1. INTRODUCTION
1.1 CRYPTO CURRENCY
What is Crypto Currency?
A cryptocurrency is a medium of exchange like normal currencies such as USD, but designed for the purpose of exchanging digital information through a process made possible by certain principles of cryptography. Cryptography is used to secure the transactions and to control the creation of new coins.
Why Crypto Currency?
Money exists to facilitate trade. Through the centuries trade has become incredibly complex everyone trades with everyone worldwide. Trade is recorded in book keeping, this information is often isolated in closed to the public. This is the reason why we use third parties and middlemen we trust to facilitate and approve our transactions. Think governments, banks, accountants, notaries and the paper money in your wallet. We call these trusted third parties. Cryptocurrency software enables a network of computers to maintain a collective bookkeeping via the internet. This bookkeeping is neither closed nor in control of one party or a central authority. Rather, it is public, and available in one digital ledger which is fully distributed across the network. We call this the blockchain. In the blockchain all the transactions are logged, including information on the time, date, participants and amount of every single transaction. Each node in the network owns a full copy of the blockchain. On the basis of complicated state-of-the-art mathematical principles the transactions are verified by the cryptocurrency miners, whom maintain the ledger. The mathematical principles also ensure that these nodes automatically and continuously agree about the current state of the ledger and every transaction in it. If anyone attempts to corrupt transaction the nodes will not arrive at a consensus and hence will refuse to incorporate the transaction in the blockchain. So every transaction is public and thousands of nodes unanimously agreed that a transaction has occurred on date X at time Y. It’s almost like there’s a notary present at every transaction. This way everyone have access to a shared single source of truth. The ledger does not care wetter a cryptocurrency represents a certain amount of Euros or Dollars, or anything else of value, or property for that matter. Users can decide for themselves what a unit of cryptocurrency represents. A cryptocurrency like Bitcoin is divisible in to 100 million units and each unit is both individually identifiable and programmable. This means that users can assign properties to each unit, users can program a unit to represent a Euro cent, or a share in a company, a kilowatt our energy or digital certificate of ownership. Because of if this cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology could be used for more than simply money and payments. A cryptocurrency can represent many kinds of property. A thousand barrels of oil, award credits or a vote during an election for example. moreover cryptocurrency protocols allows us to make our currency smarter and to automize our cash and money flows. Imagine a health care allowance in dollars or Euros that can only be used to pay for health care at certified parties. I in this case, whether someone actually follows the rules is no longer verified in the bureaucratic process afterwards. You simply program these rules into the money, compliance up front. The unit can even be programmed in such a way that it will automatically be returned to the provider if the receiver doesn’t use it after a certain amount of time. This way the provider can ensure that allowances are not horded. A company can control its spending in the same way. By programming budgets for salaries machinery, materials and maintenance so that the respective money is specified and cannot be spent on other things. automating such matters leads to considerable decrease in bureaucracy.
1.2 BITCOIN
Bitcoin is a new currency that was created in 2009 by an unknown person using the alias Satoshi Nakamoto. Transactions are made with no middle men – meaning, no banks! There are no transaction fees and no need to give your real name. More merchants are beginning to accept them. You can buy webhosting services, pizza or even m Buy on an Exchange. Bitcoins are stored in a “digital wallet,” which exists either in the cloud or on a user’s computer. The wallet is a kind of virtual bank account that allows users to send or receive bitcoins, pay for goods or save their money. Unlike bank accounts, bitcoin wallets are not insured by the FDIC. Though each bitcoin transaction is recorded in a public log, names of buyers and sellers are never revealed – only their wallet IDs. While that keeps bitcoin users’ transactions private, it also lets them buy or sell anything without easily tracing it back to them. That’s why it has become the currency of choice for people online buying drugs or other illicit activities.
Exchange Bitcoins:
Several marketplaces called “bitcoin exchanges” allow people to buy or sell bitcoins using different currencies. Mt. Gox is the largest bitcoin exchange.anicures.
