CHAPTER 3
CONCRETE HARDENING
AND STRUCTURE-FORMING
L. Dvorkin and O.Dvorkin





Concrete hardening includes the complex of processes of cement hydration.
Physical and chemical processes of structure formation of cement paste make
substantial influence on concrete hardening. Concrete hardening and forming of
concrete properties depend greatly on the mixing water, aggregates and
admixtures used.
3.1. Hardening and structure of cement stone
Hydration of cement
A chemical process of cement hardening is the processes of hydration which
occurs at mixing cement with water. Composition of new compounds is
determined by chemical nature of waterless compounds, ratio between solid and
liquid phase, temperature conditions.
55





%
de,
oxidr
m hyiulca c
tity of
Quan
Age, days
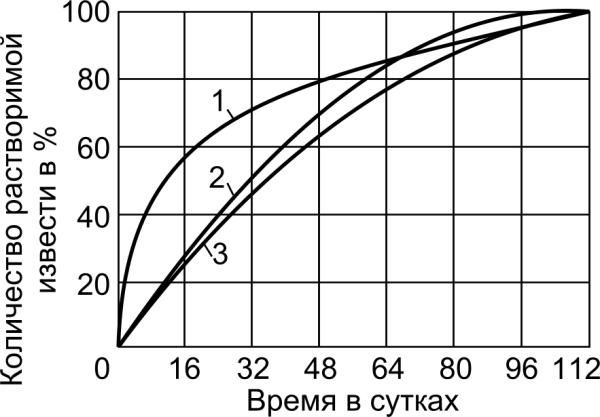
Fig.3.1. Rate of reaction of the calcium hydroxide Ca(OH)2
forming during hydration of calcium silicates:
1 – tricalcium silicate (3СаО⋅SiO2); 2 - β - modification dicalcium
silicate (β-2CaO⋅SiO2); 3 -γ - modification dicalcium silicate
(γ -2CaO⋅SiO2)
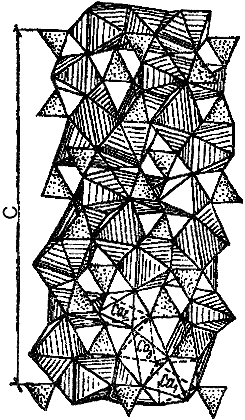
Fig.3.2. Plane section of
tricalcium silicate (C3S) structure
56





High hydration activity of aluminates minerals is caused by possibility of
structural transformations due to the instability of the concentration of Al3+
ions in the crystalline grate of these minerals.
All clinker minerals are
disposed in a row concordant
with their hydration activity:
tricalcium aluminate (C A) –
3
tetracalcium aluminoferrite
(C AF) - tricalcium silicate
4
(C S) - β dicalcium silicate
3
(β-2CaO⋅SiO ).
2
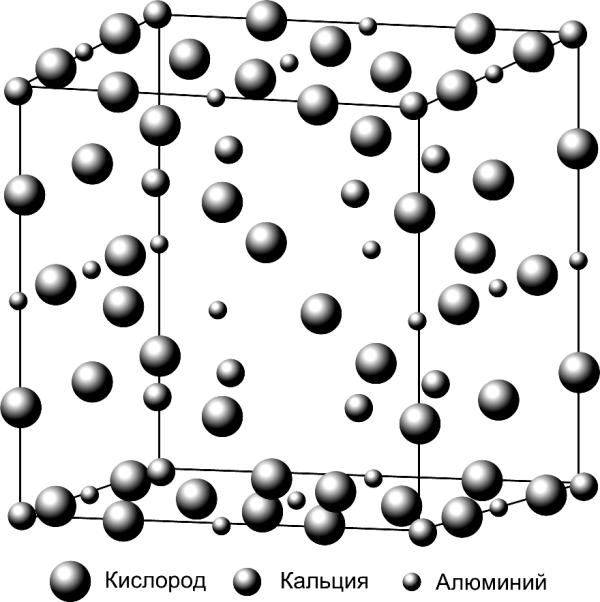
Oxygen
Calcium
Aluminium
Fig.3.3. Structure of elementary cel
of crystalline structure
of tricalcium aluminate (C3A)
57






The rate of reaction between cement and
water is accelerated if there is increasing in
temperature, that is characteristic for all
chemical reactions. Kinetics of hydration of
compounds of portland cement clinker and
their mixture in portland cement is described
by formula:
L = k lg τ +
,
В



























