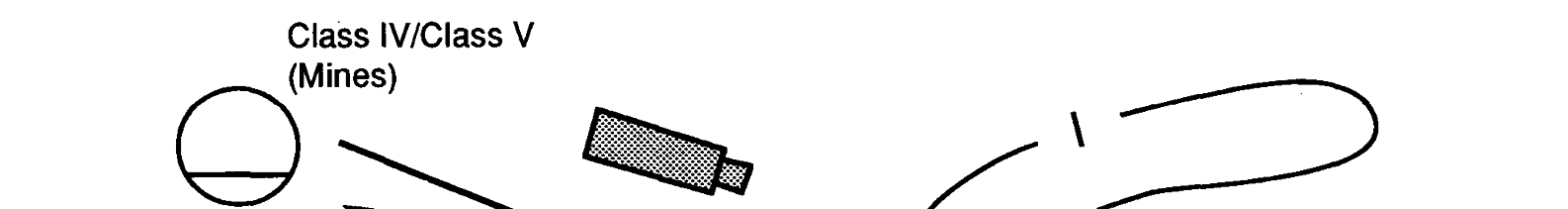
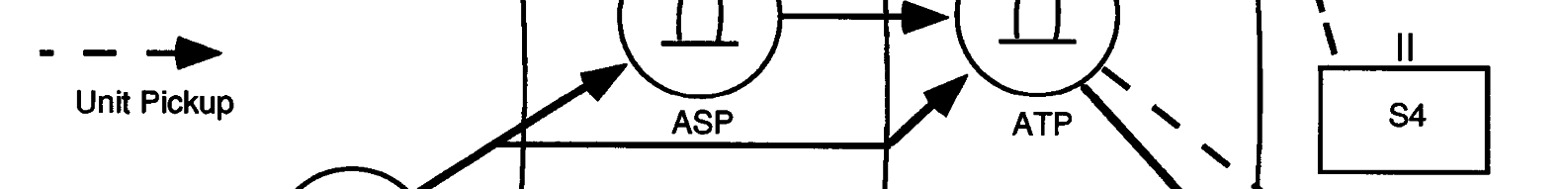
required delivery time, the transportation
somewhat differently. The TF S4 notifies
responsibilities, and a desired location. The
the brigade S4 of Class V requirements. The
quantity includes the required quantity for
brigade S4 notifies the division ammunition
each type of obstacle. There may be several
officer (DAO) in the DMMC who authorizes
Department of Defense identification codes
Class V issue by the ammunition transfer
(DODICs) and national stock numbers
point (ATP). The DAO sends requests for
(NSNs) involved, depending on the types of
Class V to the CMMC.
obstacles required. The required delivery
time is very important to ensure an early
Class V obstacle material flows from the
start on the preparation of the battlefield.
corps storage area (CSA) to the ammu-
Lack of material could adversely affect the
nition storage points (ASP) to the
mission. The transportation responsibilities
ammunition transfer points (ATP) or,
must be clearly understood. MHE is
more likely, straight to the ATP. Class V
required to ensure a rapid turnaround of
obstacle material, unlike most ammunition,
haul assets.
Obstacle Resourcing and Supply Operations C-7









FM 90-7
In addition, the brigade staff identifies the
into usable packages, and then distributed
location of Class IV/Class V points in the TF
throughout the sector based on the obstacle
sectors in coordination with the TF staff.
plan. At some point in the distribution plan,
Prompt identification of the TF Class IV/
the TF turns over control of the obstacle
Class V point is required if the obstacle
material to engineers who then emplace
material is forwarded from the corps into the
them. Obstacle logistics, especially for mine
TF sector. If the material is not forwarded
warfare, at the TF level can be complex,
into the TF sector, it becomes a brigade
require prudent use of scarce haul and
responsibility to deliver the material to the
MHE, and demand positive C2.
TF.
In the case of obstacle groups developed at
At the TF level, sustaining obstacle opera-
corps, division, or brigade level, obstacle
tions is an extremely difficult task. Central-
material supply may vary slightly. The staff
ized throughput operations by the corps or
that is at the level where the obstacle group
the division stops at the TF level. Mass
is planned in detail determines the
quantities of obstacle material, especially
resources required for the obstacle. It also
mines, are centrally received, broken down
plans how the emplacing unit will get the
C-8 Obstacle Resourcing and Supply Operations



FM 90-7
materials. For example, if the corps staff
The relative location of the Class IV/Class V
plans a reserve obstacle group, but the
supply point and mine dumps are shown in
detailed planning is done at TF level, the TF
Figure C-6.
plans the resources for the obstacle group as
it would any other obstacle group. However,
if the corps staff plans the obstacle group in
Class IV/Class V Supply Point
detail, it determines the resources required.