Transfer:
People can send bitcoins to each other using mobile apps or their computers. It’s similar to sending cash digitally.
Mining:
People compete to “mine” bitcoins using computers to solve complex math puzzles. This is how bitcoins are created. Currently, a winner is rewarded with 25 bitcoins roughly every 10 minutes.
Symbol:

Ƀ is not a logo but a symbol: Unicode Character U+0243 can be used any Unicode text editor. This unicode character was originally used as a phonetic symbol to represent or transcribe the sound [β]. Thus the context of this use does not allow any confusion with the Bitcoin currency.
Facts: The baht (sign: ฿; code: THB) is the currency of Thailand. Thailand’s population is 67 million people (vs. Bitcoin’s debated 1–4 million users) and they’re not really cool with the community trying to “steal” their sign.
Unit:
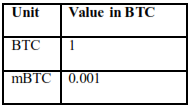
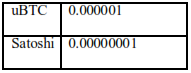
1.3 HISTORY OF BITCOIN
He is said to be from Japan but his mail ID was from Germany, plus the bitcoin software was not available in Japanese. He developed the system and the Bitcoin software (that is used to run the system) in 2009 but disappeared into thin air in 2010. The other developers of the system stopped hearing from him in 2010, and plenty of speculation turned up about his real identity. Some even suggested that his name was just a mashup of popular Japanese companies — SAmsung TOSHIba NAKAmichi MOTOrola. But what he created was definitely the fantasy of every tech guy in the world.
2007, Satoshi Nakamoto
According to legend, Satoshi Nakamoto began working on the Bitcoin concept in 2007. While he is on record as living in Japan, it is speculated that Nakamoto may be a collective pseudonym for more than one person.
August 2008, An interesting patent application
Three individuals, Neal Kin, Vladimir Oksman, and Charles Bry file an application for an encryption patent application. All three individuals deny having any connection to Satoshi Nakamoto, the alleged originator of the Bitcoin concept. The three also register the site Bitcoin.org in the same month, over on anonymousspeech.com – which allows people to buy domain names anonymously.
October 2008, The White paper is published
Despite the above, Satoshi Nakamoto releases his white paper, revealing his idea for a purely peer-to-peer version of electronic cash to the world. In his vision, he manages to solve the problem of money being copied, providing a vital foundation for Bitcoin to grow legitimately.
November 9, 2008, The Bitcoin Project hits SourceForge
The Bitcoin project is registered on SourceForge.net, a community collaboration website focused on the development and distribution of open source software.
January 3, 2009, The Genesis Block is mined
The first block, nicknamed ‘Genesis’ is launched allowing the initial ‘mining’ of Bitcoins to take place. Later that month, the first transaction takes place between Satoshi and Hal Finney, a developer and cryptographic activist.
January 9, 2009, Version 0.1 is released
Version 0.1 of Bitcoin is released. Compiled with Microsoft Visual Studio for Windows, it lacks a command line interface and is so complete that it furthers speculation that it was developed by more than one person (or by an academic with little programming experience and a great deal of theoretical know-how). It includes a Bitcoin generation system that would create a total of 21 million Bitcoins through the year 2040.
January 12, 2009, The first Bitcoin transaction
The first transaction of Bitcoin currency, in block 170, takes place between Satoshi and Hal Finney, a developer and cryptographic activist.
October 5,2009, An exchange rate is established
Bitcoin receives an equivalent value in traditional currencies. The New Liberty Standard established the value of a Bitcoin at $1 = 1,309 BTC. The equation was derived so as to include the cost of electricity to run the computer that created the Bitcoins in the first place.
Hong Kong's First Bitcoin Counter Opens To The Public
October 12, 2009, #bitcoin-dev hits freenode IRC
The #bitcoin-dev channel is registered on freenode IRC, a discussion network for free and open source development communities.
December 16, 2009, Version 0.2 is released
Version 0.2 of Bitcoin is released.
