Lesson IX Employment And Unemployment In India
Reading Objective:
After reading this lesson the candidate may be able to understand that employment denotes that all able and willing people get a job with suitable remunerations. Whereas, the concept unemployment includes, under employment and disguised unemployment. i.e. the people are not able to get a job commensurate with their qualifications or appear to be employed but the output available because of their employment is either nil or marginal. India is a country which not able to achieve full employment in spite of the efforts made by the Government in different ways. It is experiencing a situation where one side the willing and able people are not able to get a job on the other hand, there are many a positions for which the people are not available.
Lesson Outline:
-
Employment and unemployment concepts
-
Types of unemployment
-
Projection of employment and unemployment of India and the World
-
Technology and employment
-
Indian technology sector
-
Review questions
Introduction:
The principal objective of development planning is human development and the attainment of higher standard of living for the people. This requires a more equitable distribution of benefits of development and opportunities, better living environment and empowerment of the poor and marginalized. There is special need to empower women who can act as catalysts for change. In making the development process inclusive, the challenge is to formulate policies and programmes to bridge regional, social and economic disparities in as effective and sustainable a manner as possible.
The projected increase in total labour force during 11th Plan was 45 million. As against this, 58 million employment opportunities are targeted to be created during the Eleventh Plan. This is expected to reduce unemployment rate to below 5 per cent. The Eleventh Plan emphasizes that the growth in various sectors of the economy can be achieved only if supported by appropriate skill development programmes at various levels. The Eleventh Plan document has spelt out certain deficiencies in the skill development scenario in the country as it exists presently. The thrust of the plan therefore will be on creating a pool of skilled manpower in appropriate number with adequate skills, in line with the requirements of the ultimate users of manpower such as the industry, trade and service sector. Such an effort is necessary to support the employment expansion through inclusive growth including in particular a shift of surplus labour from agriculture to non-agriculture.
The basic weakness in our employment performance is the failure of the Indian economy to create a sufficient volume of additional high quality employment to absorb the new entrants into the labour force while also facilitating the absorption of surplus labour that currently exists in the agricultural sector, into higher wage, non-agricultural employment. A successful transition to inclusive growth requires migration of such surplus workers to other areas for productive and gainful employment in the organized or unorganized sector. Women agricultural workers in families where the male head has migrated, also require special attention ,given the need for credit and other inputs if they are self-employed in agriculture or for wage employment if they do not have land.
As a manager it is essential to understand the concepts related to employment and unemployment. Let us see the basic definitions.
Employment:
When persons are holding a job and they perform for any paid work. Also if workers hold jobs because of illness, strike or vacation, they are considered as employed.
Full Employment:
When 94-95% of them are employed or highest sustainable level of employment over the long run is called as full employment.
Under Employment:
Less than full employment is called as under employment.
Unemployment:
When people are not working and are actively looking for work or waiting to return to work, such a situation may be called as unemployment.
Types Of Unemployment
-
Frictional unemployment: unemployment that occurs naturally during the normal working of an economy. Temporarily caused by inefficient movement of people between regions and jobs, as it takes time for new workers to search and decide for a job. voluntary switching of jobs, fired or seeking re employment
-
Structural unemployment: The change in industrial structure of a country, change in Demand and technology ,change in requirement of skills. Mismatch between demand and supply.
-
Cyclical unemployment: unemployment is more at a particular time that is due to economic recession, depression and others.
-
Technological unemployment: due to change in technology, new production and process leads to reduction in work requirement.
-
Seasonal unemployment: in some industries the work cannot be there through out the years as it is seasonal in nature.
-
Disguised unemployment: lack of work of the type which would fully utilize the degree of skill possessed by the workers.
Various categories like, ‘workers’, ‘unemployed’, ‘labour force’, ‘out of labour force’ are as explained below:
(a) Workers (or employed): Persons who are engaged in any economic activity or who, despite their attachment to economic activity, have abstained from work for reasons of illness, injury or other physical disability, bad weather, festivals, social or religious functions or other contingencies necessitating temporary absence from work constitute workers. Unpaid helpers who assist in the operation of an economic activity in the household, farm or non-farm activities are also considered as workers. All the workers are assigned one of the detailed activity status under the broad activity category 'working or being engaged in economic activity'.
