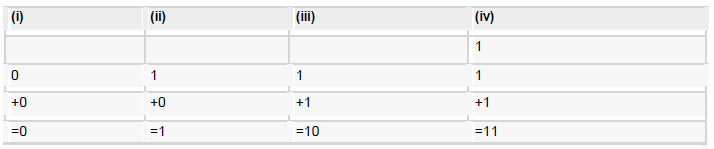Assembly Introduction
What is Assembly Language?
Each personal computer has a microprocessor that manages the computer's arithmetical, logical and control activities.
Each family of processors has its own set of instructions for handling various operations like getting input from keyboard, displaying information on screen and performing various other jobs. These set of instructions are calLed 'machine language instruction'.
Processor understands only machine language instructions which are strings of 1s and 0s. However machine language is too obscure and complex for using in software development. So the low level assembly language is designed for a specific family of processors that represents various instructions in symbolic code and a more understandable form.
Advantages of Assembly Language
An understanding of assembly language provides knowledge of:
Interface of programs with OS, processor and BIOS;
Representation of data in memory and other external devices;
How processor accesses and executes instruction;
How instructions accesses and process data;
How a program access external devices.
Other advantages of using assembly language are:
It requires less memory and execution time;
It allows hardware-specific complex jobs in an easier way;
It is suitable for time-critical jobs;
It is most suitable for writing interrupt service routines and other memory resident programs.
Basic Features of PC Hardware
The main internal hardware of a PC consists of the processor, memory and the registers. The registers are processor components that hold data and address. To execute a program the system copies it from the external device into the internal memory. The processor executes the program instructions.
The fundamental unit of computer storage is a bit; it could be on (1) or off (0). A group of nine related bits makes a byte. Eight bits are used for data and the last one is used for parity. According to the rule of parity, number of bits that are on (1) in each byte should always be odd.
So the parity bit is used to make the number of bits in a byte odd. If the parity is even, the system assumes that there had been a parity error (though rare) which might have caused due to hardware fault or electrical disturbance.
The processor supports the following data sizes:
Word: a 2-byte data item
Doubleword: a 4-byte (32 bit) data item
Quadword: an 8-byte (64 bit) data item
Paragraph: a 16-byte (128 bit) area
Kilobyte: 1024 bytes
Megabyte: 1,048,576 bytes
The Binary Number System
Every number system uses positional notation i.e., each position in which a digit is written has a different positional value. Each position is power of the base, which is 2 for binary number system, and these powers begin at 0 and increase by 1.
The following table shows the positional values for an 8-bit binary number, where al bits are set on.
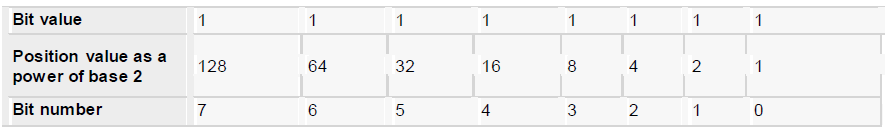
The value of a binary number is based on the presence of 1 bits and their positional value. So the value of the 8 given binary number is: 1 + 2 + 4 + 8 +16 + 32 + 64 + 128 = 255, which is same as 2 - 1.
The Hexadecimal Number System
Hexadecimal number system uses base 16. The digits range from 0 to 15. By con vention, the letters A through F is used to represent the hexadecimal digits corresponding to decimal values 10 through 15.
