),
(5.11)
m(τ)
m(max) а + τ
where а – age of loading; τ - age of concrete hardening;
C
– maximally possible creep.
m(max)
After rapid deformation at the beginning of load, deformation of creep
continues at a decreasing rate.
Amount of creep depends on the technological reasons and reasons
characterizing conditions of loading.
98





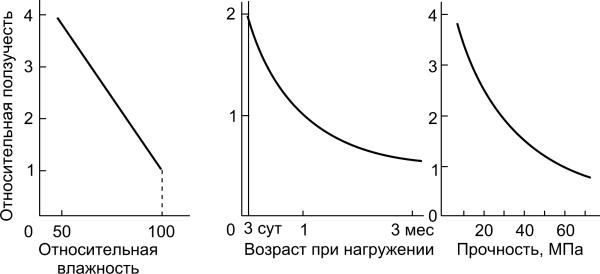
ep
cre
tivela
Re
days
month
MPa
Relative humidity
Age of the concrete when
Strength of the concrete
loading is applied
when loading is applied
Fig.5.7. Effect of conditions of loading on magnitude of creep
for typical normal-weight concrete
99





5.3. Own deformations. Concrete shrinkage
Own deformations of concrete are caused by moisture, temperature and
other influences on a concrete without applying of the external loading.
The change of concrete humidity can cause decrease or increase in
volume and accordingly deformations of shrinkage or expansion.
Deformations of expansion in cement stone and concrete at hardening
are results of formation of the crystallization stone structure.
The expanding (swelling) of concrete volume occurs during
continuous storage of the specimens in the water.
Deformation of contraction and drying shrinkage are developed due to
processes of concrete hardening.
100





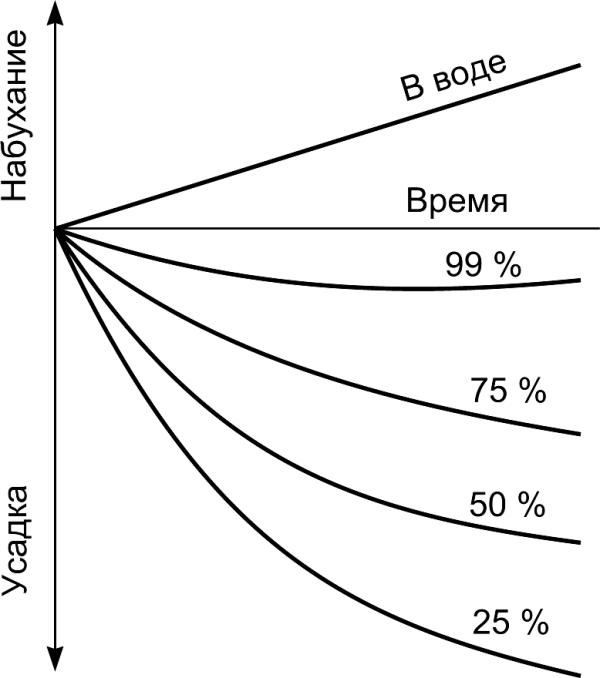

Contraction is the result of reactions
of hydration of chemical cement
g n
compounds with water, therefore
absolute volumes of hydrates less
pandi
Time
than total volumes of initial waterless
Ex
compounds and water which
necessary for hydration.
Contraction shrinkage of concrete in
5...10 times less than drying
shrinkage.
age
Shrinkage of concrete at the
ink
change of humidity develops in two
Shr
stages:
1. when a fresh concrete mixture
has initial plastic consistency
(plastic shrinkage);
Fig. 5.8. Swelling and drying shrinkage of
cement specimens which hardened and
2. at the time of continuing
stored in water and in air with a different
hardening and drying of concrete.
relative humidity
101





Drying shrinkage has the most influence on quality and exploitation of
concrete constructions.
Internal tensions, stresses and cracks can occur due to the shrinkage
deformations. Shrinkage deformation has also a negative effect on frost
resistance and watertightness of concrete.
Amount of shrinkage of cement paste and concrete depends on age of
hardening, composition, specific surface and quantity of cement, quantity
of aggregates, water-cement ratio and other factors.
Some calculating formulas for determination of concrete shrinkage (ε )
shr
Formula
Author
ε
⋅106 0.125W W
,
(5
.12)
shr
=
E.Sherbakov
W-quantity of water, liters per cubic meter
5W / C
ε
⋅106 =
(667 C
(5.


























