Lesson X Business Cycle
Reading Objective:
After reading this chapter the candidate may be able to understand that the economic conditions are changing cyclically. That is because of the changes in the total demand for certain goods and supply of the same may be due to the change in the technology or taste etc. this may be normally analysed in the form of Depression, Recovery, Boom and Recession. The depression is an economic condition where there is no demand for certain goods and services may be due to the lack of buying power in the hands of the public. The Recovery is a stage where the Governments try to halt the depressionery conditions by injecting buying power in the hands of the public. So that the increased demand will lead to production, employment, income and thus growth in the economy. The Boom period is said to be a prosperous period where economy is at equilibrium at higher level. Recession is the again the sliding stage. The recessionary conditions in America in the recent past and the president Barack Obama’s fight with it is a classic example of recession.
Lesson Outline:
-
Business cycle
-
Characteristic features of business cycle
-
Various phases of a business cycle
-
Theories on business cycle
-
Review questions
Introduction
A study of fluctuations in business activity is called business cycle. Business cycle can be defined as a periodically recurring wave like movements in aggregate economic activity (like national income, employment, investment, profits, prices) reflected in simultaneous, fluctuations in major macro economic variables.
R A Gordon defined business cycle as consisting of “recurring alteration of expansion and contraction in aggregate economic activity, the alternating movements in each direction being self-reinforcing and prevailing virtually all parts of the economy”.
Characteristic Features Of Business Cycle:
-
It occurs periodically: the fluctuations in economic activities occur periodically but not at a fixed period of interval.
-
It is international in character: the changes in any economic activity of a country have impact on economies of the world (for example financial crisis in US had impact on various other countries economic activities).
-
It is wave like: the fluctuations indicate ups and downs in various economic indicators of a country.
-
The process is cumulative: the process is cumulative in nature, that means change in income level, savings or any other activity will be in aggregates.
-
The cycles will be similar but not identical: the cycle has ups and downs but not identical spacing that means the time period of occurrence will differ.
Phases Of A Business Cycle:
The business cycle has four phases, Boom, Recession, Slump and Recovery. In economics it has been observed that income and employment tend to fluctuate regularly overtime. These fluctuations are known as business cycle or trade cycle.
Peak / Boom: when the economy is booming national income of the country is high and there is full employment, the consumption and investment is high. Tax revenue is high. Wages and profits will also increase. There will be inflationary pressure in the economy.
Recession: when the economy moves into recession, output and income fall leading to a reduction in consumption and investment. Tax revenue begins to fall and government expenditure begins to benefit the society. Wage demands moderate as unemployment rises, import and inflationary pressure declines.
Trough: economic activities of the country are low, mass unemployment exists, so consumption investment and imports will be low. Pricing may be falling (there will be deflation)
Recovery: as the economy moves into recovery, national income and output begin to increase. Unemployment falls, consumption, investment and import begins to rise. Workers demand more wages and inflationary pressure begins to mount.
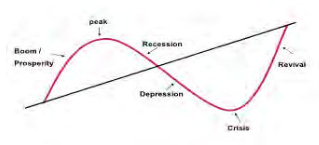
The fluctuation in the activities is measured with respect to a horizontal line indicating a given steady level of economic activity. However, if the time series reveals a significant long term trend, the vertical deviations of the reported or actual points from the estimated trend line are measured and plotted separately to obtain a clear picture of the underlying business cycle. Most economic variables go through ups and downs over time and the economy as a whole experience periods of prosperity and periods of recession. The measure of prosperity is the amount of goods/services produced (GDP) during a year. Actual business cycle are measured by changes in real GDP, that is the market value of all the goods and services produced within a nation’s borders, with market values measured in constant prices (prices of a specific base year).
Expansion or boom: is the period in the business cycle from a trough up to a peak, during which output and employment rise. Contractions, recession, or slump: is the period in the business cycle from a peak down to a trough, during which output and employment fall.
Recession: a decline in total output (real GDP) for 2 or more consecutive quarters. Reduction in investment, employment and production, reduction in income, expenditure, prices and profits reduction in bank loans. The business expansion stops that leads to depression.
Depression: the level of economic activity is extremely low. The income, production, employment, prices, profits of the country is very low. Organizations fix low price which leads to low profit, low wages, people suffer, closing down of business.
Recovery: slow increase in output, employment, income and price. Increase in demand, investment, bank loan, advances. This leads to recovery, revival of prosperity.
Theories On Business Cycle:
-
Sunspot theory / climate theory: depending on climatic changes agricultural products are produced. Based on the production other ancillary units will function therefore the base for any change in economic activity of the country is climate.
-
Psychological theory: during depression or crisis of any business organization it is completely based on the psychology of the entrepreneur as to whether the organization can be revived or shut down.
-
Monetary theory: means the demand and supply of money is the primary reason for economic fluctuations of a country.
-
Over investment theory: if the organizations and individuals save more and invest a huge amount then their expectations on increase in their returns.
-
Over savings/ under consumption theory: As per this theory the increase in savings and investment will bring down the consumption which will reduce the demand for goods in the market.
-
Innovation theory: According to this theory more innovations lead to new technology and new business that leads to prosperity in the economy.
There are two types of business cycle models, they are (i) Exogenous model; due to economic shocks like war. (ii) Endogenous model; trade cycle because of factors which lie within the economic system.
A monetarist explanation: business cycles are essentially monetary phenomena caused by changes in the money supply. Change in money supply leads to change in employment and national income which increases the price. The path to an increased price level is cyclical. The link between changes in money supply and changes in income is known as the transmission mechanism.
Review Questions:
-
Define Business cycle, list out its characteristic features.
-
Explain various phases of a business cycle.
-
Discuss the theories on business cycle.
-
Explain the managerial uses of business cycle.
-
Are cyclical fluctuations necessary for economic growth?
*****




