Lesson XI Inflation
Reading Objective:
The purpose of studying this chapter is to acquaint with economic phenomenon of rising prices of goods and services. The law of demand states the supply remaining constant whenever the demand increases the prices will grow up. If this happens for a substantially continuous period it is called as inflation. Depending upon the nature of the rise in prices the inflation will be called as a creping inflation, walking inflation, running inflation, galloping inflation and hyper inflation. The tendency of the rise in prices is not always unwanted. In fact the moderate rise in prices may lead to additional investment, production, employment and income. But however the alarming rate of rise in prices may lead to distortions in the economy. It may Rob Paul and Pay Peter. ie It will affect the fixed income group of people and benefit the business community .This rise in the prices will decrease the demand for goods and services and this in turn will lead to fall in demand for production, investments, output, employment, income and the GDP .Therefore there is a need for regulating it.
Lesson Outline:
-
Inflation
-
Types of inflation
-
Effects of inflation
-
Methods of controlling inflation Review questions
Introduction
Inflation is an economic condition in which the aggregate prices are always increasing in a country. The value of money is falling. Inflation is nothing but too much of money chasing too few goods. For example in Zimbabwe the inflationary rate is too high as more than 1000 % and in turn they require bag full of money for a meal. And the value of their currency is very low in the market. Inflation means not only sustainable rise in the price of the goods and services, but the value of the currency falls in the market and the supply of money in circulation is more.
Deflation is the opposite of inflation. It is a state of disequilibrium in which a contraction of purchasing power tends to cause or is the effect of a decline of the price level.
Types Of Inflation On The Basis Of Speed:
-
Creeping inflation: the inflationary rate is less than 2% that means prices are increasing gradually.
-
Walking inflation: the inflationary rate of a country is around 5% little more than creeping.
-
Running inflation: the rate of growth in prices are more i.e. the inflation is growing at the rate of 10%.
-
Galloping inflation: higher growth rate compared to the earlier stages i.e. the change is around 25%.
The major four types of inflation is depicted graphically in the following graph. ‘X’ axis denotes the year and ‘Y’ axis for rise in price level. Based on the elasticity and slope we can understand over a period of time sustainable inflationary situation leads to higher level of inflation in the economy.
Graph – Types Of Inflation
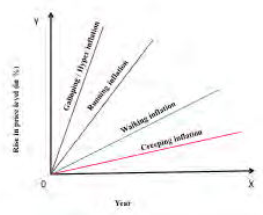
On The Basis Of Inducement:
-
Deficit induced: the deficit in the balance of payments of the country or fiscal deficit is the reasons for inflation. The value of the currency is falling due to the above mentioned reasons.
-
Wage induced: due to higher wages and salaries the money supply in the country increases leading to inflation.
-
Profit induced: higher the profit the organizations earn, they tend to share with their stakeholders which induces the money supply and reduces the value of money.
-
Scarcity induced: the raw material and other input factor scarcity (for example petrol) may induce the price hike in the market.
-
Currency induced: the value of currency fluctuates due to various internal and external forces.
-
Sectoral inflation: a particular sector of a country may be the reason for economic growth or money supply. (for example in India the growth in service sector particularly IT)
-
Foreign trade induced: if the country has unfavorable balance of payments, that means the country’s exports are less than the imports, then we need more of foreign currency to make payments to the exporters ultimately this increases the demand for other currencies in the market.
-
War time, Post war, Peace time: During war period the government expenditure on various amenities will induce the inflation and the production, availability of the commodities will be low which leads to price hike. To settle down the economy after war or natural calamities the government spending will be more.
On the basis of extent of coverage:
Based on the coverage, economists classify the inflation as open and repressed; Comprehensive and sporadic.
Effects Of Inflation On Various Economic Activities Of The Country:
On Producers: Producers will earn more profit due to higher prices.
On debtors and creditors: Creditors will be happy to receive more returns on their lending.
On wage and salary earners: Wage holders will struggle to purchase the goods and services.
On fixed income group: Income is fixed but the value of the currency is falling and prices are increasing therefore it is difficult to manage the normal life. i.e. they are affected.
On investors: Investors will receive more returns on their investments.
On farmers: Farmers will suffer.
On social, moral and political effects: Due to money supply and higher the cash in hand the social, moral values are declining in the society with political disturbances.
Demand Pull Inflation:
Inflation will result if there is too much spending when compared to output. Aggregate demand is greater than aggregate supply which leads to price hike and inflation. An increase in aggregate demand when the economy is at less than full employment level will result in an increase in both price and output. If the economy is at full employment then the demand will increase which leads to inflation.
Cost Push Inflation:
Inflation is caused by change in the supply side of the economy, it increases cost of production, prices and inflation. Initially increase in costs leads to a chain of wage increases which leads to increase in demand and cost.
Methods Of Controlling Inflation
Control Of Inflation:
It is clear that the inflationary situation in the long run is not going to help the economy to grow. Therefore the Government has to take many steps to overcome this problem. The given list of measures was taken through monetary and fiscal policy of our country and is explained in detail in the following chapters.
1. Monetary measures : to control inflation are: Bank rate
Open market operations
Higher reserve ratio
Consumer credit control
Higher margin requirements
2. Fiscal measures:
Regulating to Government expenditure
Taxation
Public borrowing
Debt management
Over valuation of home currency
3. Others:
Wage policy
Price control measures and rationing the essential supplies
Moral suasion
Anti Inflationary Measures:
The two important tools of macro level economic policy are monetary policy and fiscal policy. The monetary policy regulates the supply of money and availability of credit in the economy. It deals with both the lending and borrowing rates of interest for commercial banks. These two tools are used to control inflation and mitigate its severity.
Monetary measures: Since too much money is the fundamental problem in the economy, the central banking authorities use various instruments to reduce the money supply and credit.
Fiscal measures: By adopting suitable measures in taxation, public expenditure and borrowing, the government can curb inflation. The following chapter discusses these two measures in detail.
Review Questions
-
What is inflation? What are the types of inflation?
-
Write short note on demand pull inflation and cost push inflation.
-
List out the major factors influencing inflation in India.
-
Explain the effects of inflation on various groups of people in the society.
-
Discuss the causes and control measures of the inflation.
*****