December 30, 2009, The difficulty increases
The first difficulty increase occurs at 06:11:04 GMT.
February 6,2010, A currency exchange is born
The world’s first Bitcoin market is established by the now defunct dwdollar.
February 18, 2010, Encryption patent is published
The encryption patent application that was filed on August 15, 2008 by Neal Kin, Vladimir Oksman, and Charles Bry was published.
May 22, 2010, 10,000 BTC spent on pizza
A programmer living in Florida named Laslo Hanyecz sends 10,000BTC to a volunteer in England, who spent about $25 to order Hanyecz a pizza from Papa John’s. Today that pizza is valued at £1,961,034 and stands as a major milestone in Bitcoin’s history.
July 7, 2010, Version 0.3 released
Version 0.3 of Bitcoin is released.
July 11, 2010, Slashdot drives surge in Bitcoin users.
Mention of Bitcoin v0.3 on slashdot brings in a large number of new Bitcoin users.
July 12, 2010, Bitcoin value increases tenfold
Over a five day period beginning on July 12, the exchange value of Bitcoin increases ten times from US$0.008/BTC to US$0.080/BTC.
July 17, 2010, MtGox is established
The MtGox Bitcoin currency exchange market is established by Jed McCaleb.
July 18, 2010, OpenGL GPU hash farm and ArtForz
ArtForz establishes an OpenGL GPU hash farm and generates his first Bitcoin block.
August 15,2010, Exploit generates 184 billion Bitcoins
Bitcoin is hacked. A vulnerability in how the system verifies the value of Bitcoin is discovered, leading to the generation of 184 billion Bitcoins. The value of the currency – from a high of $0.80 to $1 in June drops through the floor.
September 14, 2010, An offer for CUDA
An offer is made by jgarzik, in the name of the Bitcoin Store, to puddinpop to open source their Windows-based CUDA client. The offer was in the form of 10,000 BTC which, at the time, was valued at around US$600 to US$650.
September 14, 2010, Block 79,764
Split allocation of the generation reward used to mine Block 79,764.
September 18, 2010, CUDA becomes open-source
Under the MIT license, puddinpop releases the source of their Windows-based CUDA client, open sourced by the Bitcoin Store, following a contribution by jgarzik.
September 18, 2010, Slush's Pool mines its first block
Bitcoin Pooled Mining (operated by slush), a method by which several users work collectively to mine Bitcoins and share in the benefits, mines its first block.
September 29, 2010, Another exploit discovered
A microtransactions exploit is discovered by kermit, precipitating the release of Version 0.3.13.
October 2010
Financial task force issues warning
Bitcoin goes under the spotlight. After the hack in August – and a subsequent discovery of other vulnerabilities in the blockchain in September – an inter-governmental group publishes a report on money laundering using new payment methods. Bitcoin, it suggested could help people finance terrorist groups.
OpenCL miner released
The first public version of an OpenCL miner is released.
October 7, 2010, Stalled Bitcoin value begins climb
The Bitcoin exchange rate, stalled at US$0.06/BTC for several months, begins to climb.
October 10, 2010, MtGox switches to Liberty Reserve
MtGox changes its main funding option from PayPal to Liberty Reserve.
October 16, 2010, First escrow transaction takes place
Bitcoin Forum members Diablo-D3 and nanotube conduct the first recorded escrow trade of Bitcoins with theymos as escrow.
October 17, 2010, #bitcoin-otc trading channel opens
The #bitcoin-otc trading channel is registered on freenode IRC as a marketplace for over-the-counter trading of Bitcoins.
October 28, 2010, First ever short sale
Facilitated by #bitcoin-otc, the first recorded short sale of Bitcoins is initiated in the form of a 100 BTC loan from nanotube to kiba.
November 6,2010
Bitcoin reaches $1 million. Based on the number of Bitcoins in circulation at the time, the valuation leads to a surge in Bitcoin value to $0.50/BTC
December 7, 2010, Bitcoind compiled for Nokia N900
Bitcoin Forum member doublec compiles Bitcoind, which was written for the Nokia N900 mobile computer.
December 8, 2010, First mobile Bitcoin transaction
The first portable-to-portable transaction of Bitcoins occurs when ribuck sends doublec 0.42 BTC using Bitcoind.
December 9, 2010, First call option contract sold
The first call option contract for Bitcoins is sold on the #bitcoin-otc market. The transaction occurs between nanotube and sgomick.
December 9, 2010, Difficulty increases
The generation difficulty exceeds 10,000
January 2011, Silk Road opens for business
The Silk Road, an illicit drugs marketplace is established, using Bitcoin as an untraceable way to buy and sell drugs online.
January 2, 2011, Tonal Bitcoin standardizes its units
Tonal Bitcoin, designed for those who prefer the Tonal number system, standardizes its units.
February 2011, Bitcoin reaches parity with US dollar
Bitcoin reaches parity with the US dollar for the first time. By June each Bitcoin is worth $31 giving the currency a market cap of $206 million.
February 14, 2011, Vehicle offered for Bitcoins
An Australian member of the Bitcoin Forum attempts to sell his 1984 Celica Supra for 3000 BTC, and becomes the first person to offer a vehicle in exchange for Bitcoins.
February 25, 2011, WeUseCoins.com is created
WeUseCoins.com is registered and built into a Bitcoin resource and creates one of the most watched videos on Bitcoin.
April 23, 2011, Bitcoin passes parity with Euro
On MtGox, the BTC/USD exchange rate reaches and passes parity with the Euro and the British Sterling Pound. The value of Bitcoin money stock passes US$10 million.
June 13, 2011, Largest ever Bitcoin theft reported
The first major theft takes place. Bitcoin Forum founder allinvain reports having 25,000 BTC taken from his digital wallet, which had an equivalent value of $375,000. In the same month, a major breach of security sees the value of the currency go from $17.51 to $0.01 per Bitcoin.
June 2012, Coinbase is founded
Coinbase, a bitcoin wallet and platform, is founded in San Francisco, California.
November 15, 2012, WordPress.com accepts Bitcoin
WordPress.com announces that it accepts Bitcoins as a form of payment for users to purchase upgrades.
November 28, 2012, Halving Day
On Halving Day, Block 210,000 is the first with a block reward subsidy of 25 BTC.
March 18, 2013, FinCEN defines stance on Bitcoin
The US Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FINCEN) issues some of the world’s first bitcoin regulation in the form of a guidance report for persons administering, exchanging or using virtual currency. This marked the beginning of an ongoing debate on how best to regulate bitcoin.
March 28, 2013, Market cap reaches $1 billion
Bitcoin market capitalisation reaches $1bn.
May 2, 2013, First Bitcoin ATM unveiled
The first Bitcoin ATM in the world is debuted in San Diego, California.
May 18, 2013, PrimeDice.com launches online casino
PrimeDice.com launches as an online casino platform that accepts Bitcoin wager
August 20,2013, Bitcoin ruled private money in Germany
Federal Judge Mazzant claims: “It is clear that Bitcoin can be used as money” and “It can be used to purchase goods or services” in a case against Trendon Shavers, the so-called ‘Bernie Madoff of bitcoin’. Bloomberg begins testing bitcoin data on its terminal. Although alternative tickers exist, endorsement from Bloomberg gives bitcoin more institutional legitimacy.
November 2013, The US Senate holds its first hearings on the digital currency
Bitcoin price climbs to $700 in as the US Senate holds its first hearings on the digital currency. The Federal Reserve chairman at the time, Ben Bernanke, gives his blessing to bitcoin. In his letter to the Senate homeland security and government affairs committee, Bernanke states that bitcoin “may hold long-term promise, particularly if the innovations promote a faster, more secure and more efficient payment system”.
