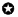6. STRATEGY
Dr, M. Schilling is analyzing the fifth element of deep analytics - strategy [Figure 1.6]. This element can be analyzed from different dimensions such as R&D policy, learning curve, SWOT analysis, technology life-cycle analysis and knowledge management strategy. An intelligent R&D policy should be defined in terms of shared vision, goal, strategic alliance, collaborative, collective and business intelligence. Top technological innovations are closely associated with various strategies of organization learning and knowledge management, more specifically creation, storage, transfer and intelligent application of knowledge. It is essential to analyze strength, weakness, opportunities, threats, technological trajectories, technology diffusion and dominant design of top innovations today. Diffusion is the movement of molecules from high density zone to low density zone of a solution. Can an emerging technology diffuse in the same way globally? What is the pressure acting on technology diffusion? Is the external pressure natural or artificial? Another analogy is osmosis where the molecules move from low density zone to high density zone through a barrier? Can the emerging technology spread and move from low to high density zone smoothly like osmosis or reverse osmosis?
Technological innovation is closely associated with R&D policy and organizational learning strategies in new product development and process innovation. There are various strategies of learning such as learning-by-doing and learning-before-doing. Learning by doing is effective in semi-conductor manufacturing and bio-technology sectors which demand low level of theoretical and practical knowledge. On the other side, learning-before-doing is possible through various methods such as prototype testing, computer simulations, pilot production run and laboratory experiments. It is effective in chemical and metallurgical engineering where deep practical and theoretical knowledge can be achieved through laboratory experiments that model future commercial production experience.
Let us explore the role of deep analytics on technological innovation. It is interesting to analyze the impact of different learning strategies and timing of technology transfer on product development performance, process re-engineering and R&D cost of top technological innovations. It is important to compare the effectiveness of various types of learning strategies in terms of cost, quality and time. It is also critical to analyze the relationship between process innovation and learning curve in terms of dynamic cost reduction and improvements in yield. In case of learning-by- doing, it is possible to acquire knowledge of new process development in specific production environment. But, some knowledge may be lost when a new process is transferred to commercial production environment. It is also interesting to analyze the impact of dedicated process development facilities, geographic proximity between R&D lab and production plant and the duplication of equipment between development and production facilities on practical implementation, speed and effectiveness of top technological innovations. It is essential to identify the critical success factors (e.g. resource allocation, ERP and SCM strategies) that influence the rate of learning and superior performance.
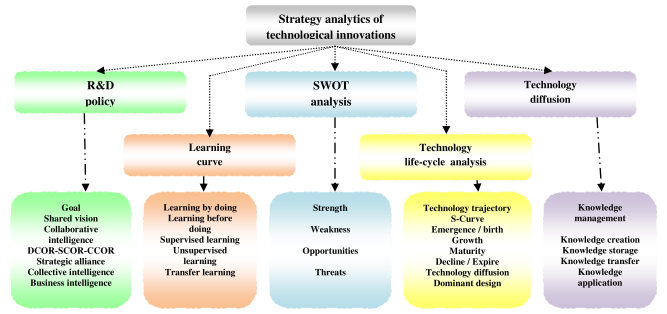
Figure 1.6: Strategy analytics
SWOT Analysis
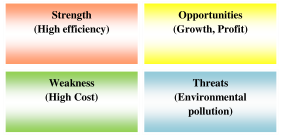
Figure 1.7 : SWOT Analysis
It is rational to evaluate strength, weakness, opportunities and threats of a technological innovation [Figure 1.7]. There may be major and minor strengths and weaknesses. Strength indicates positive aspects, benefits and advantages of a strategic option. Weakness indicates negative aspects, limitations and disadvantages of that option. Opportunities indicate the areas of growth of market and industries from the perspective of profit. Threats are the risks or challenges posed by an unfavorable trend causing deterioration of profit or revenue and losses.
