Towards mass production
The car body is the most important constructive, most responsible, materialintensive and expensive part of the car. It makes up about half of the car in terms of weight, cost and manufacturing complexity. The body is the basis for the installation and fastening of all systems and mechanisms of the vehicle. The body ensures the safety of the vehicle. The body structure and its parameters have a serious impact on the performance properties that ensure the movement of the vehicle (maneuverability, stability, smoothness,), and on performance properties not related to vehicle movement (capacity, strength, durability, maintainability, suitability for loading and unloading). DUBINA EVO has a fiberglass monocoque body. He perceives all the loads that act on the car while driving. This means that all elements of the body, with the exception of doors and hatches, are load-bearing. The body support system allows you to reduce the weight of the vehicle, its overall height, lower the center of gravity and, therefore, increase its stability.
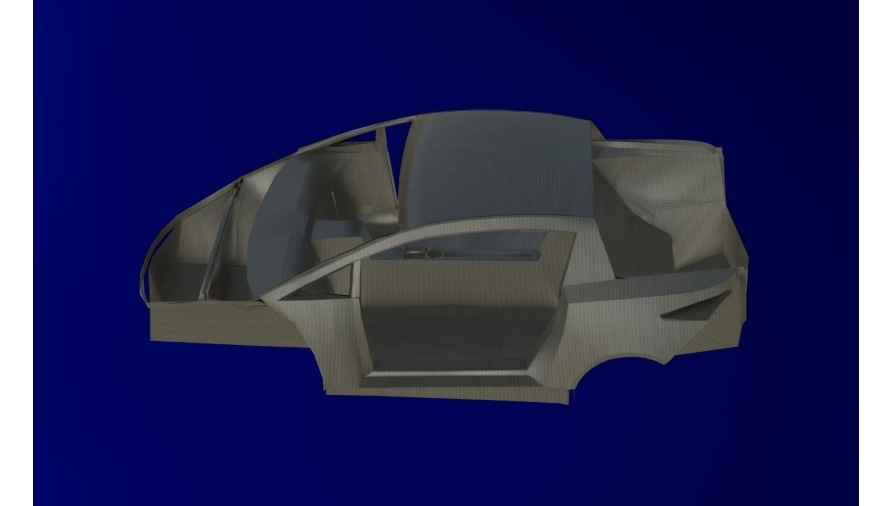
The supporting body is made of fiberglass.
The design of the monocoque body consists in the most rational distribution of material in each element, allowing the best use of the maximum possible load-bearing capacity of the material. In order to give the structure a clear and continuous shape, providing direct transfer of the load from the point of its application to the point at which the reaction occurs. The structure of the monocoque body must be rigid enough to allow precise control, be light enough to allow inertial loads and the loads caused by the oscillatory angular movement of the sprung parts about the vertical axis were small, to be strong and durable to withstand the cyclic road loads, the loads from the power plant, the driver and the passenger. Hence, it is clear that the structure of a car is assessed not by strength, but by rigidity, and the study of the state of the structure is associated with the study of its deformability rather than the stress state. Bending deflections in the middle of the vehicle span should not exceed 1.3 mm, and the deformations of the contour of door openings should not exceed 1.2 mm in the event of a load concentrated in the middle of the span equal to 6700 N. Fiberglass is not as rigid as steel or aluminum, therefore, reinforcing plates, brackets and stiffeners are used in the body structure. Fiberglass is a durable and lightweight material.