December 2013, China's Central Bank bans Bitcoin transactions
China’s central bank bars financial institutions from handling bitcoin transactions. This ban was issued after the People’s Bank of China said bitcoin is not a currency with “real meaning” and does not have the same legal status as fiat currency. The ban reflects the risk bitcoin poses to China’s capital controls and financial stability. Today China remains the world’s biggest bitcoin trader, with 80% of global bitcoin transactions being processed in China.
January 2014, First insured bitcoin storage service
Bitcoin custodians Elliptic launch the world’s first insured bitcoin storage service for institutional clients. All deposits are comprehensively insured by a Fortune 100 insurer and held in full reserve. This means Elliptic never re-invests client assets; instead they secure them in deep cold storage. Overstock.com becomes the first major online retailer to embrace bitcoin, accepting payments in the US. Overstock was the first in what is now an expeditiously growing list of large businesses that accept bitcoin.
February 2014, HMRC classifies bitcoin as assets
HMRC classifies bitcoin as assets or private money, meaning that no VAT will be charged on the mining or exchange of bitcoin. This is important as it is the world’s first and most progressive treatment of bitcoin, positioning the UK government as the most forward thinking and comprehensive with regard to bitcoin taxation.
June 2014, The illegal online marketplace
The US government auctions off more than 29,000 bitcoins seized from the Silk Road, the illegal online marketplace. The sale and closure of the marketplace marks growing institutional understanding of the potential use cases of bitcoin. Additionally, the closure and auction of the Silk Road has helped bitcoin gain legitimacy as it demonstrates that bitcoin is not an easy way for online criminals to avoid the rule of law.
From this point onwards bitcoin can no longer be considered as a currency for criminals. The use of the bitcoin blockchain means that the identity of users can often be established.
July 2014, Bit Licence’
The ‘Bit Licence’ edges towards reality as the New York State Department of Financial Services releases the first draft of the agency’s proposed rules for regulating virtual currencies. The European Banking Authority publishes its opinion on ‘virtual currencies’. Their analytical report recommends that EU legislators consider declaring virtual currency exchanges as ‘obliged entities’ must comply with anti-money laundering (AML) and counter-terrorist financing requirements.
The EBA report is important as it acts as a catalyst to launch bitcoin into the financial mainstream by highlighting the fact that virtual currencies require a regulatory approach to strive for an international coordination to achieve a successful regulatory regime. Also that month GABI (Global Advisors Bitcoin Investment Fund) launches the world’s first regulated Bitcoin Investment fund. This is important to the bitcoin ecosystem as the launch of this investment vehicle adds further legitimacy to bitcoin in addition to allowing regulated investors a way to invest in bitcoin.
August 2014, HM Treasury’s positive outlook on bitcoin
The Chancellor of the Exchequer, George Osborne, demonstrates his and HM Treasury’s positive outlook on bitcoin when he purchases £20 worth of bitcoin and announces HM Treasury’s Call for Information on digital currencies, offering digital currency businesses the chance to comment on the risks and benefits and potentially influence future government policy.
October 2014, TeraExchange
TeraExchange announces that the first bitcoin derivative transaction was executed on a regulated exchange, adding a new hedging instrument to bitcoin and instilling credibility and institutional confidence in the entire bitcoin community.
December 2014, Microsoft accept bitcoin
Tech giant Microsoft begins accepting bitcoin payments.
January 2015, NYSE
The New York Stock Exchange is a minority investor in Coinbase’s $75M funding round. The NYSE aims to tap into the new asset class by bringing transparency, security and confidence to bitcoin.
March 2015, UK Treasury’s call
The results of the UK Treasury’s call for information on digital currency are announced.
Future predictions
There are several possible ways Bitcoin can go at this point, all of which point to a legitimate, widespread adoption by large institutions through tighter regulation. Recently, New York’s BitLicense became the world’s first digital currency-specific regulatory regime. It has been through a couple of rounds of consultations and is expected to come into force in a couple of weeks.
