Lesson VI Analysis Of Risk And Uncertainty
Reading Objective:
After reading this chapter reader will be able to understand that an entrepreneur is always working under uncertainty and has to bear risks. In economic parlance profit is considered as a reward for risk taking. From the reading of this chapter the reader will understand what are the risks which are prevalent in the business. Only when an entrepreneur understands the nature of risks he can secure himself from the risks and uncertainty.
Certainty is what is prevalent today and we can see or realize it., But uncertainty is a situation where one is unsure of what will happen tomorrow. For instance even the meteorological department may not be a able to say with any amount of certainty when the south west monsoon, will set in and how much rain fall it may bring. Therefore the managers will have to safeguard institutions by making sufficient precautions the measures.
Lesson Outline:
-
Types of risks
-
Managers attitude towards risk
-
Decisions under uncertainty
-
Review questions
Introduction:
Various managerial decision making theories were discussed in the previous chapters under certainty but many of the choices that business people make involve considerable uncertainty. A manager investing in new product development, adoption of new technology or new market entry faces various risks. Therefore this chapter focuses on the factors to be considered by the managers to take better decisions with risk under uncertain situations.
Types Of Risks:
Economic risk: Choice of loss due the fact that all possible outcomes and their probability of occurrence are unknown.
Uncertainty: When the outcomes of managerial decisions cannot be predicted with absolute accuracy but all possibilities and their associated probabilities of occurrence are known.
Business risk: Chance of loss associated with a given managerial decision.
Market risk: Chance that a portfolio of investments can lose money due to volatility in the financial market.
Inflation risk: A general increase in the price level will undermine the real economic value of any legal agreement that involves a fixed promise to pay over an extended period.
Interest rate risk: The changing interest rates affect the value of any agreement that involves a fixed promise to pay over a specified period.
Credit risk: May arise when the other party fails to abide by the contractual obligations.
Liquidity risk: Difficulty of selling corporate assets and investments.
Derivative risk: Chance that volatile financial derivatives could create losses on investments by increasing price volatility.
Cultural risk: Risk may arise due to loss of markets differences due to distinctive social customs.
Currency risk: Is the probable loss due to changes in the domestic currency value in terms of expected foreign currency.
Government policy risk: Chance of loss because of domestic and foreign government policies.
The above listed various types of risks are involved in business. Therefore it is essential for the manager to understand the type of risk and strategies to overcome the same. The manager must know the possible outcomes of a particular event, action or decision.The manager must be aware of the probability of risks in business. (Probability means likelihood that a given outcome will occur)
For example; a purchase of share may lead to three probable results i.e. either the price will increase, decrease or it can be the same. Objective interpretation relies on the frequency with which certain events tend to occur. Out of 100 shares, if 25 have increased and 75 have remained in the same level in the market then the probability of incurring profit is ¼. If there is no past experience then we go for subjective probability and based on our perception of occurrence we may measure the probability. But manager’s perceptions differ therefore they make different choices. In general probabilities are measured in two ways they are expected value and variability.
Expected value: The probable payoffs associated with all possible outcomes are called as expected value.
Expected value = P(s) (40/share) + P (f ) (20/share)
= ¼(40) + ¾ (20) = 25.
Variability: The extent to which the possible outcomes of an uncertain situation differ. This difference is called as deviation; it means difference between expected outcome and the actual outcome.
Manager’s attitudes toward risk affect the decision making. The preference towards risk is classified as, risk loving, risk aversion and risk neutral.
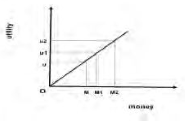
Risk loving: Arises when the payoff is greater than the expected value.
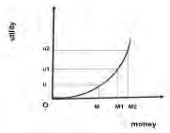
Risk Aversion: Is the behavior of the mangers when the pay off is less than the expected value.
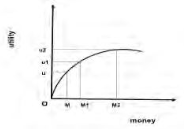
Risk neutral: Behavior takes place when the expected value is equal to the payoff.
There are four ways to manage the risk and uncertainty:
-
Insurance ( Business risks are transferred through Insurance Policies)
-
Hedging is a mechanism whereby the expected loss is to be offset by an expected profit from another contract.
-
Diversification is a method of managing the risk where the risk is spread to various investments and thus the risk is minimized to each investment.
-
Adjusting risk is the mechanism whereby the provision is made to offset the expected loss.
Decision Under Uncertainty:
-
The maximax rule: Deals with selecting the best possible outcome for each decision and choosing the decision with the maximum payoff for all the best outcomes.
-
The Maximin rule: Deals with selecting a worst outcome for each investment decision and choosing the decision with the maximum worst payoff.
-
The Minimax rule: Deals with determining the worst potential regret associated with each, decision, then choosing the decision with the minimum worst potential regret.
The above mentioned criteria may help to measure the minimum expected opportunity loss. The game theory may help the manager to overcome various problems and at the same time to take a better decision in the uncertain business world with minimum risk. Computer based simulation methods are also available to solve this problem. Sensitivity analysis which is less expensive and commonly used can also be used.
Review Questions:
-
Discuss the types of risks faced by a business firm.
-
Explain the manager’s attitude towards risk.
-
Critically examine the Maximin criteria for decision making under uncertainty.
*****






