CHAPTER 1
INTRODUCTION
1.1. Background
Along with the development of globalization is rapidly increasing, the importance of economic improvement is also increasingly felt in the future. Although it is regularly criticized because of the limitations of economic growth in improving living quality standards may conflict with the environment and social condition, but economic growth is still very important for almost everyone within that economy in dealing with several problems such as poverty, unemployment, government budget deficits, and competitiveness with other countries.
There are some factors that affect economic growth like productivity, demographic changes, and technology innovation. Productivity advancement generates economic growth by making products and services less expensive to increase market demand. Demographic changes means there are some changes in population, age, and gender that also affect production, consumption, and business activity. Technology innovation creates the business process activity became more effective and efficient.
The economic growth can be measured by the growth rate of Gross Domestic Product (GDP). GDP is the total market value of all the goods and services produces over a . It is not only normally used to assess the economic performance of a whole country or region, but can also evaluate the relative contribution of an industry sector and specified area.
The calculation of GDP can be solved in three ways: production approach, income approach, or expenditure approach. Investopedia argues the expenditure method is the most common approach and is calculated by adding total consumption, investment, government spending and net exports. chart, the Indonesia GDP growth rate in 2005-2015 created unique pattern: increased continuously from Q1 to Q3 but declined in the last quarter (Q4).
GDP = Consumption + Investment + Government Spending + Net Export



Nevertheless, some investors suffer difficulties in investing on their financial portfolio. Investors usually use investment strategy as important guideline to select investment portfolio: some of them will decide to maximize expected returns by investing in risky assets, others will go for minimizing risk but most will struggle to hit a balance between maximizing their profits from their portfolio and risk they are willing to take by diversification. While passive strategies (index fund) are regularly applied to reduce transaction costs, active strategies such as market timing are an effort to get optimal returns. Unfortunately, countless studies show that inexpert investors do not trust these rules and expect to have low risk and high return. As a -high, sell-l
An active strategy that can be applied to accomplish the excellent return is sector rotation. The concept in managing portfolio is implying the money transfer from one industry sector to another in an attempt to beat the market. Due not all sectors of the economy perform well at the same time, investors take advantages by investing more funds in some industries or sectors that are going up and avoiding them that are falling down. Investors can predict which corporations will be successful in the coming stages of a business cycle by identifying informative signs from aggregate production, trade, and activity over several months or years in a market economy. In general, business cycle is categorized into the following four basic phases: peak, downturn, trough, and upturn (Collander, 2004, Pg 495).
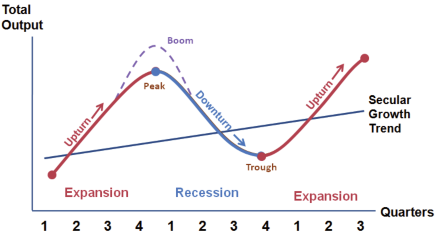
Figure 1.2. Business Cycle Phase (Source: Collander, D. C. (2004). Economics Fifth Edition. McGraw-Hill).
The business cycle can be rationally used to arrange stock collection. For example, during the early expansion phase, cyclical stocks in sectors such as commodities and technology tend to outperform. On the other hand, the defensive groups like health care, consumer staples and utilities outperform in the recession period because of their steady cash flows and dividend yields. Hence, this research plans to capture the pattern of relationship between business cycle and particular stocks in Indonesia Stock Exchange. In addition, this research also wants to formulate investment portfolio optimization by selecting based on industry sectors.
1.2. Problem Identification
With the purpose of maximizing return and diversifying financial assets, every investor would use special strategy to select. Sector rotation strategy should not be simplified and have to be examined since business cycle of each nation has different effects to the industry sectors. In that case, the outcome of this study is expected to fulfill these problems below:
1. How is the pattern of relationship between business cycle and selected stocks performance in Indonesia Stock Exchange?
2. Does sector rotation strategy give better investment portfolio result rather than passive strategy?
3. What recommendations and solutions for investors in achieving optimal investment portfolio in the future?
1.3. Research Objectives
The main objectives of this research are explained below:
1. Identify the pattern of relationship between business cycle and selected stocks performance in Indonesia Stock Exchange.
2. Measure the effectiveness of sector rotation strategy implementation to investment portfolio by comparing with passive strategy.
3. Provide recommendations and solutions that should be taken for investors in achieving optimal investment portfolio in the future.
1.4. Research Limitations
This research is limited through several scopes and assumptions as follows:
1. The historical data of research is selected from Q1/2000 to Q4/2014 as identification of Indonesia business c