The European Central Bank and European Banking authority have both released detailed reports on digital currencies, and suggested regulation of the industry by the EU to further control price fluctuations. The Winklevoss brothers, they of Facebook fame, are on the verge of launching their own exchange-traded fund holding Bitcoins.
Bitcoin’s journey into the financial mainstream has already begun, with HM Treasury’s report on digital currencies marking encouraging progress toward the predictions in this infographic. The report introduces anti-money laundering, consumer protection and technical standardisation for digital currency companies in the UK, which will encourage traditional financial services to engage more with digital currency businesses and accelerate the integration of blockchain technology within financial services.
1.4 THINGS TO KNOW ABOUT BITCOIN
Special About the Bitcoin System:
The Bitcoin is a system which allows you to do anonymous currency transactions and no one will come to know about the payment or about all other info related to the payment, including who sent it, who received it, etc.
Satoshi did it by making the system – a peer-to-peer network – controlled by no central authority but run by a network of contributors and freedom enthusiasts, who donated their time and energy to this innovation. Essentially, people can do money transactions and no authority or organization will come to know about it. Satoshi Nakamoto was so talented that he even solved the problem of double spending of digital currency in his system
Double Spending:
We can make many copies of digital data, e.g. people copy software and sell it as counterfeit or pirated copies. We may face the same problem with digital currency – one can copy the digital currency (let’s suppose USD100) and use it as many time as he/she like (as many notes of USD100). Satoshi solved this problem by showing all transactions in a public list. Whenever a new transaction is made, its validity is checked by confirming from the list that the digital currency was not used before. This way, no one can copy the currency and use it for more than one time. It’s a simple but effective idea to stop double spending of the same bitcoin.
Anonymity:
The public listing only shows the transaction ID and the amount of currency transferred. You will be anonymous in the system because you don’t need to provide any of your personal details like your name, address, email, phone number, etc. In comparison, when you use payment gateways like Paypal you have to give up all these personal details.
Using of Bitcoin:
Bitcoins are kept in a digital wallet which you can keep in your computer, or on a website online, which will manage and secure your wallet for you. You can have as many wallets and bitcoin addresses (where you receive money from others) as you like. What’s more, you can use Bitcoin software on top of Tor to prevent anyone from tracking your IP address – total anonymity guaranteed!
Total Bitcoins:
At this very moment, 10.71 million Bitcoins are in existence, which is like 207.929 million USD worth! In fact, the Canadian government is working on their own crypto-currency, named MintChip. (a glance:)
Mintchip, In one day, more than 45,000 transactions of a total of BTC 2.5 million (worth of USD48.5 million) is handled by the bitcoin network.
Spend Bitcoins:
Spending Bitcoins is a bit easier. You can send Bitcoins to a person, buy goods, or donate to non-profit foundations who accept it, such as Wikileaks, P2P Foundation, Operation Anonymous, Free Software Foundation, Archive.org.
You can send Bitcoins to anyone once you know their bitcoin address.
For merchandise, you can buy products from merchants that accept Bitcoins. Example – BitcoinDeals.
1.5 ALTERNATIVES TO BITCOIN
Best Alternatives
Litecoin
Price: $25.26
Market Capitalization: $600 million
Of all the competing cryptocurrencies, Litecoin is the most similar to Bitcoin. It has been thought of as silver to Bitcoin’s gold, or MasterCard to Bitcoin’s Visa. It has also managed to gain the second-highest market capitalization amongst digital currencies. One key difference includes a different hashing algorithm designed so that mining Litecoins won’t result in a similar hardware arms race to the one Bitcoin is currently involved in. Litecoin mining these days involves rigs of video cards, or GPUs. It’s similar to how Bitcoin mining was a few years ago, until its ASICs (application-specific integrated circuits) were designed from the ground up to mine Bitcoins. Litecoins also feature faster confirmation times due to shorter and faster block rewards. It’s scheduled to produce 84 million Litecoins, four times as much as Bitcoin’s 21 million.
Peercoin
Price: $6.26<