(b) Seeking or available for work (or unemployed): Persons, who, owing to lack of work, had not worked but either sought work through employment exchanges, intermediaries, friends or relatives or by making applications to prospective employers or expressed their willingness or availability for work under the prevailing condition of work and remuneration are considered as those who are ‘seeking or available for work’ (or unemployed).
(c) Labour force: Persons who are either 'working' (or employed) or 'seeking or available for work' (or unemployed) during the reference period together constitute the labour force.
(d) Out of labour force: Persons who are neither 'working' and at the same time nor 'seeking or available for work' for various reasons during the reference period are considered to be 'out of labour force'. The persons under this category are students, those engaged in domestic duties, renters, pensioners, recipients of remittances, those living on alms, infirm or disabled persons, too young or too old persons, prostitutes, etc.
Workers have been further categorized as self-employed, regular salaried/wage employee and casual wage labourers. These categories are defined in the following paragraphs.
Self-Employed:
Persons who operate their own farm or non-farm enterprises or are engaged independently in a profession or trade on own-account or with one or a few partners are self-employed in household enterprises. The essential feature of the self-employed is that they have autonomy (i.e., regarding how, where and when to produce) and economic independence (i.e., regarding market, scale of operation and money) for carrying out operation. The fee or remuneration received by them consists of two parts - the share of their labour and profit of the enterprise. In other words, their remuneration is determined wholly or mainly by sales or profits of the goods or services which are produced by themselves. The Indian scenario is given below.
Distribution Of Urban Household Type Per Thousand
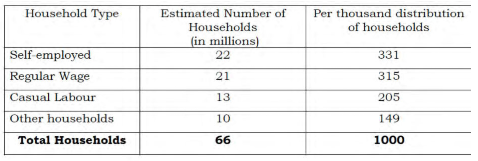
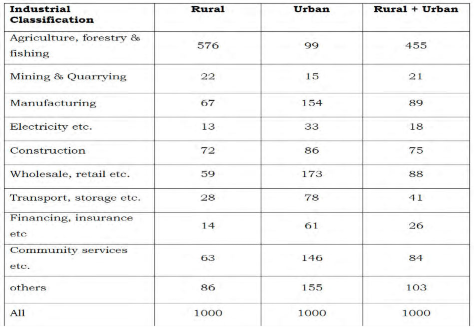
The distribution of employed persons under various broad Industry group is given in the following table. Around 50% of the population are engaged in the primary sectors like agriculture, forestry and fisheries followed by manufacturing and wholesale, retail business. Construction industry and retail business are booming in our country and also provides more employment opportunities in the urban areas. High risk jobs like mining, financing etc.,do not create much employment.
Distribution Of Employed Person By Broad Industry Group Per Thousand
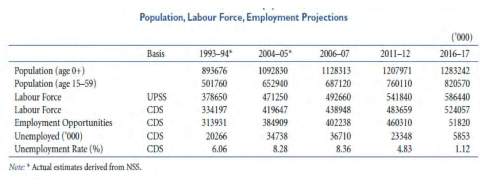
From the following table on population, labour force, employment projections in India for the year 2016-2017 it is observed that the population in the age group of 15-59 is growing along with the total population. The forecast says the employment opportunities to be created in 2016-17 will more. On the other hand the unemployment rate is going to be reduced to 1.12% from 6.06 %. The global trend for the same year is also discussed below.
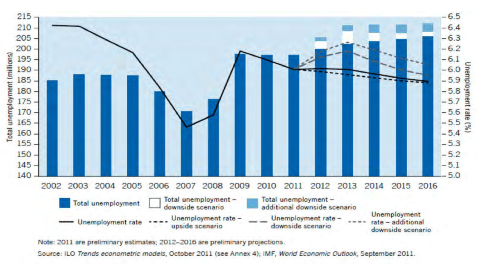
The following two graphs on employment and unemployment projections for 2016 explains clearly that the total employment opportunities created by the world is going to grow from 3 % in 2002 to 61% in 2016. But on the other hand the employment to population ratio is declining. Due to this decline unemployment rate is growing. Understanding the world trend and the Indian scenario will help managers take various decisions regarding the human resource allocation and availability. But the world employment creation is more towards services sector which consists of more technology oriented jobs. We will understand this in detail in the following chapter.
Global Employment Trends And Projections 2002-2016
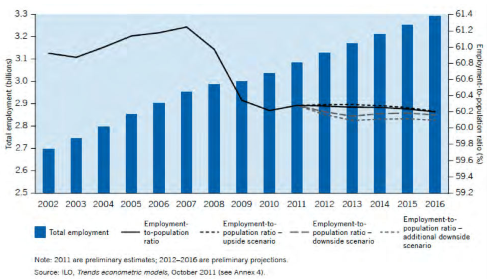
Global Unemployment Trends And Projections 2002-2016
Technology And Employment
The forecasted demand for IT and IT enabled services are going to grow to the extent of 5.3 million in 2022 which indicates that the technology is going to play a major role in creating employment opportunities in the future. The technology based human requirement of the world is also growing at a faster way. The developing countries like India and other Asian countries have more population particularly, India has the highest young population. India produces more engineers every year therefore the opportunities can be optimally utilized by our country. In the recent past, the BPO organizations mushroomed in India but due to political and economic crisis of USA it has changed now. Therefore the change in economic activities of the world has an impact in determining the employment generation of a country.
The next chapter discusses the economic changes of a country with the help of business cycle model.
Human Resource Requirement In 2022
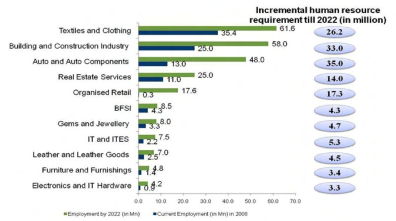
Source: National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC)
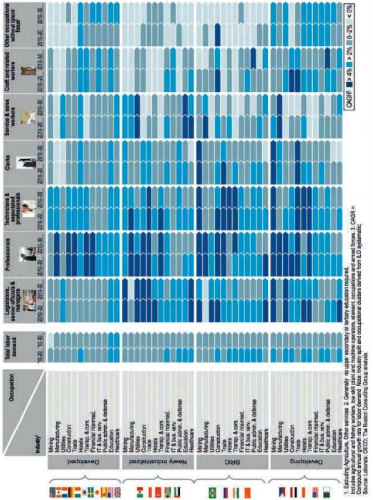
The above table provides detailed information on the human resource requirement in the world. Industry wise regional requirement is forecasted for the year 2030. In developed countries due to aging population for human resource they depend on developing countries like India. Therefore we have potential to cater to their requirement in the future.
The Indian Technology Sector – A Profile
-
The key contributor to the Services Sector accounting for 5.8% of India’s overall GDP
-
Among the largest employment generators in the organized sector employing 7.5 million people, estimated to cross the 10 million mark by 2010
-
Revenues estimated at USD 71 billion in 2008-09, consistent rise in growth with 5 year compound annual growth (CAGR) at 27%
-
Exports constitute two-thirds of overall revenues with a marginally higher 5 year CAGR of 28.7%.The US and UK remain the largest export geographies – 79%, steady expansion of other export destinations notably Continental Europe – CAGR more than 50% over FY 2004-08.
-
Domestic IT revenues estimated at USD 24.3 billion, with a 5 year CAGR of 24%.
-
Industry’s vertical market exposure well diversified across several mature and emerging sectors.
-
BFSI, Telecom and Manufacturing: Among the top 4 verticals for both export and domest ic market.
-
ITeS-BPO sector the fastest growing segment of the IT industry in both the export and domestic market.
-
Export earnings in 2008-09 estimated at USD 12.8 billion (a 5 year CAGR of 32.9%)
-
Domestic revenues at USD 1.9 billion – a growth of 45.3%
Source: CRISIL, Nasscom
We can conclude that according to NSDC, Nasscom reports the opportunities specifically technology based is growing in a faster rate and in other hand the ageing population of these countries are growing. Therefore India has huge potential of young engineers to cater the needs of developed countries.
Review Questions
-
Define the concepts employment, full employment, under employment and unemployment.
-
Explain briefly the major types of unemployment existing in India.
-
What do you mean by labour force?
-
Who is called as self employed?
-
Give an account on Indian employment scenario.
-
Discuss the global trend and projection on employment and unemployment.
-
What do you understand by observing the distribution of employed by different industry?
-
Discuss the unemployment situation of our country.
-
Is growth in technology creates employment opportunities?
-
As a manager what are the managerial decisions would you like to take in your organization.
*****










