Chapter 1.1 Getting Started

To link this template with boostrap you have to write just one <link> and <script> tag as follows.
 You must save following file in your extracted bootstrap directory otherwise the code will not work
You must save following file in your extracted bootstrap directory otherwise the code will not work

Disabling Responsiveness
Bootstrap automatically adapts your pages for various screen sizes. Here's how to disable this feature so your page works like this http://getbootstrap.com/examples/non-responsive/
Steps to disable page responsiveness:
Omit the viewport <meta> mentioned in the CSS docs
1.Override the width on the .container for each grid tier with a single width, for example width: 970px !important; Be sure that this comes after the default Bootstrap CSS. You can optionally avoid the !important with media queries or some selector- fu.
2.1f using navbars, remove all navbar collapsing and expanding behavior.
3.For grid layouts, use .col-xs- classes in addition to, or in place of, the medium/large ones. Don't worry, the extra-small device grid scales to all resolutions.
 You'll still need Respond.js for 1EB (since our media queries are still there and need to be processed). This disables the "mobile site" aspects of Bootstrap.
You'll still need Respond.js for 1EB (since our media queries are still there and need to be processed). This disables the "mobile site" aspects of Bootstrap.
Browser And Device Support
Bootstrap is built to work best in the latest desktop and mobile browsers, meaning older browsers might display differently styled, though fully functional, renderings of certain components.
Supported browsers
Specifically, bootstrap support the latest versions of the following browsers and platforms. On Windows, bootstrap support Internet Explorer 8·11. More specific support information is provided below.
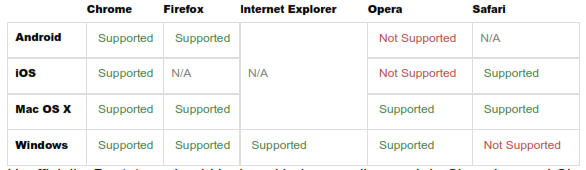
Unofficially, Bootstrap should look and behave well enough in Chromium and Chrome for Linux, Firefox for Linux, and Internet Explorer 7, though they are not officially supported.