Technological life-cycle analysis : Deep analytics evaluate and explores top technological innovations in terms of technology life-cycle, technology trajectory, S-curve, technology diffusion and dominant design. No element in this universe exists eternally. Similarly, each technology emerges, grows to some level of maturity and then declines and eventually expires [Figure 1.8]. It is essential to evaluate the status of each technological innovation through TLC analysis. Some technologies may have relatively long technology life-cycle; others never reach a maturity stage. Emergence of new technologies follows a complex nonlinear process. It is hard to understand how the technology life-cycle interacts with other technologies, systems, cultures, enterprise activities and impacts on society. All technologies evolve from their parents at birth or emergence phase; they interact with each other to form complex technological ecologies. The parents add their technological DNA which interacts to form the new development. A new technological development must be nurtured; many technologies perish before they are embedded in their environments. Next phase is growth; if a technology survives its early phases, it adapts and forwards to its intended environment with the emergence of competitors. This is a question of struggle for existence and survival for the fittest. Next phase is a stable maturity state with a set of incremental changes. At some point, all technologies reach a point of unstable maturity i.e. a strategic inflection point. The final stage is decline and phase out or expire; all technologies eventually decline and are phased out or expire at a substantial cost. TLC may have other different types of phases such as acquisition, utilization, and phase-out and disposal; preparation or initiation, implementation and operation; organization, directive, delegation, coordinate, collaborative, and dissolution; acquisition; emergence, diffusion, development and maturity.
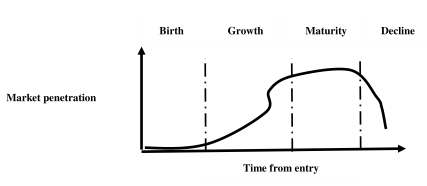
Figure 1.8 : Technology life–cycle analysis
Let us consider the analysis of the performance of a new technology vs. effort; it is basically S-curve. Initially, it is difficult and costly to improve the performance of a new technology. The performance begins to improve with better understanding of the fundamental principles and system architecture. Finally, the technology approaches its inherent limits with diminishing returns. Next, let us analyze the adoption of a new technology over time which is also an S curve. Initially, a new technology is costly for the adopters due to various uncertainties and risks. Gradually, this new technology is adopted by large segments of the market due to reduced cost and risks. Gradually, the diffusion of new technology slows with the saturation of market or due to the threats imposed by other new technologies.
The rate of improvement of a new technology is often faster than the rate of market demand over time; the market share increases with high performance. Technological change follows a cyclical pattern. The evolution of a technology passes through a phase of turbulence and uncertainty; various stakeholders of a supply chain explore different competing design options of the new technology and a dominant design emerges alongwih a consensus and convergence of structure. Then, the producers try to improve the efficiency and design of products based on stable benchmark of the industry. The dominant design considers an optimal set of most advanced technological features which meet the demand of the customer, supply and design chain in the best possible way.
Technology trajectory is the path that a technology takes through its time and life- cycle from the perspectives of rate of performance improvement, rate of diffusion or rate of adoption in the market. It is really interesting to analyze the impact of various factors and patterns of technology trajectories of top innovations today. How to manage evolution of technological innovation? The nature of innovation shifts markedly after a dominant design emerges. The pace of performance improvement utilizing a particular technological approach is expected to follow S- curve pattern. The evolution of innovation is determined by intersecting trajectories of performance demanded in the market vs. performance supplied by technologies. Technology diffusion indicates how new technologies spread through a population of potential adopters. It is controlled by characteristics of innovation, characteristics of social environment and characteristics of the adopters such as innovators, early adopters, early majority, late majority and laggards.
Technology forecasting : From the perspectives of technology management, the basic objectives of deep analytics involve integrated strategic planning, forecasting, design, optimization, operation and control of various technological products, processes and services to understand the dynamics of technology innovation, hype, priority, capability, maturity, adoption, diffusion, infusion, transfer, life-cycle, dominant design, spillover effects, blind spots and also the value of emerging technologies for our society. The basic objective of technology forecasting is to predict the future characteristics of emerging technologies for humanity (e.g. machines, procedures, speed, power, accuracy or precision) through a set of commonly adopted methods such as Delphi method, forecast by analogy, growth curves and extrapolation; may not have to state how these characteristics will be achieved. It is possible to combine two forecast methods (e.g. growth and trend curves) to offset the weaknesses of a method with the strengths of another method and to give the forecaster more insight.