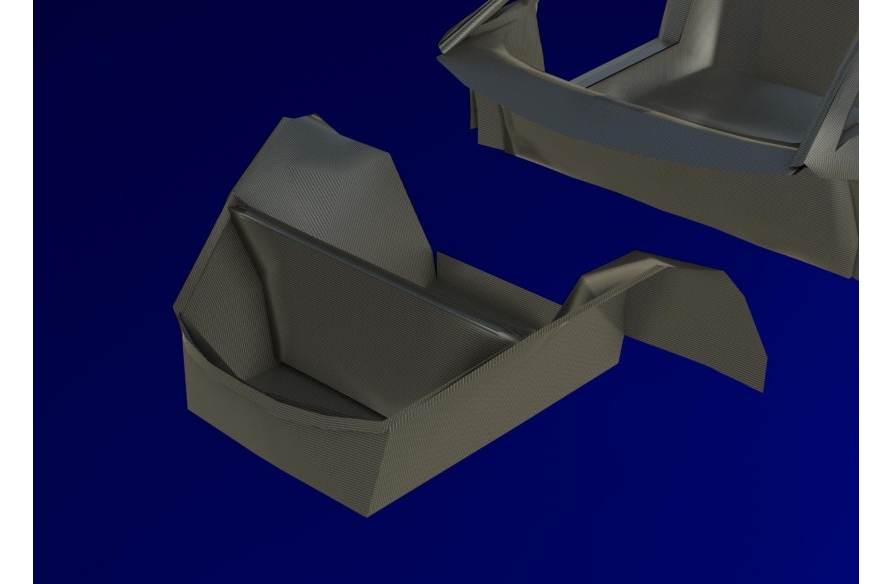
Front part of the body.
Another great advantage of fiberglass is the absence of corrosion. Important parts that contribute to the overall rigidity of the structure are roof rails, head rails and pillars of the windshield frame, door hinges, front and rear body frame spars, rear side panels, door pillars. The body supporting system made of fiberglass provides good insulation of the passenger compartment from vibration and noise of operating units and mechanisms, as well as from the noise of tires that occurs when they roll on the road surface. Body parts are made of fiberglass 2 … 3 mm thick. The body of the DUBINA EVO is shaped like an engine compartment, a passenger compartment and luggage compartments.
It has a fiberglass one-piece cockpit, left and right sidewalls with rear fenders, roof and front fenders. The resulting body structure is uneven. Its individual parts have different rigidity and, therefore, different resistance. shock in road accidents. As a result, in collisions of the car due to the deformation of the front and rear parts of the body, the impact energy is extinguished, and the passenger compartment is protected from deformation. This ensures that the survival space of people in vehicle collisions is maintained. The body of the DUBINA EVO is assembled on an assembly jig for the first stage of the production line. Two workers connect the bottom of the cockpit to the tunnel using epoxy glue, then the battery compartment is attached to the bottom of the cockpit, then the front and rear are attached part, then the left half and the right half at the end of the roof is installed.
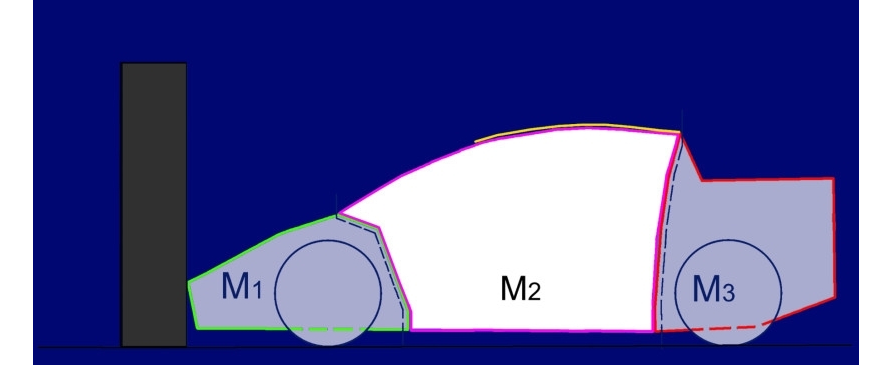
A three-mass model of a hitting car.
All body parts are made of fiberglass by hand molding. Forming of body parts consists of applying layers of fiberglass into a matrix. Since only the outer surface of the part experiences maximum stresses during bending, it is the area where high modulus carbon fibers are laid. The first layer of fiberglass is the thinnest (300 g/m2), which ensures the most smooth surface of the product. The fiberglass must follow all the bends exactly matrix shape without detachment and formation of air cavities. Cutting of fiberglass is performed according to a template made of dense cardboard according to the dimensions of the matrix. Body parts with complex shapes use fiberglass cutting, consisting of several separate elements. Depending on the thickness of the part, the required number of layers of material is prepared, which are stored in a convenient, easily accessible place, in the order of their molding in the matrix.
