Lesson XVI Industrial Finance And Foreign Direct Investments
Outline:
-
Industrial finance
-
Foreign Direct Investment
-
Advantages and disadvantages of FDI
-
FDI in India
-
Cross border Mergers and Acquisitions
-
Review questions
Industrial Finance
Finance is the life blood of business. It is of vital significance for modern business which requires huge capital. Funds required for a business may be classified as long term and short term. It is required for purchasing fixed assets like land, building, machinery etc., the capital required to purchase fixed assets is called as fixed capital.
Purpose Of Industrial Finance:
To finance fixed assets
To finance the permanent part of working capital
To finance the growth and expansion of business.
The nature of business determines the amount of fixed capital. Nature of goods produced determines the level of financial requirement. If a business is engaged in manufacturing small and simple articles then it requires small amount of capital. The financial need depends upon the technology adopted in the organization. The major sources of finance are: shares, debentures, public deposits, retained earnings, term loans from bank, loans from financial institution etc.,.
The financial sources are expanded and a major source of finance comes from foreign direct investment (FDI) due to our economic reforms.
Foreign Direct Investment
Foreign capital plays a vital role in the industrialization and economic development of a country, as it forms one of the essential determinants of economic growth of developing countries. Over the past two decades many countries around the world have experienced substantial growth in their economies with even faster growth in international transactions, especially in the form of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI). The share of FDI in the world GDP has grown fivefold.
FDI refers to the net inflows of investments to acquire a lasting management interest (10% or more of voting stock) in an enterprise operating in an economy other than that of the investor.
FDI = Equity capital + reinvestment of earnings + short term capital + long term capital.
FDI is classified as inward FDI and outward FDI. It can be a loan, collaboration or borrowing. The major investors in FDI are individual, group, private and public entity.
Need For FDI In India
As India is a developing country, capital has been one of the scarce resources that are usually required for economic development. Capital is limited and there are many issues such as Health, poverty, employment, education, research and development, technology obsolesce, global competition. The flow of FDI in India from across the world will help in acquiring the funds at cheaper cost, better technology, employment generation, and upgraded technology transfer, scope for more trade, linkages and spillovers to domestic firms. The following arguments are advanced in favor of foreign capital
Sustaining a high level of investment: As all the under-developed and the developing countries want to industrialize and develop themselves, therefore it becomes necessary to raise the level to investment substantially. Due to poverty and low GDP the saving are low. Therefore there is a need to fill the gap between income and savings through foreign direct investments.
Technological gap: In Indian scenario we need technical assistance from foreign source for provision if expert services, training of Indian personnel and educational, research and training institutions in the industry. It only comes through private foreign investment or foreign collaborations.
Exploitation of natural resources: in India we have abundant natural resources such as coal, iron and steel but to extract the resources we require foreign collaboration.
Understanding the initial risk: In developing countries as capital is a scare resource, the risk of investments in new ventures or projects for industrialization is high. Therefore foreign capital helps in these investments which require high risk.
Development of basic infrastructure: In the recent years foreign financial institutions and government of advanced countries have made substantial capital available to the under developed countries. FDI will help in developing the infrastructure by establishing firm’s different parts of the country.
Improvement in the balance of payments position: The inflow FDI will help in improving the balance of payment. Firms which feel that the goods produced in India will have a low cost, will produce the goods and export the same to other country. This helps in increasing the exports.
Foreign firm’s helps in increasing the competition: Foreign firms have always come up with better technology, process, and innovations comparing with the domestic firms. They develop a completion in which the domestic firms will perform better it survive in the market.
Determinants Of FDI
The determinant varies from one country to another due their unique characteristics and opportunities for the potential investors. In specific the determinants of FDI in India are:
Stable Policies: India’s stable economic and socio policies have attracted investors across border.
Economic factors: Different economic factors encourage inward FDI. These include interest loans, tax breaks, grants, subsidies and the removal of restrictions and limitation.
Cheap and skilled labour: There is abundant labor available in India in terms of skilled and unskilled human resources. Foreign investors will to take advantage of the difference in the cost of labor as we have cheap and skilled labors.
Basic infrastructure: India though is a developing country, it has developed special economic zone where there have focused to build required infrastructure.
Unexplored markets: In India there is large scope for the investors because there is a large section of markets have not explored or unutilized.
Availability of natural resources: India has large volume of natural resources such as coal, iron ore, Natural gas etc. If natural resources are available they can be used in production process or for extraction of mines by the foreign investors.
Advantages Of FDI To The Host Country:
-
Availability of scarce factors of production
-
Improves the balance of payments
-
Building of economic and social infrastructure
-
Fostering the economic linkage
-
Strengthening of the government budget.
Disadvantages To Host Country:
-
Balance of payment depends on improvement of technology
-
Employment of expatriates
-
Unhealthy competition
-
Cultural and political issues
Advantages Of FDI To Home Country:
-
Improves the availability of raw material
-
Improves the Balance of payments of the country
-
It creates more Employment
-
Creates more Revenue
-
Builds Political relations
-
Gets better investment opportunity.
