8.  (Mángrén mō xiàng)
(Mángrén mō xiàng)
Blind Men and an Elephant
Listen to the whole story
Note: If you are reading this story via Adobe Reader, Foxit Reader or PDF-XChange, you can listen to the audio files by scrolling over the red speaker button and double-clicking.
Cóngqián, yǒu sì gè mángrén hěn xiǎng zhīdào dàxiàng shì shénme yàngzi.

In ancient times, there were four blind men. They were curious to know what an elephant looked like.
Kěshì tāmen kàn bú jiàn, zhǐhǎo yòng shǒu qù mō dàxiàng.

Since they couldn't see anything, they had no way but to touch an elephant.
Pàng mángrén mō dào le dàxiàng de yáchǐ. Tā jiù shuō: "Wǒ zhīdào le, dàxiàng jiù xiàng yí gè yòu dà yòu cū de luóbo.”

The fat blind man touched the elephant's teeth, and said, "I see, an elephant is just like a big and thick radish."
Gāo gèzi mángrén mō dào de shì dàxiàng de ěrduo. Tā shuō: "Bú duì, dàxiàng míngmíng shì yì bǎ dà púshàn ma!”
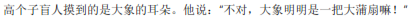
The tall blind man touched one of the elephant's ears, and said, "You are wrong, an elephant is just like a palm-leaf fan."
"Nǐmen jìng xiāshuō, dàxiàng zhǐshì gēn dà zhùzi." Ǎi gèzi mángrén hǎn qǐlái, yīnwèi tā mō dào le dàxiàng de tuǐ.
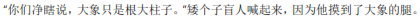
"What nonsense are you talking about? An elephant is just a big pillar!" The short blind man shouted, because he just touched a leg of the elephant.
Dì sì wèi niánlǎo de mángrén ne, tā mō dào le wěiba, dūnang zhe: "Āi, dàxiàng nǎ yǒu nàme dà, tā zhǐ búguò shì yì gēn cǎoshéng."

The fourth old blind man touched the tail and burbled, "Hey, how can an elephant be so big? It is just a straw rope!"
The four men quarreled with each other endlessly and they all thought themselves were right. In fact, none of them was right and really knew what an elephant looks like. This Chinese story tells us that we can't draw conclusions from incomplete information.
 Key Learning Points
Key Learning Points
1. 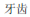 (yáchǐ): n. Teeth.
(yáchǐ): n. Teeth.
Example:
Xiǎohái chī tài duō táng duì yáchǐ bù hǎo.

Eating too much sugar will do harm to kids' teeth.
2. 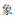 (xiàng): n. Elephant.
(xiàng): n. Elephant.
In spoken Chinese, we often use "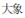 (dàxiàng)" to refer to elephant.
(dàxiàng)" to refer to elephant.
Dialogue:
A: Māma, nǐ xiàwǔ néng dài wǒ qù dòngwùyuán ma? Wǒ xiǎng qù kàn dàxiàng, háiyǒu lǎohǔ.
A: 
A: Mum, can you take me to the zoo in the afternoon? I want to see elephants and tigers.
B: Hǎo ā, bǎobèi.
B: 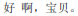
B: Ok, baby.

1. 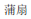 (púshàn): n. Palm-leaf fan.
(púshàn): n. Palm-leaf fan.
2. 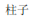 (zhùzi): n. Pillar.
(zhùzi): n. Pillar.
3. 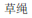 (cǎoshéng): n. Straw rope.
(cǎoshéng): n. Straw rope.








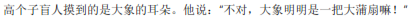
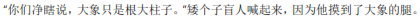

 Key Learning Points
Key Learning Points 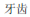 (yáchǐ): n.
(yáchǐ): n.
 (xiàng): n.
(xiàng): n.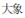 (dàxiàng)" to refer to elephant.
(dàxiàng)" to refer to elephant.
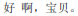

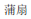 (púshàn): n. Palm-leaf
(púshàn): n. Palm-leaf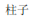 (zhùzi): n.
(zhùzi): n.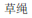 (cǎoshéng): n. Straw
(cǎoshéng): n. Straw