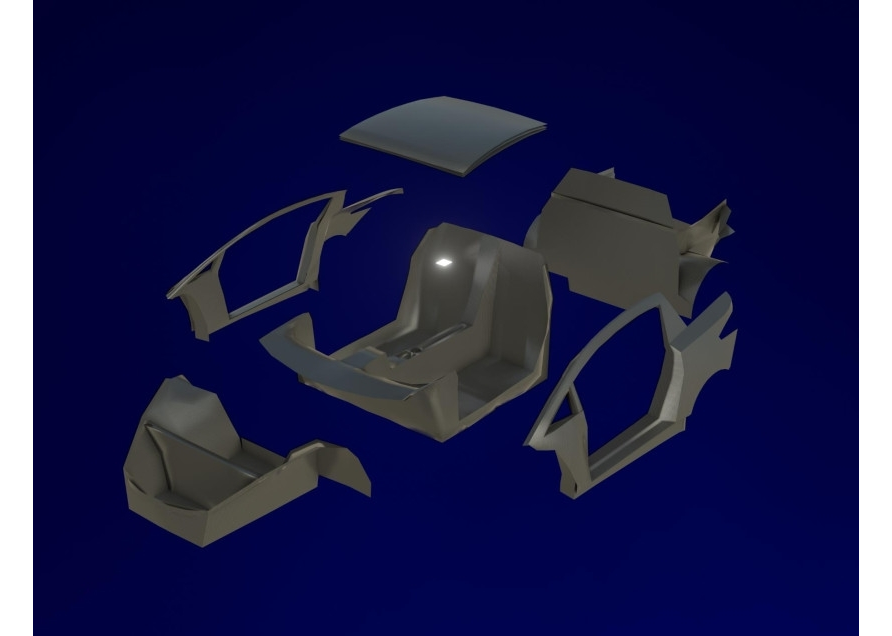
Main body parts.
A release layer applied to the mold surface of the matrix serves to ensure that the finished product can be safely removed after the resin has dried. The separation layer is made of wax and PVA alcohol. Glass material is placed in the prepared matrix, then the matrix is covered with a lid that repeats the shape of the part. This cover presses the glass material tightly against the die and creates the correct part. The process of creating a part is easier with such a cover. After the matrix is closed with a lid, air is pumped out of it and epoxy is pumped in. After the resin has dried, the part is removed from the matrix and sent to the machining room. To increase the strength of the matrix, stiffeners are glued to it made of polyethylene foam. After that, they are pasted over with fiberglass. Complex body parts are made from a three-dimensional matrix consisting of several parts.
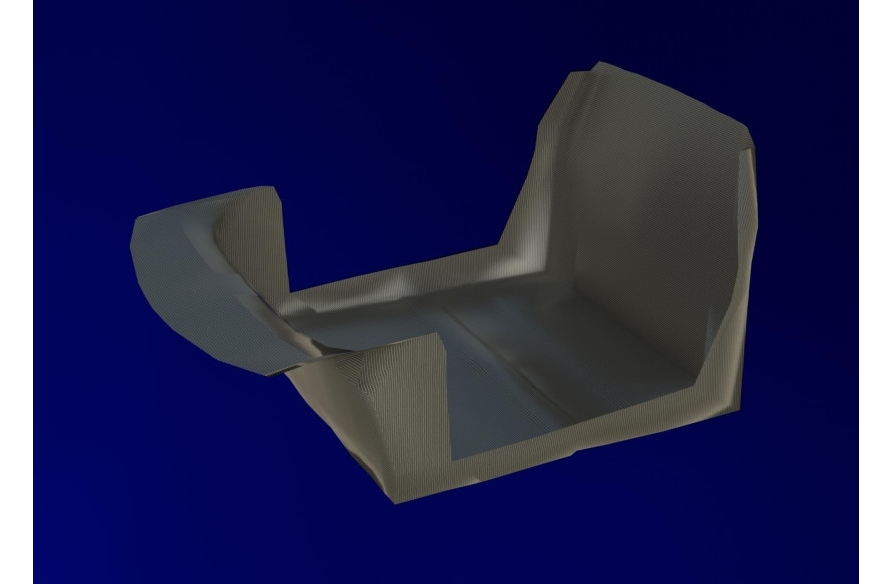
The lower part of the cockpit.
