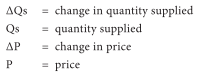Lesson III Supply Analysis
Reading Objectives:
At the end of this lesson the reader will be able understand that supply is an independent economic activity but it is based on the demand for commodities. The managers’ ability to make more profits depends upon his ability to adjust the supply to the demand without creating a surplus while at the same time not t creating a scarcity that will spoil the image of the company in the eyes of the public. Supply is also sometimes inelastic and sometimes elastic. The managers have to take wise decisions to maximize the profits of the firm.
Lesson Outline:
-
Law of supply
-
Determinants of supply
-
Elasticity of supply
-
Factors influencing supply
-
Review questions
Supply of a commodity refers to the various quantities of the commodity which a seller is willing and able to sell at different prices in a given market at a point of time, other things remaining the same. Supply is what the seller is able and willing to offer for sale. The Quantity supplied is the amount of a particular commodity that a firm is willing and able to offer for sale at a particular price during a given time period.
Supply Schedule: is a table showing how much of a commodity, firms can sell at different prices.
Law of Supply: is the relationship between price of the commodity and quantity of that commodity supplied. i.e. an increase in price will lead to an increase in quantity supplied and vice versa.
Supply Curve: A graphical representation of how much of a commodity a firm sells at different prices. The supply curve is upward sloping from left to right. Therefore the price elasticity of supply will be positive. Graph - Supply curve
Determinants Of Supply:
-
The cost of factors of production: Cost depends on the price of factors. Increase in factor cost increases the cost of production, and reduces supply.
-
The state of technology: Use of advanced technology increases productivity of the organization and increases its supply.
-
External factors: External factors like weather influence the supply. If there is a flood, this reduces supply of various agricultural products.
-
Tax and subsidy: Increase in government subsidies results in more production and higher supply.
-
Transport: Better transport facilities will increase the supply.
-
Price: If the prices are high, the sellers are willing to supply more goods to increase their profit.
-
Price of other goods: The price of other goods is more than ‘X’ then the supply of ‘X’ will be increased.
Elasticity of Supply: Elasticity of supply of a commodity is defined as the responsiveness of a quantity supplied to a unit change in price of that commodity.

Kinds Of Supply Elasticity
Price elasticity of supply: Price elasticity of supply measures the responsiveness of changes in quantity supplied to a change in price.
Perfectly inelastic: If there is no response in supply to a change in price. (Es = 0)
Inelastic supply: The proportionate change in supply is less than the change in price (Es =0-1)
Unitary elastic: The percentage change in quantity supplied equals the change in price (Es=1)
Elastic: The change in quantity supplied is more than the change in price (Ex= 1- ∞)
Perfectly elastic: Suppliers are willing to supply any amount at a given price (Es=∞) 43
The major determinants of elasticity of supply are availability of substitutes in the market and the time period, Shorter the period higher will be the elasticity.
Factors Influencing Elasticity Of Supply
-
Nature of the commodity: If the commodity is perishable in nature then the elasticity of supply will be less. Durable goods have high elasticity of supply.
-
Time period: If the operational time period is short then supply is inelastic. When the the production process period is longer the elasticity of supply will be relatively elastic.
-
Scale of production: Small scale producer’s supply is inelastic in nature compared to the large producers.
-
Size of the firm and number of products: If the firm is a large scale industry and has more variety of products then it can easily transfer the resources. Therefore supply of such products is highly elastic.
-
Natural factors: Natural calamities can affect the production of agricultural products so they are relatively inelastic.
-
Nature of production: If the commodities need more workmanship, or for artistic goods the elasticity of supply will be high.
Apart from the above mentioned factors future expectations of the market, natural resources of the country and government controls can also play a role in determining supply of a good. In the long run, supply is affected by cost of production. If costs are rising, some of the existing producers may with draw from the field and new entrepreneurs may be scared of entering the field.
Review Questions:
-
Define the concept supply and the law of supply.
-
Collect relevant data and derive a supply curve of an organization.
-
What do you understand by Price elasticity of supply?
-
Mention the types of supply elasticity with example.
-
Explain the factors influencing the elasticity of supply in the market with an example.
*****