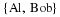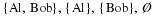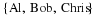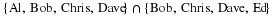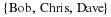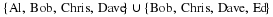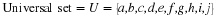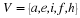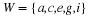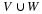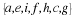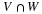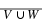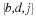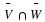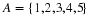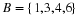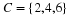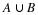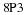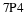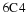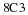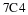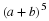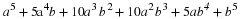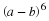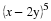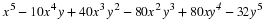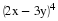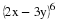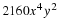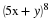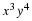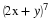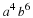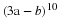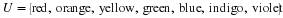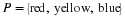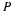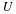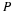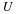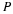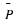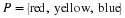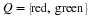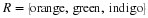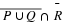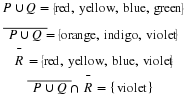In December 1995, President Clinton ordered the first of 20,000 U. S. troops to be sent into Bosnia-Herzegovina as a peace keeping force. Unfortunately, the heavy fog made visibility very poor at the Tuzla airfield, and at the same time increased the threat of sniper attacks from the Serbian forces. U. S. Air Force Col. Neal Patton, and Lt. Col. Sid Kooyman, the advance specialists, had two choices: either to send in the troops by air with the difficulties already described or by road thus exposing the troops to ambush by the Serbian forces. The Serbian army, with its limited resources, had a choice of deploying its forces near the airport or along the road route.
If the U. S. lands its troops on the airfield in the fog while the Serbs are concentrating on the road route, the payoff for U. S. is 20 points. But if the U. S. lands its troops on the airfield, and Serbians are there hiding in the fog, U. S. wins only 5 points. On the other hand, if U. S. transports its troops by road and avoids Serbs its payoff is 35 points, but if U. S. meets Serb resistance on the road route, it loses 50 points.
Write a payoff matrix for the game.
If you were Air Force Col. Neal Patton's advisor, what advice would you give him?