On the sheet of patterns, the parts are indicated by model numbers, the color of the pattern outline (red, blue, green or black) is named. The part numbers are the same color as the outline of the pattern. The pattern must be printed on a 1: 1 scale on a strong matte banner fabric 3.2 m wide. To create a stencil of the pattern detail, place the printed pattern on thick cardboard and trace the outline of the part with a soft pencil. Cut out the pattern piece from the cardboard.
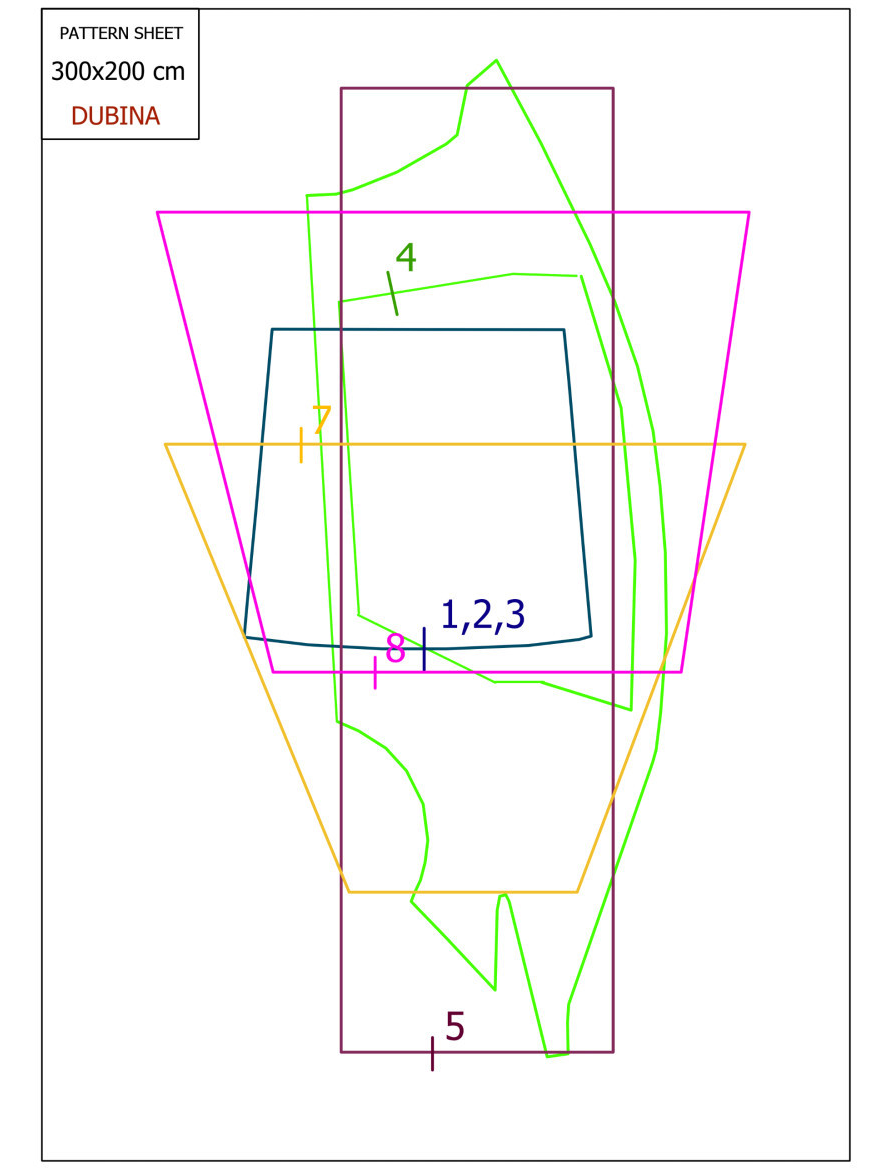
Pattern sheet.