Dominant design : Dominant design is a concept of technology management, identifies key technological features that become a de facto standard. The innovators must try to explore dominant design to win the market share. Dominant design may be a new technology, product or a set of key features as the outcome of a set of independent technological innovations. When a new technology emerges, different firms introduce a number of alternative designs based on incremental improvements. The dominant design enforces standardization, results economies of scale and competition starts based on cost, scale, product features and performance. Dominant design may not be better than other designs; simply incorporate a set of key features that emerge due to technological path-dependence and not necessarily strict customer preferences. Dominant designs are expected to acquire more than 50% of the market share. The process of dominance passes through a few milestones. An innovator conducts R&D to create a new product or service or improve an existing design. The first working prototype of emerging technology sends a signal to competitors to review the feasibility of their research programs. The first commercial product is launched and directed at a small group of customers and force the competitors to review and speed up their research efforts. A clear front runner emerges from the early market. Finally, a particular technological trajectory achieves dominance.
Technology innovation: What is diffusion innovation theory developed by E.M. Rogers (1962)? It explains how, over time, an idea or product gains momentum and diffuses or spreads through a specific population or social system. What is the difference between innovation and diffusion? Diffusion refers to the process by which innovations spread among the members of a social system over time in an organizations, adoption is a decision of implementing innovations based on knowledge, and persuasion of individuals within a given system. An organization seeks to improve efficiency through the adoption of innovative information and communication technologies such as better safety, competitive advantage, fewer errors, greater accuracy, higher quality products, improved communications, increased efficiency and productivity, efficient administration, and improved financial and managerial performance. What is product innovation and diffusion process? The diffusion of innovation is the process by which new products are adopted (or not) by their intended audiences. It allows designers and marketers to examine why it is that some inferior products are successful when some superior products are not. Why is diffusion of innovation important? Diffusion of innovation is responsible for the launch and spread of some of the most important advanced technologies in human history, What is technology absorption? It is the acquisition, development, assimilation and utilization of technological knowledge and capability by a firm from an external source; it occurs between transferring and receiving entities. What is technology innovation management? The basic objective is to train aspiring entrepreneurs on creating wealth at the early stages of a venture or opportunity life cycles; it focuses on the launch and growth of technology companies and growth seeking initiatives of existing companies.
What is the diffusion of innovation curve? The diffusion of innovations curve (innovation adoption curve) of Rogers is useful to understand that trying to quickly and massively convince the mass of a new controversial idea is useless. It makes more sense in these circumstances to start with convincing innovators and early adopters first. What factors influence the rate of adoption and diffusion of innovations? There are specific products and service attributes that affect the diffusion process and can influence consumer acceptance of new products and services; these factors are relative advantage, compatibility, complexity, trialability, and observability. What is technology export? High- technology exports are products with high R&D intensity such as in aerospace, computers, pharmaceuticals, scientific instruments, and electrical machinery. What are the two advantages of technology management? The advantages of new technology is that it allows companies to automate functions that previously required employees. Tasks like data entry and analytics, bookkeeping, and contact management can be partially or completely automated, which allows businesses to work more efficiently without the risk of human errors. How is technology transferred? Transfer of technology is the process of transferring or disseminating technology from the person or organization that owns or holds it to another person or organization, Horizontal transfer is the movement of technologies from one area to another. The diffusion of an innovation is the spread of a product, process, or idea perceived as new, through communication channels, among the members of a social system over time.
What are the disadvantages of a technology? The machines are becoming more intelligent, advanced and efficient and support innovation. The disadvantages are loss of job opportunities. Can we survive without technology? Yes, for most people, technology is not something we give a second thought but some people can't live without it For some people, the existence of technology is the difference between silence and laughter, loneliness and interaction and even life and death. How does a technology affect our life? Technology can affect life both positively and negatively. New technology always changes our life very much and takes it to a new level. It is like the new way of thinking or doing the normal things differently, better and much more faster with less hassle and at a much affordable rate.
