Annex 2. Glossary: Financial services and delivery channels in Russia
Credit products
This category includes typical loan products offered in Russia by banks and MFIs. For the purposes of the research, these products were grouped into the following main categories:
-
Mortgage loan. A long-term loan from a bank to buy real estate, which is then used as loan collateral. In Russia, banks often require that borrowers buy insurance when they are issued a mortgage loan (e.g., life and health insurance, disability insurance, property insurance, etc.).
-
Car loan. A loan from a bank to buy a car, which is then used as loan collateral. Most banks require that borrowers buy motor hull insurance when they are issued a car loan, and sometimes other types of insurance as well (e.g., life insurance). Bank may require loan collateral or guarantees.
-
Cash loan from bank. A consumer loan from a bank disbursed in cash or transferred to a customer bank account. These loans are normally issued at bank branches, for a specified term, and have a regular repayment schedule.
-
Credit card. A payment card linked to a customer bank account, including products that allow customers to top up the card balance with their own money (i.e., use as a debit card). Credit card loans normally do not have a specified loan term; customers can use credit for a certain grace period interest-free, but they must pay annual service fees.
-
Point-of-sale (POS) credit. A short-term loan issued by banks to buy goods, at stores selling these goods. At each store, there may be several bank staff present to serve customers. Such loans are usually issued within one hour; customers are not required to go to a bank branch.
-
Microloan. A short-term loan issued by MFIs, usually without collateral or guarantees, in the amount not exceeding RUB 1 million (approximately US$20,400). These include so-called payday loans, although there is no official legal definition of this term in Russia (see Chapter 2).
Card-based products
This category includes debit cards linked to bank accounts; they are used primarily for cash withdrawals and payments.
-
Salary card. A bank-issued debit card that is provided to salaried employees by their employers to transfer salaries and other cash disbursements (e.g., benefits, travel allowances, etc.). As a rule, the issuance of salary cards is initiated by employer, per employer agreement with a bank — i.e., the cardholder does not choose the bank. These cards are regular debit cards that can be used for cash withdrawal and transactions; some cards may have an overdraft facility depending on a bank (usually linked to salary size).
-
Social card. A bank-issued debit card provided by government to recipients of government support (e.g., pensioners, students, disabled, and low-income people, etc.), linked to a bank account. As in the case of salary cards, cardholders usually do not choose a bank.
-
Debit card. A debit card issued by a bank, linked to a bank account, often without an overdraft facility.
Savings products
This category includes all savings instruments offered by banks, credit cooperatives, and mutual funds:
-
Current account. A bank account used to keep funds that can be easily withdrawn at any time, as well as for transactions. Current account can often be accessed via debit cards linked to this account.
-
Demand deposit/Savings account. A demand deposit with a bank or savings with a credit cooperative. Bank-offered demand deposits include a variety of savings products, including those with flexible multiple top-ups and withdrawals, tiered interest rates accrued on established minimum balances, etc.
-
Term deposit. A deposit with a bank for a specified amount of time.
-
Mutual fund. A mutual investment fund where investors are co-owners of shares in the fund property. The fund management is done by a professional investment management company.
For all types of bank accounts and deposits, according to the Russian law, funds can be withdrawn by customers at any time. Depending on a deposit agreement, in the case of pre-term withdrawal, interest rates on deposits are usually reduced. Withdrawal of funds from credit cooperatives and mutual funds depends on the terms of agreements concluded between customers and these organizations.
Insurance products
Insurance products are divided into three categories: car insurance, personal insurance, and property and financial insurance.
The car insurance category includes all types of insurance products that involve the insurance of cars and car owners:
-
Mandatory motor third-party liability (MTPL) insurance. A mandatory insurance product required by law for all car owners and insuring risks related to car owner liability to third parties.
-
Voluntary MTPL insurance. A voluntary insurance product for car owners complementing mandatory MTPL insurance; provides a larger payout.
-
Motor hull insurance. A voluntary insurance product involving the insurance of a vehicle against damage or theft (excluding any property transported in the vehicle and car owner liability to third parties).
-
Green Card insurance. A mandatory insurance product for car owners visiting countries — members of the International Motor Insurance Card System (an arrangement between authorities and insurance organizations of multiple states to ensure that victims of road traffic accidents do not suffer from the fact that injuries or damage sustained by them were caused by a visiting motorist rather than a motorist resident in the same country).
The personal insurance category includes all types of insurance products that involve insuring the life and health of an insurance policy holder:
-
Voluntary health insurance, issued independently. Includes a number of medical services to be paid for by the insurance company and either a total payout amount or a payout for each type of the medical services, as well as the names of eligible medical institutions.
-
Voluntary health insurance, issued by employer. Same as above, only issued by an employer as part of a benefits package for employees.
-
Life and health insurance. Voluntary insurance against certain events, such as death, reaching a certain age, or illness (except accidents).
-
Insurance for traveling abroad. A voluntary medical insurance for travelers abroad. For some countries (e.g., Schengen), this insurance is mandatory.
-
Disability insurance. Voluntary insurance against external events leading to temporary or permanent disability of the insurance policy holder.
-
Risk life insurance. Voluntary insurance against external events leading to the death of the insurance policy holder.
The property and financial insurance category includes all types of insurance products that involve insuring the property of an insurance policy holder or financial risks:
-
Property (casualty and theft) insurance. A voluntary insurance product involving the insurance of property (except vehicles) against the risks related to property ownership, usage, or disposal (e.g., loss, theft, damage).
-
Bank insurance. Insurance products against risks arising during loan contracts, as well as risks related to fraud committed by third parties with respect to financial products of the insurance policy holder (e.g., credit card fraud). While not mandatory by law, these insurance products may be required by banks as part of their loan products.
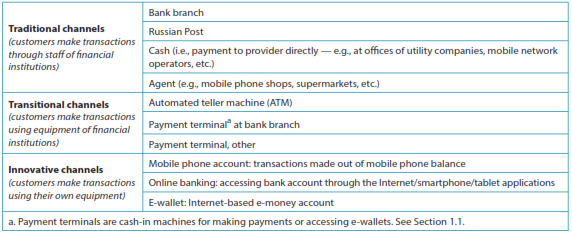
Delivery channels
For the purposes of the research, financial service delivery channels were divided into the following categories: