Step 1. Access graphing mode.
, ❬❙❚❆❚ P▲❖❚❪
Step 2. Select <✶✿♣❧♦t ✶> To access plotting - first graph.
Step 3. Use the arrows navigate go to <❖◆> to turn on Plot 1.
<❖◆> ,
Step 4. Use the arrows to go to the histogram picture and select the histogram.
Step 5. Use the arrows to navigate to <❳❧✐st>
Step 6. If "L1" is not selected, select it.
, ❬▲✶❪ ,
Step 7. Use the arrows to navigate to <❋r❡q>.
Step 8. Assign the frequencies to ❬▲✷❪.
, ❬▲✷❪ ,
Step 9. Go back to access other graphs.
, ❬❙❚❆❚ P▲❖❚❪
Step 10. Use the arrows to turn off the remaining plots.
Step 11. Be sure to deselect or clear all equations before graphing.
To deselect equations:
Step 1. Access the list of equations.
Step 2. Select each equal sign (=).
Step 3. Continue, until all equations are deselected.
To clear equations:
Available for free at Connexions <http://cnx.org/content/col10522/1.40>
APPENDIX
661
Step 1. Access the list of equations.
Step 2. Use the arrow keys to navigate to the right of each equal sign (=) and clear them.
Step 3. Repeat until all equations are deleted.
To draw default histogram:
Step 1. Access the ZOOM menu.
Step 2. Select <✾✿❩♦♦♠❙t❛t>
Step 3. The histogram will show with a window automatically set.
To draw custom histogram:
Step 1. Access
to set the graph parameters.
Step 2.
• Xmin = −2.5
• Xmax = 3.5
• Xscl = 1 (width of bars)
• Ymin = 0
• Ymax = 10
• Yscl = 1 (spacing of tick marks on y-axis)
• Xres = 1
Step 3. Access
to see the histogram.
To draw box plots:
Step 1. Access graphing mode.
, ❬❙❚❆❚ P▲❖❚❪
Step 2. Select <✶✿P❧♦t ✶> to access the first graph.
Step 3. Use the arrows to select <❖◆> and turn on Plot 1.
Step 4. Use the arrows to select the box plot picture and enable it.
Step 5. Use the arrows to navigate to <❳❧✐st>
Step 6. If "L1" is not selected, select it.
, ❬▲✶❪ ,
Step 7. Use the arrows to navigate to <❋r❡q>.
Step 8. Indicate that the frequencies are in ❬▲✷❪.
, ❬▲✷❪ ,
Step 9. Go back to access other graphs.
, ❬❙❚❆❚ P▲❖❚❪
Step 10. Be sure to deselect or clear all equations before graphing using the method mentioned above.
Step 11. View the box plot.
, ❬❙❚❆❚ P▲❖❚❪
Available for free at Connexions <http://cnx.org/content/col10522/1.40>
662
APPENDIX
14.9.4 Linear Regression
14.9.4.1 Sample Data
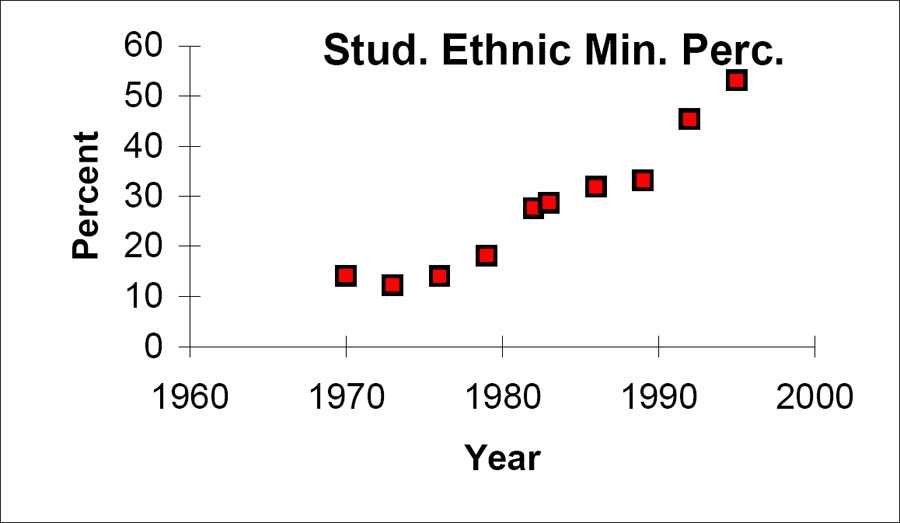
The following data is real. The percent of declared ethnic minority students at De Anza College for selected
years from 1970 - 1995 was:
Year
Student Ethnic Minority Percentage
1970
14.13
1973
12.27
1976
14.08
1979
18.16
1982
27.64
1983
28.72
1986
31.86
1989
33.14
1992
45.37
1995
53.1
Table 14.19 : The independent variable is "Year," while the independent variable is "Student Ethnic Minority
Percent."