Technology diffusion : Diffusion is a physical process that refers to the net movement of molecules from a region of high concentration to one of lower concentration. The material that diffuses may be a solid, liquid or gas. A drop of ink coloring diffuses throughout the water in a glass; the smell of perfume diffuses everywhere in a room. What is diffusion mechanism? The diffusion of a particular lattice atom by a vacancy mechanism is inextricably linked to the movements of vacancies, but is something different! Others are indirect interstitial mechanisms. What is the principle of diffusion? It is the movement of a component through space under the influence of a physical stimulus. The most common cause of diffusion is a concentration gradient which tends to adjust the component concentration until it reaches equilibrium. In short, diffusion is the physical flow of material. What is the difference between imbibition and diffusion? Imbibition is a reversible process whereas diffusion is an irreversible process. Imbibition is the absorption of water by general surface whereas diffusion is the movement of solid, liquid or gaseous molecules from the region of higher concentration to lower concentration. Can we explore the concept of technology osmosis?
Technology diffusion is the process by which innovations of emerging technologies are adopted by a population. The rate of diffusion depends on several factors such as nature and quality of innovation, how information about the innovation is communicated and characteristics of the population into which the technology is introduced. Why is technology diffusion important? Technology diffusion plays a major role in most of the countries today. We can increase the trade by removing the diffusion barriers since the countries achieve higher productivity by taking the technology from the diffusion process. What is meant by technology diffusion? Technological diffusion is the process by which innovations (new products, new processes or new methods) spread within and across economies. What are the steps of diffusion? Diffusion occurs through a five step decision making process. It occurs through a series of communication channels over a period of time among the members of a similar social system. Rogers' five stages are awareness, interest, evaluation, trial, and adoption of technologies. What are the five adopter categories? Market researchers have classified consumers into five categories on the basis of their adoption of a product during different stages of that product's life cycle. The five adopter categories are innovators, early adopters, early majority, late majority and laggards. What are different diffusion strategies? The goal of any diffusion strategy is to spread the word about your innovation and encourage users to adopt it. These strategies may also be modified and used to target any other user group. What is rate of diffusion in technology management? Diffusion is the process by which a new idea or new product is accepted by the market. The rate of diffusion is the speed with which the new idea spreads from one consumer to the next.
Technology adoption: Within the rate of adoption, there is a point at which an innovation reaches critical mass. The categories of adopters are innovators, early adopters, early majority, late majority, and laggards. What is the difference between diffusion and adoption process? Diffusion is a macro process concerned with the spread of a new product from its source to the consuming public. Adoption is a micro process that focuses on the stages through which an individual consumer passes when deciding to accept or reject a new product. What is the late majority? Late majority refers to the second to last segment of a population to adopt an innovative technology. The late majority accounts for roughly 34% of the population and may adopt a new product only after seeing that the majority of the population already has successfully adopted it. What is diffusion and adoption of innovation? There are various strategies of technology adoption : align technology and strategy; communicate for buy-in and engagement; perform a current systems analysis; develop training approach early and integrate technology deployment with change management; create an effective governance structure. Technology diffusion is a measure of how widely technology is spread throughout an organization. Technology infusion, on the other hand, is the extent to which technology permeates an area or department. Technology infusion is the process of strategically binding technical needs and potential solutions.
Technology spillover effects: A group of firms from emerging economies may enjoy unintentional technological benefits from R&D efforts of leading firms from advanced economies without any additional cost sharing. Successful technology spillovers depend on the absorptive capability of the receiving firms, technological gaps, interactions, information symmetry and knowledge flows between sending and receiving firms and also geographical and cultural proximity of a social process. Technology spillover is ultimately a learning experience for both sending and receiving firms. In economics, a spillover may be an economic event resulting positive or negative spillover effects. Negative spillover effects may occur when a market or economy suffers due to the slowdown in a different economy. For example, odors from a rendering plant or a flower garden are negative or positive spillover effects upon its neighbors. Spillover benefits are the opposite of spillover costs; the benefits that third parties or society receive from the actions of others. It may be considered as third party effect. For example, the economic benefits of increased trade are the spillover effects anticipated in the formation of strategic alliances (e.g. SAARC, ASEAN).
Strategy Analytics
Agents: System analysts, business analysts, technology management consultants;
Objects / entities: sustainable smart cities, smart villages, communities, smart world, smart universe;
Strategic moves :
 Call deep analytics ‘7-S’ model; explore how to ensure a perfect fit among 7- S elements – scope, system, structure, security, strategy, staff-resources, skill- style-support;
Call deep analytics ‘7-S’ model; explore how to ensure a perfect fit among 7- S elements – scope, system, structure, security, strategy, staff-resources, skill- style-support;
 Define a set of sustainable development goals and emerging technologies accordingly. /* Refer to scope and system analytics, sections 1 and 2 */
Define a set of sustainable development goals and emerging technologies accordingly. /* Refer to scope and system analytics, sections 1 and 2 */
 Business model innovation
Business model innovation
-
- Who are the consumers?