The Class IV/Class V supply point is the cen-
In this case, the corps staff would also plan
tral receiving point of obstacle material in
for delivery of the obstacle materials to the
the TF sector. It is the point at which the TF
emplacing unit. Alternately, the corps staff receives and transfers control of obstacle could direct the emplacing unit to pick up the
material pushed forward by higher levels.
obstacle materials from a location such as
the CSA.
The supply point is established and operated
by the TF and is centrally located to support
all planned obstacles within the TF sector.
OBSTACLE RESUPPLY NODES
Where the tactical obstacle plan allows, the
There are two critical obstacle resupply
supply point should be located near the TF
nodes within the TF sector. Each of them has
combat trains to better facilitate C2 and the
a different function in the obstacle resupply
availability of equipment.
process if the material is not delivered
directly to the emplacement site. They are
The main purpose of the Class IV/Class V
the—
supply-point operation is to receive obstacle
Class IV/Class V supply point.
materials and then reconfigure them based
Mine dump.
on the requirements for each obstacle group.
Obstacle Resourcing and Supply Operations C-9

FM 90-7
This requires that the supply point must
is not always used; it depends on the
have a dedicated S4 representative to track
method of minefield resupply. These tech-
the flow of obstacle material in and out of
niques are discussed in more detail below.
the supply point. The supply point should
When used, one mine dump supports a
have dedicated MHE to off-load the bulk
single obstacle group. It is activated or
quantities of obstacle material and reconfig-
deactivated upon initiation and comple-
ure them into obstacle packages, if required.
tion of emplacing the obstacle group. Mine
Obstacle materials are normally broken
dump operations are primarily an engineer
down into obstacle packages if the materials
company or platoon responsibility. However,
are not already delivered in combat config-
it is a good technique to augment mine
ured loads. This may require a dedicated
dump operations with personnel from the
engineer representative to ensure that the
company team overmatching the obstacle
obstacle materials are configured properly.
group being emplaced. The mine dump may
The most labor-intensive task at the Class
be located either in the vicinity of the com-
IV/Class V supply point is uncrating the
pany team position or nearer to the obstacle
mines. This requires dedicated manpower
group.
equipped with tools to break shipping bands
There are three critical tasks that must be
and uncrate the mines from their containers.
accomplished at the mine dump.
Another important aspect of uncrating
mines is tracking fuzes and booster charges.
As minefield packages are transported
As the mines are uncrated, fuzes and booster
to the mine dump, they are further
charges are separated; however, the same
task organized into strip packages,
number and type of fuzes and boosters must
complete with the right number, type,
be task organized with minefield packages.
and mix of fuzes and boosters. For
This requires strict supervision because mis-
example, if the platoon is emplacing a
takes can quickly lead to confusion and a
standard disrupt row minefield, mines
waste of emplacement time.
are task organized into three packages.
As the engineer platoon moves to the
Because of the assets involved in the Class
mine dump to resupply, each emplac-
IV/Class V supply point, a TF is normally
ing vehicle loads a designated package.
capable of operating only one supply point at
The mines are prepared for emplace-
any given time.
If the TF sector is
ment. They are not fuzed at the mine
extremely wide or deep, several supply
dump. Preparation includes loosening
points may be planned; however, only one
and greasing fuze and booster wells
can be operated at a time, based on the com-
and checking to ensure proper func-
mander’s priorities for obstacle emplace-
tioning.
ment.
The mines are loaded onto the emplac-
ing vehicles or delivery system.
Mine Dump
Transportation of mines from the Class IV/
The mine dump is the most forward mine
Class V supply point to the mine dump is a
resupply node. It is the point at which
supported TF responsibility; however, it is
mines are task organized into mine strip
usually shared between the engineer com-
packages and inspected, prepared, and
pany and the TF since neither one has the
loaded onto the emplacing vehicle. It is
haul capability to simultaneously service all
not a permanent supply point. A mine dump
active mine dumps.
