CHAPTER 4
UNDERSTANDING BUYER BEHAVIOR
Influencing Factors of Consumer Behavior
While the decision-making process appears quite standardized, no two people make a deci-
sion in exactly the same way. As individuals, we have inherited and learned a great many
behavioral tendencies: some controllable, some beyond our control. Further, the ways in
which all these factors interact with one another ensures uniqueness. Although it is impos-
sible for a marketer to
to the particular profile of a single consumer, it is possible to
identify factors that tend to influence most consumers in predictable ways
The
that influence the consumer problem-solving process are numerous and
complex. For example, the needs of men and women are different in respect to cosmetics;
the extent of infonnation search for a low-income person would be much greater when con-
sidering a new au::omobile
opposed to a loaf of bread; a consumer with extensive past
purchasing experience in
product category might well approach the problem differently
from one with no experience. Such influences must be understood to draw realistic con-
clusions about consumer behavior.
of discussion, it may be helpful to group these various influences into
related sets. Figure 4.2 provides
a framework. Situational, external, and internal influ-
ences are shown as having an impact on the consumer problem solving process. Situation
influences include the consumer's immediate buying task, the market offerings that are available to the consumer, and demographic traits . Internal influences relate to the consumer's learning and socialization, motivation and personality,
lifestyle. External influences deal
with factors outside the individual that have a strong bearing on personal behaviors. Cur-
rent purchase behavior is
as influencing future behavior through the internal influ-
of learning .
us now tum to the nature and
of each of these sets
of influences on consumer
solving. Figure 4.2
on the specific elements
that influence the consumer's decision to purchase and evaluate products and services .
Situational Influences
Buying Task
The nature of
buying task has considerable impact on a customer's
approach to solving a particular problem. When a decision involves a low-cost item that is
SITUATIONAL INFLUENCES
• Market offerings
• Demographics
• Complexity
EXTERNAL INFLUENCES
INTERNAL FACTORS AND PROCESSES
Cultural
Psychological
Decision Making
Social class
Characteristics
- Recognize needs
Refe rence groups
Motivation
- Search for
- Learning/socialization
information
- Personality
- Evaluate alternatives
- Attitudes
- Make purchase
- Lifestyle
- Postpurchase
Experience
I Purchase and Evaluation I
FIGURE 4.2
A model of consumer



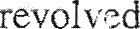
BUYER BEHAVIOR AS PROBLEM SOLVING
83
frequently purchased, such as bread, the buying process is typically quick and routinized.
A decision concerning a new car is quite different. The extent to which a decision is
sidered complex or simple depends on (1) whether the decision is novel or routine, and on
(2) the extent of the customers' involvement with the decision. A great deal of discussion
has
around this issue of involvement. High -involvement decisions are those that
are important to the buyer. Such decisions are closely tied to the consumer's ego and self-
image. They also involve some risk to the consumer; financial risk (highl y priced
Now you can get
rid of annoying
commercials and
annoying
cable company at
the same time.
AD 4.1
Ordering Di shPVR is a hig h-invo lvement decisi on.

8 4