Main use of hexadecimal numbers in computing is for abbreviating lengthy binary representations. Basically hexadecimal number system represents a binary data by di viding each byte in half and expressing the value of each half-byte. The following table provides the decimal, binary and hexadecimal equivalents:
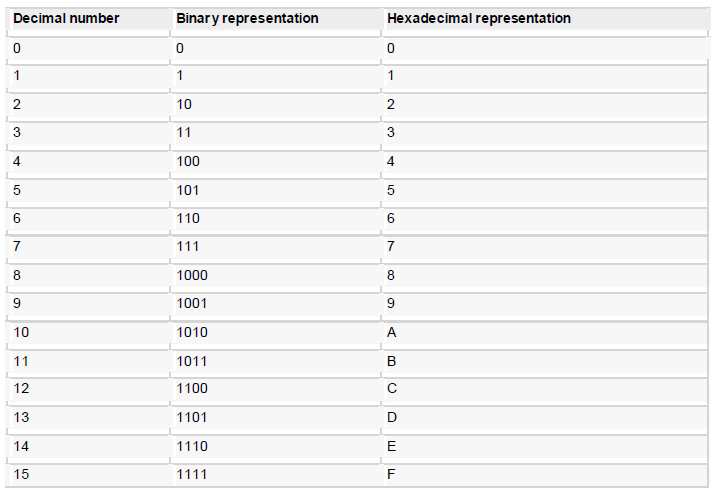
To convert a binary number to its hexadecimal equivalent, break it into groups of 4 consecutive groups each, starting from the right, and write those groups over the corresponding digits of the hexadecimal number.
Example: Binary number 1000 1100 1101 0001 is equivalent to hexadecimal - 8CD1
To convert a hexadecimal number to binary just write each hexadecimal digit into its 4 -digit binary equivalent.
Example: Hexadecimal number FAD8 is equivalent to binary - 1111 1010 1101 1000
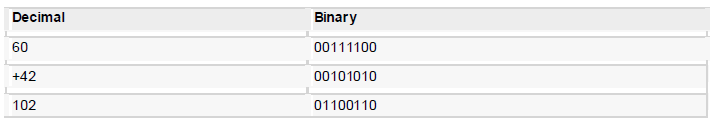
Binary Arithmetic
The following table illustrates four simple rules for binary addition:
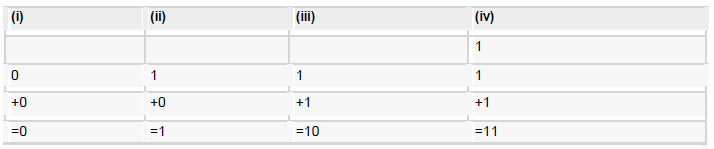
Rules (ii ) and (iv) shows a carry of a 1-bit into the next left position.
Example :
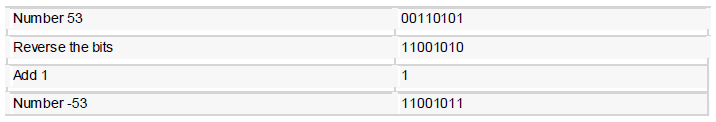
A negative binary value is expressed in two's complement notation. According to this rule, to convert a binary number to its negative value is to reverse its bit values and add 1.
Example :
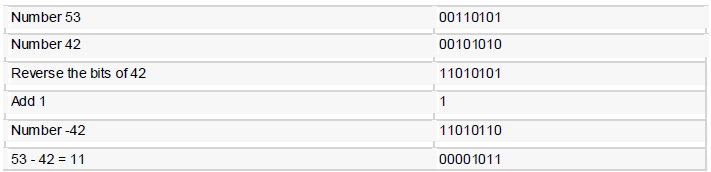
To subtract one value from another, convert the number b eing sub tracted to two's complement format and add the numbers.
Example : Subtract 42 from 53
Overflow of the last 1 bit is lost.
Addressing Data in Memory
The process through which the processor controls the execution of instructions is referred as the fetch -decode- execute cycle, or the execution cycle. It consists of three continuous steps:
Fetching the instruction from memory
Decoding or identifying the instruction
Executing the instruction
The processor may access one or more bytes of memory at a time. Let us consider a hexadecimal number 0725H. This number will require two bytes of memory. The high-order byte or most significant byte is 07 and the low order byte is 25.
The processor stores data in reverse-byte sequence i.e., the low-order byte is stored in low memory address and high-order byte in high memory address. So if processor brings the value 0725H from register to memory, it will transfer 25 first to the lower memory address and 07 to the next memory address.
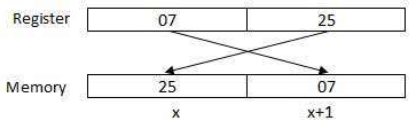
x: memory address
When the processor gets the numeric data from memory to register, it again reverses the bytes. There are two kinds of memory addresses:
An absolute address - a direct reference of specific location.
The segment address (or offset) - starting address of a memory segment with the offset value