C-10 Obstacle Resourcing and Supply Operations


FM 90-7
OBSTACLE RESUPPLY RULES
Traffic Circuit
The following rules govern obstacle material
Vehicles must be able to enter, load, unload,
resupply:
and exit without interfering with the load-
Uncrate mines at the Class IV/Class V
ing and unloading of other vehicles.
supply point to preserve transportation
assets going forward.
Camouflage and Cover
Task organize obstacle material into
Protection from observation and thermal
type packages at the Class IV/Class V
imaging is desired. Protection from artillery
supply points.
and air attack should be considered. Residue
Transport materials from the Class IV/
must be removed.
Class V supply point to the mine dump
(a shared engineer and maneuver unit
responsibility) when a mine dump is
Defense
used.
The site must be organized for defense
Inspect and prepare mines at the last
against enemy patrols and saboteurs.
supply node (Class IV/Class V supply
point or mine dump) before loading
Time
them onto the emplacing vehicle or dis-
pensing system.
Time factors to handle the obstacle
material—to include all unloading, uncrat-
Set up Class IV/Class V supply points
ing, inspecting, and loading—must be con-
using authorized ammunition proce-
sidered. Use of soldiers other than engineers
dures and distance requirements.
to perform these functions can have a signif-
icant impact on obstacle capability.
OBSTACLE SUPPLY LOCATIONS
Considerations for selecting a location for
Operators
the Class IV/Class V supply point and/or
Leaders and soldiers must be specifically
mine dump are—
allocated to operate mine dumps. They will
Carrying capacity.
probably remain there until the task is com-
Traffic circuit.
plete. The supply node may have to be collo-
Camouflage and cover.
cated with or be near a source of manpower.
Defense.
Table C-4, page C-12, provides general guidance on how much manpower is required to
Time.
sustain mine resupply operations.
Operators.
OBSTACLE MATERIAL RESUPPLY
Carrying Capacity
METHODS
The location of key supply nodes depends in
The methods for obstacle material resupply
part on the type, amount, and availability of
are—
haul assets. The carrying capacity plays a
Supply point.
large role. In short, the more material a
Service station.
vehicle can carry, the more turn-around
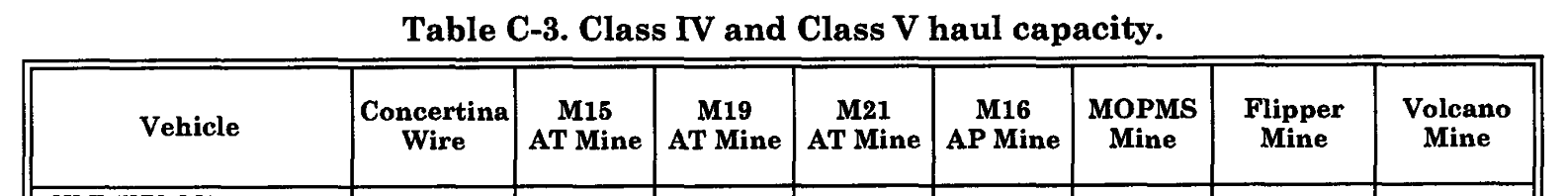
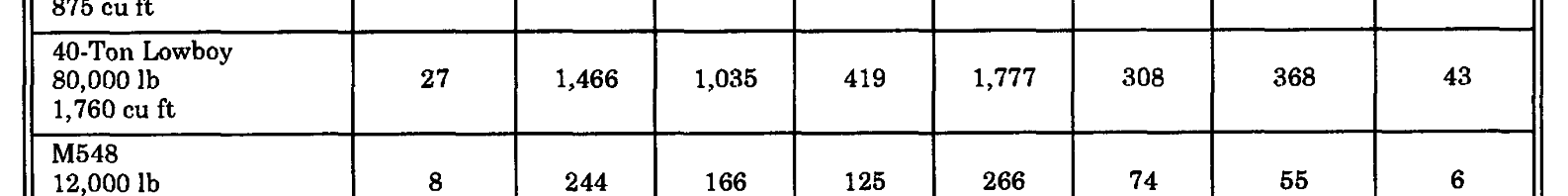
time you can afford. Table C-3, page C-12, Tailgate.
provides the Class IV and Class V haul
In each method, corps or division transport
capacity for various types of vehicles.