Student Ethnic Minority Percentage
Figure 14.6: By hand, verify the scatterplot above.
Available for free at Connexions <http://cnx.org/content/col10522/1.40>
APPENDIX
663
NOTE: The TI-83 has a built-in linear regression feature, which allows the data to be edited.The
x-values will be in ❬▲✶❪; the y-values in ❬▲✷❪.
To enter data and do linear regression:
Step 1. ON Turns calculator on
Step 2. Before accessing this program, be sure to turn off all plots.
• Access graphing mode.
, ❬❙❚❆❚ P▲❖❚❪
• Turn off all plots.
,
Step 3. Round to 3 decimal places. To do so:
• Access the mode menu.
, ❬❙❚❆❚ P▲❖❚❪
• Navigate to <❋❧♦❛t> and then to the right to <✸>.
• All numbers will be rounded to 3 decimal places until changed.
Step 4. Enter statistics mode and clear lists ❬▲✶❪ and ❬▲✷❪, as describe above.
,
Step 5. Enter editing mode to insert values for x and y.
,
Step 6. Enter each value. Press
to continue.
To display the correlation coefficient:
Step 1. Access the catalog.
, ❬❈❆❚❆▲❖●❪
Step 2. Arrow down and select <❉✐❛❣♥♦st✐❝❖♥>
... ,
,
Step 3. r and r2 will be displayed during regression calculations.
Step 4. Access linear regression.
Step 5. Select the form of y = a + bx
,
The display will show:
LinReg
• y = a + bx
• a = −3176.909
• b = 1.617
• r2 = 0.924
• r = 0.961
Available for free at Connexions <http://cnx.org/content/col10522/1.40>
664
APPENDIX
This means the Line of Best Fit (Least Squares Line) is:
• y = −3176.909 + 1.617x
• Percent = −3176.909 + 1.617(year #)
The correlation coefficient r = 0.961
To see the scatter plot:
Step 1. Access graphing mode.
, ❬❙❚❆❚ P▲❖❚❪
Step 2. Select <✶✿♣❧♦t ✶> To access plotting - first graph.
Step 3. Navigate and select <❖◆> to turn on Plot 1.
<❖◆>
Step 4. Navigate to the first picture.
Step 5. Select the scatter plot.
Step 6. Navigate to <❳❧✐st>
Step 7. If ❬▲✶❪ is not selected, press
, ❬▲✶❪ to select it.
Step 8. Confirm that the data values are in ❬▲✶❪.
<❖◆>
Step 9. Navigate to <❨❧✐st>
Step 10. Select that the frequencies are in ❬▲✷❪.
, ❬▲✷❪ ,
Step 11. Go back to access other graphs.
, ❬❙❚❆❚ P▲❖❚❪
Step 12. Use the arrows to turn off the remaining plots.
Step 13. Access
to set the graph parameters.
• Xmin = 1970
• Xmax = 2000
• Xscl = 10 (spacing of tick marks on x-axis)
• Ymin = −0.05
• Ymax = 60
• Yscl = 10 (spacing of tick marks on y-axis)
• Xres = 1
Step 14. Be sure to deselect or clear all equations before graphing, using the instructions above.
Step 15. Press
to see the scatter plot.
To see the regression graph:
Step 1. Access the equation menu. The regression equation will be put into Y1.
Step 2. Access the vars menu and navigate to <✺✿ ❙t❛t✐st✐❝s>
,
Step 3. Navigate to <❊◗>.
Step 4. <✶✿ ❘❡❣❊◗> contains the regression equation which will be entered in Y1.
Available for free at Connexions <http://cnx.org/content/col10522/1.40>
Page 1 Page 2 Page 3 Page 4 Page 5 Page 6 Page 7 Page 8 Page 9 Page 10 Page 11 Page 12 Page 13 Page 14 Page 15 Page 16 Page 17 Page 18 Page 19 Page 20 Page 21 Page 22 Page 23 Page 24 Page 25 Page 26 Page 27 Page 28 Page 29 Page 30 Page 31 Page 32 Page 33 Page 34