- What should be the offering of products and services?
- What do the consumers value?
- What is the revenue stream ?
- How to deliver values to the consumers at rational cost?
 Define R&D policy : shared vision (refer : scope analytics, section 1), sustainable development goals, collaborative intelligence, collective intelligence, business intelligence;
Define R&D policy : shared vision (refer : scope analytics, section 1), sustainable development goals, collaborative intelligence, collective intelligence, business intelligence;
 Do learning curve analysis – learning by doing, learning before doing;
Do learning curve analysis – learning by doing, learning before doing;
 Do SWOT analysis – strength, weakness, opportunities, threats.
Do SWOT analysis – strength, weakness, opportunities, threats.
 Explore dominant design.
Explore dominant design.
 Do technology life-cycle analysis and technology spillover effects.
Do technology life-cycle analysis and technology spillover effects.
 Explore technology innovation-adoption-diffusion strategy.
Explore technology innovation-adoption-diffusion strategy.
 Explore innovation model and knowledge management model for creation, storage, sharing and application of knowledge.
Explore innovation model and knowledge management model for creation, storage, sharing and application of knowledge.
 Adopt ‘4E’ approach : Envision, Explore, Exercise, and Extend.
Adopt ‘4E’ approach : Envision, Explore, Exercise, and Extend.
Let us first explain the motivation of the problem on ‘Business Analytics – Technology for Humanity’. We can consider a technology tree for the sustainable goal of human civilization based on security, global economic growth, generation of new job opportunities, elimination of poverty, business model innovation and the regulation of environmental pollution, global warming and climate change. Is it possible to ensure security of the people of the world from different perspectives such as physical safety from natural disasters and acts of terrorism, social security, financial security, food, garment, accommodation, education, healthcare, communication, culture, energy and utilities globally? We have selected a set of emerging technologies for sustainable goals : solar power, electrical and hybrid vehicles, solar computing, deep analytics, Adaptive security for Supervisory Control & Data Acquisition (SCADA) & Industrial Control System (ICS), railtech security & safety, cancer care : deep learning, precision medicine and genomics, biomedical technology for cancercare, artificial rainfall through cloud seeding, real-time moving target search against astronomical hazards and digital technologies including secure adaptive filter and secure multiparty quantum computing, 5G-6G- 7G-8G wireless communication technologies and cloud computing. With the significant advancement of information and communication technology, computing is perceived to be used as the next utility after water, electricity, gas and telecommunication. Session 15 has explored the classification of emerging digital technology through a technology tree. Digital technology is classified into communication and information technologies at level 1 of the technology tree. The scope of emerging communication technology is explored in terms of [cloud computing, cloud streaming, cloud analytics], [Internet of Things (IoT), Industrial IoT, edge computing], next generation wireless and mobile communication, broadcast and satellite communication, RFID and sensor networks at level 2. The scope of emerging information technology is explored in terms of [adaptive security, secure adaptive filter, dynamic data protection, cyber security, crash proof code]; [applied AI and machine learning, soft computing, deep learning, robotics]; [deep analytics, predictive analytics, collaborative analytics], virtual and augmented reality, digital twins, solar computing, pervasive computing, wearable computing, secure multiparty quantum computing and ray tracing.
In today’s business environment of increasing globalization, rapid technological advancement and knowledge based economy, human capital should be considered as a strategic asset and a sustainable resource of competitive advantage in improving performance of a research organization. Intelligent analytics should be integrated with human resource information system (HRIS) for efficient, consistent and correct decision making of top management on various strategic issues of research and development of emerging technological innovations. Analytics is positively associated with decision taking on human resource management and can predict future workforce planning rationally. Deep analytics is the backbone of HRIS which uses information technologies to acquire, store, manipulate, analyze, retrieve and distribute strategic data for effective management of various HR functions such as workforce planning, employee benefits, administration, payroll, recruitment; in