delivers Class IV/Class V supplies forward
Obstacle Resourcing and Supply Operations C-11








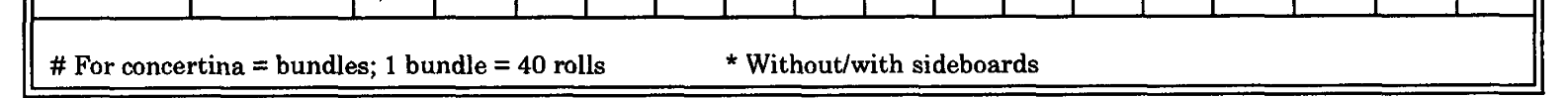






FM 90-7
C-12 Obstacle Resourcing and Supply Operations




FM 90-7
to a designated Class IV/Class V point in
May disrupt the emplacement of indi-
each TF sector. The primary differences in
vidual obstacles when emplacing vehi-
each method are how the material is deliv-
cles cannot carry enough material to
ered from the Class IV/Class V point to the
start and complete the obstacle. This
obstacle location and whether or not a mine
causes emplacing vehicles to stop work,
dump is activated in the resupply chain.
reload, and pick up where they left off.
Requires a larger Class IV/Class V sup-
ply point capable of receiving mass
Supply Point
quantities of obstacle material and
The supply-point technique requires that the
loading platoons simultaneously.
emplacing engineer platoon return to the
Does not afford an opportunity to task
Class IV/Class V supply point each time it
organize obstacle packages.
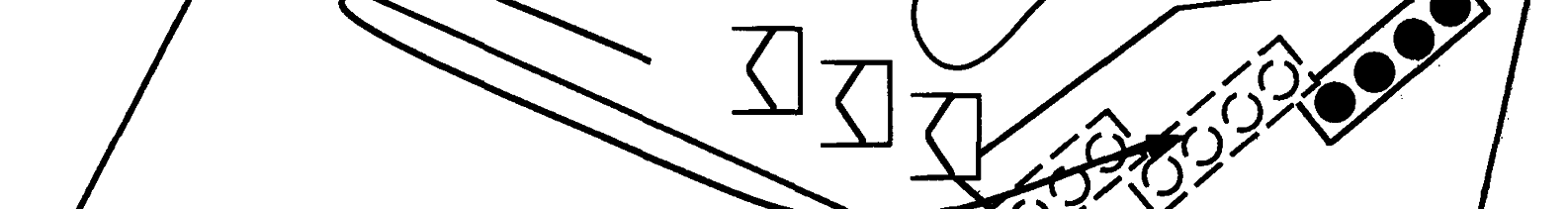
must resupply. Figure C- 7, page C-14, illustrates the supply point method of resupply.
The supply-point technique does not activate
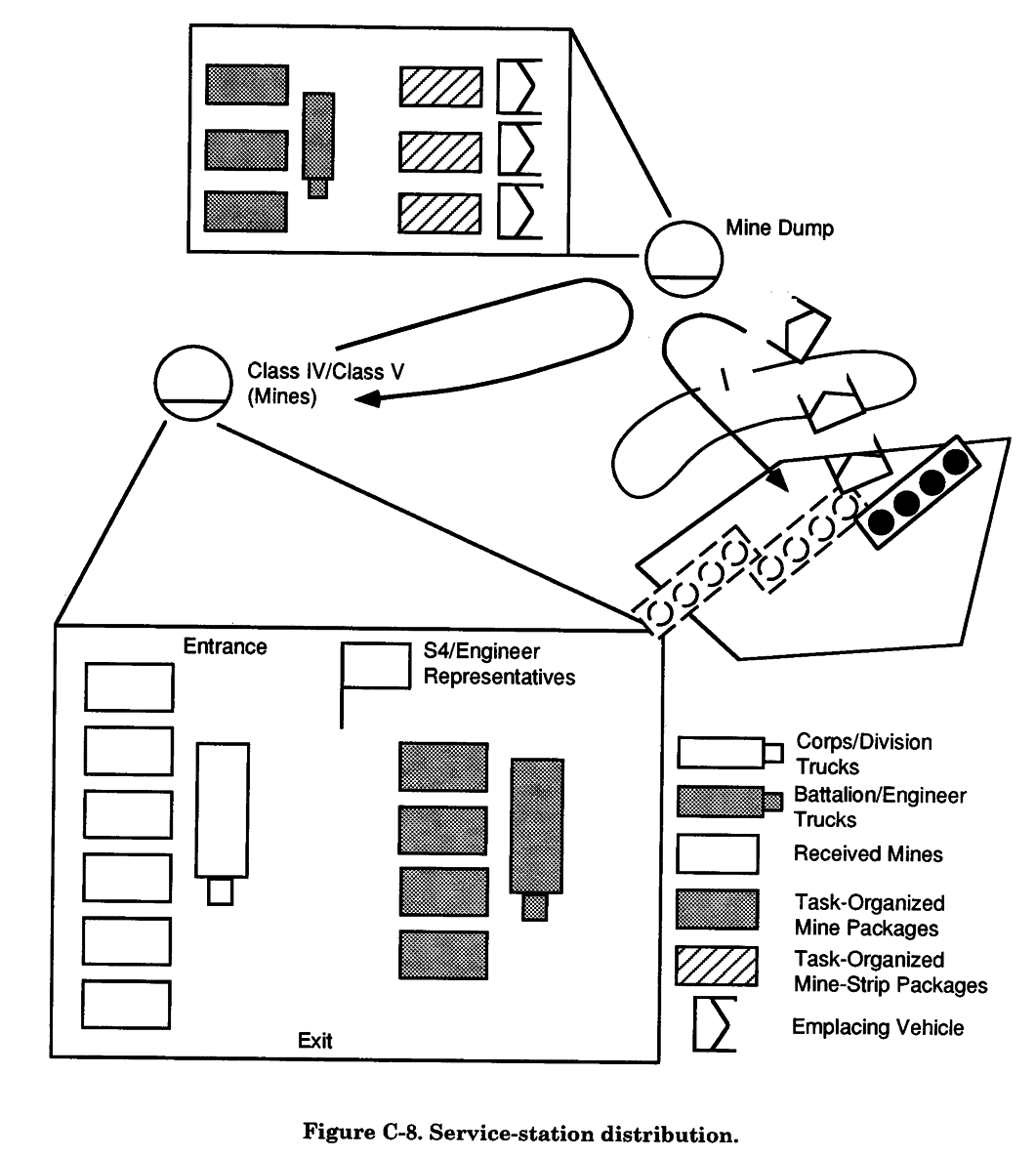
Service Station
a separate mine dump. In effect, it moves the
The service-station technique centers on the
normal tasks associated with a mine dump
activation of a mine/obstacle dump forward
to the supply point. Mines are prepared and
of the Class IV/Class V supply point (see
inspected at the supply point as they are
Figure C-8, page C-15). In the service-sta-loaded onto the emplacing vehicle or dis-