Disadvantages To Home Country:
-
Too much Exploitation of factors of production
-
Conflict with the government of host country.
Now let us analyze the sources (countries) from where the FDI’s are coming into India. And a sector wise inflow of FDI’s into India.
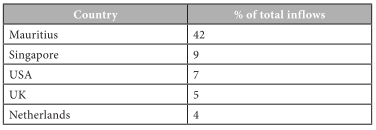
The Top 5 Countries Directing Their FDI To India Country
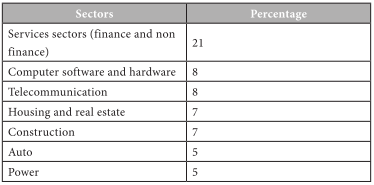
Sector Wise FDI Inflow
From the above table it can be understood that around 42% of FDI to India comes from Mauritius followed by Singapore, USA, UK and Netherlands. Mauritius is the number one leading FDI investor in the world as well as for India. The reason is their favourable polices and legal environment of the country in the form of avoidance of double taxation when the FDI comes through Mauritius.
If we look at the sector wise classification - financial sector receives around 20% of the over all FDI of the country followed by computer software and telecommunication sectors. At present the overseas investment on real estate and construction has started growing. The auto industry and power sector receives around 5% each.
The Flow Of FDI And FII In US Million $
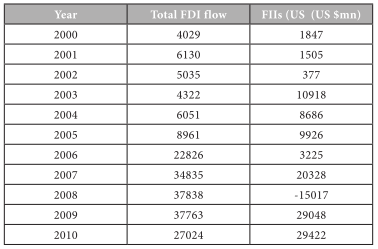
The above trend indicates that the FDI and FII of our country have grown seven fold with in these 10 years. FII has grown more than 20 times during this period. But in the first half, it started growing gradually but after 2005 the growth rate has been very high. It is evident that the economy is growing in various dimensions. The financial requirements are met through cross border mergers and acquisitions along with the direct investments. Thus it can be concluded that India is taking advantage of the FDI and FII sources for its development.
Review Questions:
-
Distinguish between FDI and FII.
-
Explain the advantages and disadvantages of FDI to the host and home country.
-
What are the different forms of foreign funds available to India?
-
Give an account on trend in FDI pre and post liberalization.
-
Discuss the sector wise inflow of FDI in India.
-
What is cross border mergers and acquisition?
Case: Future outlook of Indian IT Sector:
IT sector has made significant contributions to India’s economic growth in terms of GDP increase in foreign exchange earnings as well as employment generation. Its contribution to GDP has increased tenfold in the last decade from 0.6% to 6% till 2009-10. The sector has helped India transform from a rural and agriculture-based economy to a knowledge-based economy. Besides this, the lives of people have been positively influenced by direct or indirect contribution of IT sector to various parameters such as employment, standard of living, per-capita income etc. In the last ten years the IT sector in India has grown at an average annual rate of 28%. India accounts for almost 51% of the global sourcing market. India has emerged as the preferred destination for IT services owing to the cost advantage and talent pool. Exports contribute around 75% of the total revenue from the IT sector in India. However due to increased export-orientation and lesser domestic consumption the sector suffered a major hit in the recession that shook the globe in 2008-09. In the year 2010, different economies have started recovering but at varying pace. Indian companies have subsequently begun tapping other geographical markets and domestic consumption has also relatively increased.
According to NASSCOM, India can reach $ 130 Billion in IT revenue by 2015, with CAGR of 14%. With this, it would be contributing to 7% of annual GDP and creating 14.3 million employment opportunities. With the government taking active measures to stimulate the growth of IT sector with the emergence of BPO and KPO over last few years, India is expected to climb the global value and knowledge chain. In long-term we can expect the Indian IT sector to see good growth. Different segments of the sector are set to experience different growth rates. BPO industry have experienced high growth but the Software and Information Technology Enabled Services (ITES) segment is expected to see slower growth.
However, on an individual basis each company has to compete with other domestic as well as global players. They have to adapt new business models to compete with global players e.g. Cloud, On-demand services, and SaaS. With increased threat from countries like China, the companies will suffer loss unless they change business models.
It is very important that while investing in a company, an investor selects a sector, where the long-term future prospects are bright. In the above case, we have seen that the IT sector is expected to have good growth in the long run. Also, it is equally important that the company has an excellent financial track record and its long-term future prospects are Green (Very Good).
-
What are the growth drivers of the IT sector in India?
-
Why was the Indian IT industry hit more severely during the US recession?
-
Has Globalization helped India to gain employment opportunities?
-
What is the role of Private sector in IT Industry?
-
Explain the role of IT sector in FDI of India.
*****










