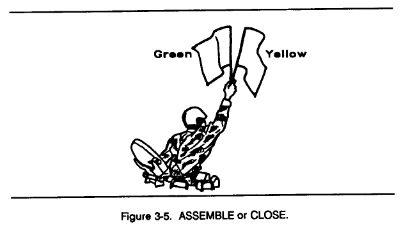
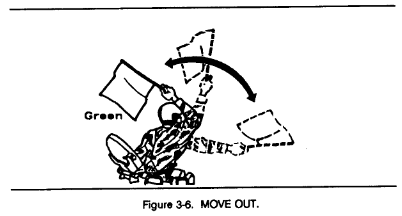
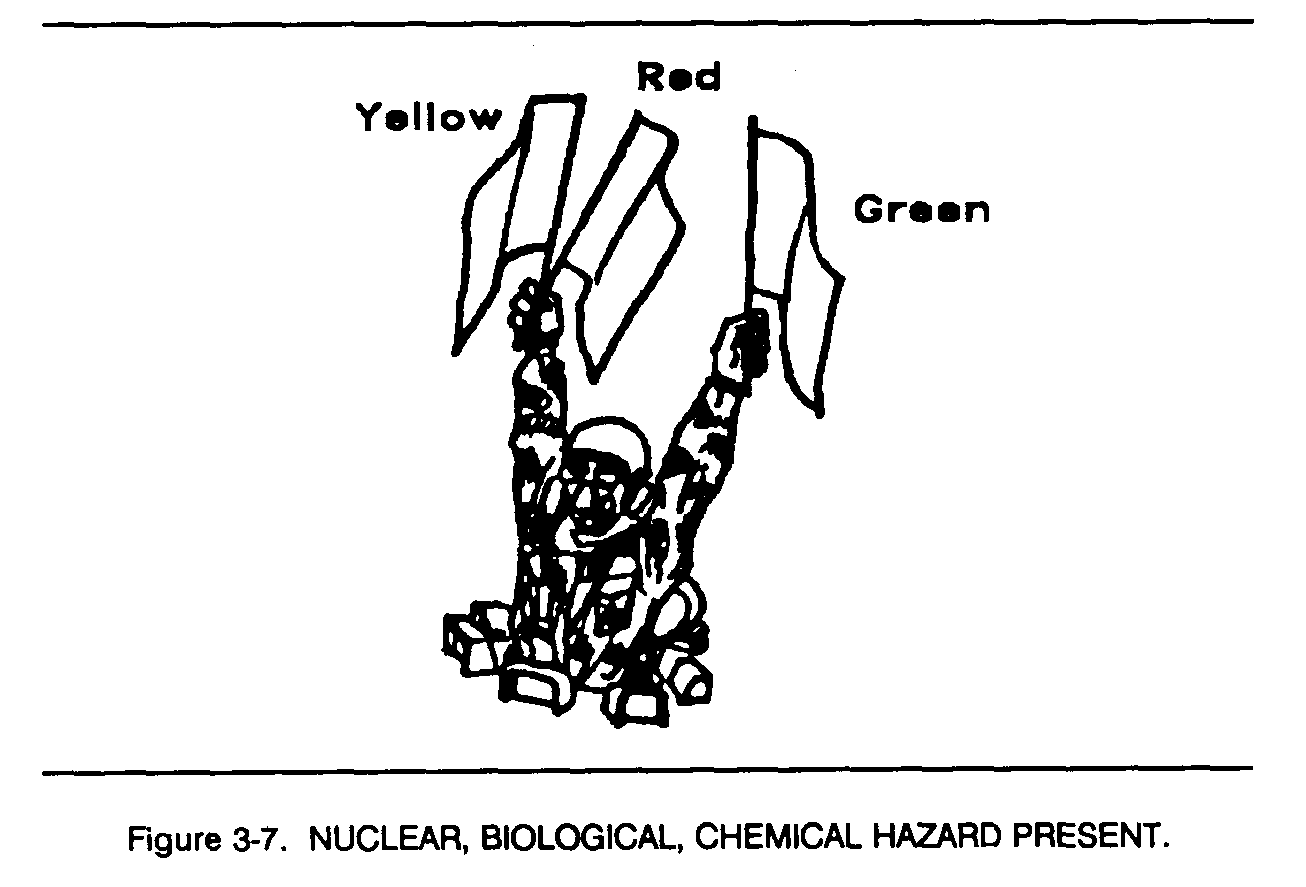
a. Flags are issued to armored and mechanized units for control purposes and as an alternate means of communication within these units. Each combat vehicle is equipped with a flag set consisting of one red, one yellow, and one green flag. Flag signals may be given by using a single flag or a combination of two or three flags, according to a prearranged code. Flag signals, when understood, are repeated and executed at once (Figures 3-1 through 3-7).
b. Flags are used to:
(1) Mark vehicle positions. For example, a quartering party member uses colored flags in an assembly area to mark positions.
(2) Identify disabled vehicles.
(3) Warn friendly elements of an advancing enemy. For example, an observation post uses a flag to signal a platoon to move to its fighting position.