tion method, mines/material are transported
penser.
to a mine/obstacle dump using a combina-
Several considerations may affect the use of
tion of engineer and TF haul assets that are
supply point resupply. First, if there are no
normally under the control of the emplacing
additional haul assets to transport obstacle
engineer. At the mine/obstacle dump, mate-
material forward from the Class IV/Class V
rial is stockpiled and prepared by the
supply point, the supply-point method may
mine/obstacle dump party. Obstacle mate-
be the only viable technique. Second, the
rial is further task organized into packages.
obstacle may be close enough to the supply
The emplacing platoon moves to the mine/
point that any other method is less efficient.
obstacle dump to resupply emplacing vehi-
cles or dispensers. Once the obstacle group
Advantages. The advantages to a supply is emplaced, the mine/obstacle dump is
point are that it—
deactivated or moved to support another
Minimizes unloading and loading of
obstacle group.
material.
Requires minimal augmentation of
There are several considerations for using
haul assets.
the service-station resupply method:
Allows manpower and equipment to be
It is used when the obstacle group is
massed at a single supply point.
located too far from the Class IV/Class
Streamlines C2 of material.
V supply point to allow efficient turn-
around.
Disadvantages. The disadvantages to a It is used when available haul assets
supply point are that it—
have a relatively small capacity. This
Requires more movement of the pla-
requires frequent short-duration
toon, which may take away from
resupply trips and stocking mines to
emplacement time.
keep pace with emplacement.
