,
.3)
Where A-coefficient, specified in Table 7.1 depending on the different
factors; R – strength of cement at 28 days, MPa; R
– compressive
c
cmp
strength of concrete at 28 days, MPa.
Additional possibilities are opened at the use in the formula of strength in
place of ordinary multiplicative coefficient pA.
Equation of multiplicative coefficient pA can be presented as follows:
рА = А А1…Аi…Аn, (7.4)
Where А is a coefficient, taking into account additional influence on the
i
value of strength of i-factor (i=1…n).
Ordinary technological information allows to take into account in the
multiplicative coefficient pA to 2 or 3 additional coefficients А .i
135





Table 7.1
Recommended values of coefficient A (from V.Sizov)
Contents of harmful
Value of coefficient A for concrete made
Kind of
substances (clay, silt, soft
with the use of
aggregates
particles) in crushed stone
(gravel) and sand, %
Crushed
Gravel
Gravel river
stone
mountain
and marine
Crushed stone
0
(gravel)
0.64
0.6
0.57
Sand 0
Crushed stone
0
(gravel)
0.61
0.56
0.53
Sand
3
Crushed stone
1
(gravel)
0.58
0.53
0.5
Sand 3
Crushed stone
2
(gravel)
0.55
0.5
0.47
Sand 3
Crushed stone
2
(gravel)
0.52
0.47
0.44
Sand
5
136





Additional possibilities for expansion of range of the decided tasks of
designing concrete mixtures are possible at the use of the “modified cementwater ratio (C/W)
”:
mod
C + К
D
(C / W )
c.e
=
, (7.5)
mod
W + Vair
Where К
- coefficient of "cementing efficiency" of mineral admixtures, that
c.e
is content of cement in kg, commutable by 1 kg of mineral admixture: D content of mineral admixture, kg/m3; C and W – accordingly contents of
cement and water, kg/m3; V - volume of the entrained air, liters per m3.
air
In this case, formula (7.3) can be presented as follows:
C + К D
R
= pAR
c.e
− 0.5
. (7.6)
cmp
c W + V
air
Where R – strength of cement at 28 days, MPa; R
– compressive
c
cmp
strength of concrete at 28 days, MPa.
137





The coefficient of “cementing efficiency” can be easily defined from
experimental data for the concretes with identical strength by the following:
C − C
K
1
2
=
, (7.7)
c.e
D
Where C - content of cement in the concrete without mineral admixture; C
1
2
- content of cement in the concrete with mineral admixture; D - amount of
mineral admixture.
Application of the “modified cement-water ratio” is rational and useful in
particular for the concrete mixtures design with the limited or small amount
of cement at adding of mineral admixtures.
Calculation of water content.
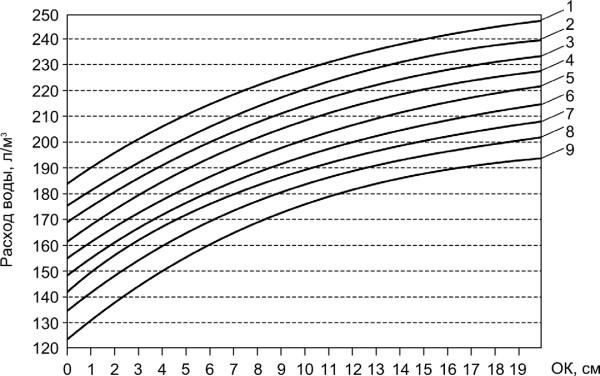
In practice of designing concrete mixtures the water content of concrete
mixtures is determined usually from empiric data by the graphs (Fig.7.3) or
tables which offer some base values of water content (kg/m3) depending on
the indexes of consistency of concrete mix and specified depending on the
features of initial materials. The rule of constancy of water content, in
accordance with which the water content for achievement necessary
consistency of concrete mix remains practically permanent in the certain
range of cement content or cement-water ratio, is widely used thus.
138





3
/mg, k
tera
of w
ount
Am
Slump,
cm
Fig. 7.3. Relationship between amount of water per cubic meter and slump
of concrete mix:
1 – Sand (Fineness modulus is equal 3); 2-9 – Granite crushed stone (Particle
sizes are 10, 15, 20, 30, 40, 60, 80 и 150 mm)
139





Calculation of aggregates content.
One of basic tasks of optimization of concrete mixtures is determination of
aggregates ratio, which provides the minimum amount of cement.
Widely applied in Russia and Ukraine the calculation-experimental methods
of designing concrete mixtures, use the coefficient (α) which characterizes
filling of voids between crushed stone (gravel) particles with cement-sand
pastes (mortar) (taking into account some stock of the paste for
achievement demanded consistency of the concrete mix) for determination
of quantities of sand and crushed stone (gravel).
Quantities of coarse and fine aggregates can be easily defined by decision
of system of two equations of material balance. The first equation
expresses equality of volume of the concrete mix to the sum of absolute
volumes of the initial components of concrete, the second - conformity of
volume of the cement - sandy paste (mortar) to volume of voids in the
coarse aggregates (taking into account some stock of the paste for
achievement demanded consistency of the concrete mix):
140





C
W
F
C
ag
ag
+
+
+
=1000
ρc ρw ρf ag
.
ρ ag
.
c
C
W
F
C
ag
+
+
= Р
ag
α
(7.


