(4) Control movement. Flags serve as an extension of arm-andhand signals when distances between vehicles become too great.
c. When used alone, flag colors have the following meanings. (1) Red DANGER, or ENEMY IN SIGHT.
(2) Green ALL CLEAR, READY, or UNDERSTOOD.
(3) Yellow DISREGARD, or VEHICLE OUT OF ACTION.
d. During periods of limited visibility flashlights with colored filters or colored chemical lights maybe substituted for flags.
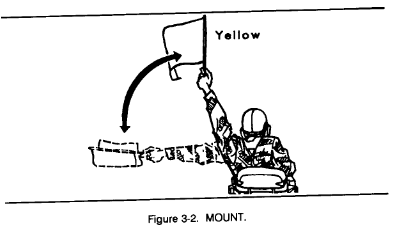
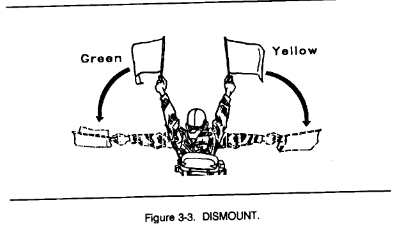
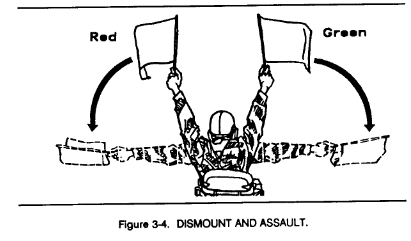
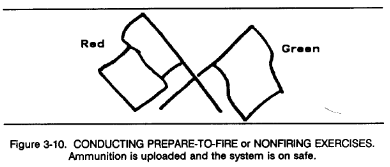
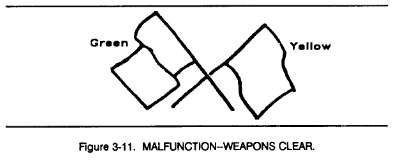
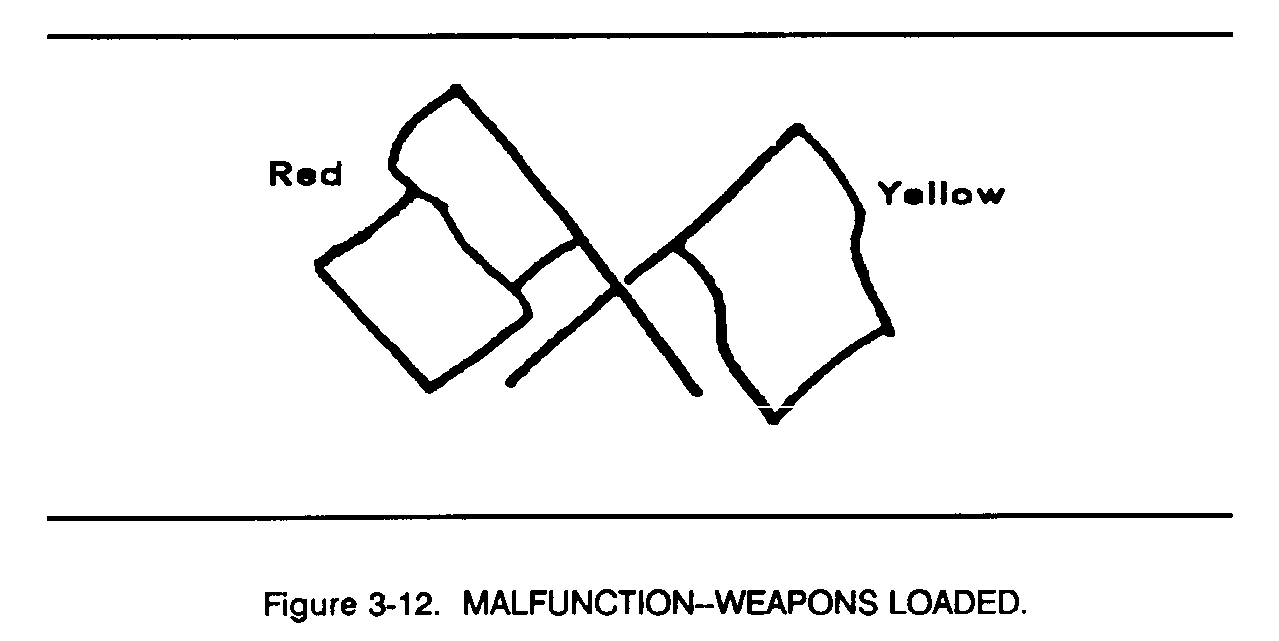
3-2. Firing Range Flag Signals
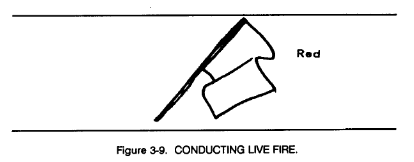
Signal flags are used on firing ranges for tanks or fighting vehicles to indicate the status of the range and the status of the individual vehicle. A red flag at the control point indicates that firing may be conducted, wide a green flag indicates that it may not (Figures 3-8 through 3-12).

3-5