Requires that the platoon move in and
It streamlines emplacement since
out of the area.
there is an opportunity to task organize
Obstacle Resourcing and Supply Operations C-13


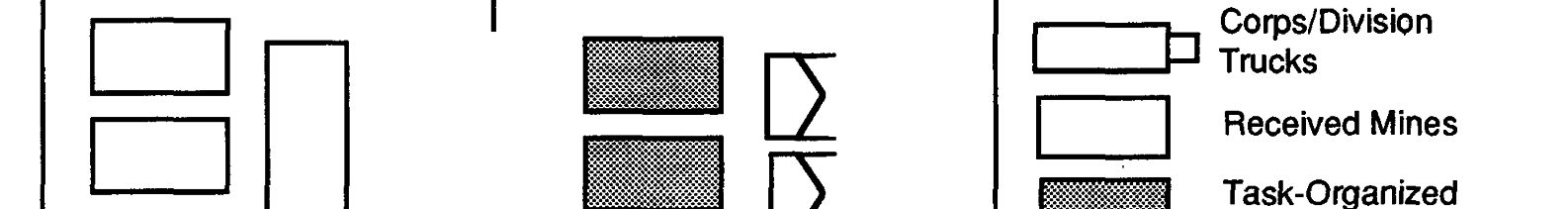
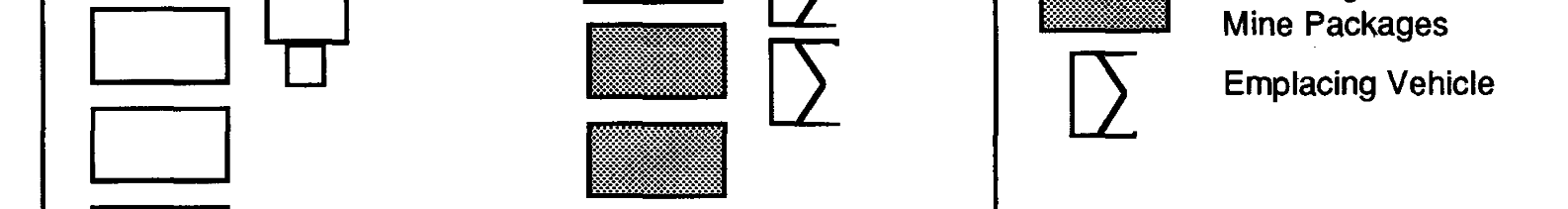
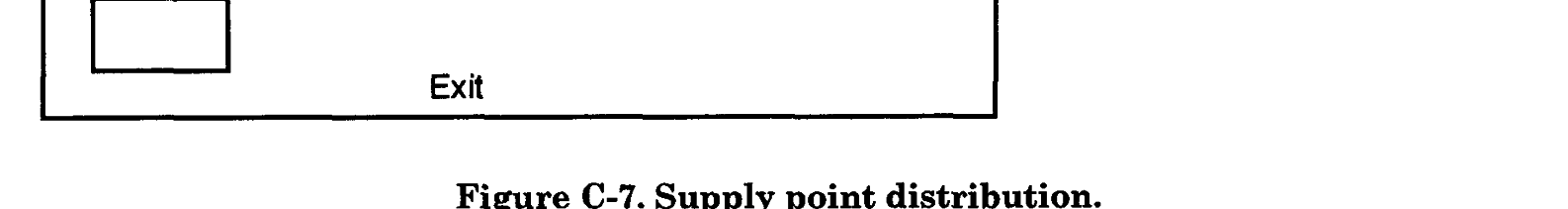



FM 90-7
the mines into strip packages based
Minimizes the distance and time the
on the emplacement method and type of
emplacing platoon must travel to
minefield.
reload.
Allows for obstacle packages.
While it still requires the emplacing
May provide additional manpower and
platoon to stop laying and resupply, it
minimizes the distance and time the
security if it is located near a company
team.
platoon must travel to reload. This
requires that a small party be left at the
Disadvantages. The disadvantages to the minefield to assist in picking up where
service-station resupply method are that it—
emplacement stopped.
Requires additional loading and
unloading of obstacle material.
Advantages. The advantages to the service-May require augmentation with haul
station resupply method are that it—
assets.
Allows for prestockage of obstacle mate-
Disrupts emplacement by requiring the
rial to keep pace with emplacement.
emplacing platoon to stop obstacle
C-14 Obstacle Resourcing and Supply Operations
FM 90-7
Obstacle Resourcing and Supply Operations C-15