4. STRUCTURE
Structure Analytics
Agents: System analysts, business analysts;
Moves: Design and configure
-
- Organization structure : Technology forums; National level : Government, NGOs, research organizations; International level : strategic alliance among global organizations;
- System architecture ; Innovate a set of emerging technologies;
-
- Level 1: earth science, information technology, electrical, electronics, chemical, mechanical, civil, biotechnology, pharmaceutical engineering;
- Level 2:
-
- Earth Science
-
- Receiving antenna, satellite, laser pulse transmission unit, automated data processing unit; / * for artificial rainfall) */
- Astromonical hazards : telescopes, search agents, sensors,;
- Information technology :
-
- Define computing, data, networking, security and application schema of artificial immune system, e- governance, real-time data tracking system.
Mr. Lin and Dr. S. Chakraborty are giving the basic overview of the structure on emerging technologies against natural disaster. The laser induced artificial rainfall system consists of a receiver unit, processor unit and transmission unit. These components communicate with each other through satellites. The receiver unit receives the data about the clouds (e.g. temperature, humidity, height from earth surface, pressure) and the data of demand of rain for a zone. The processor unit processes the transmitted data, computes the intensity and pulse duration of plasma laser and selects the right transmission unit to trigger laser induced artificial rainfall. A particular zone may be assigned to more than one transmission units as per demand. The transmission unit sends a laser pulse in the given direction of the intensity computed by the processor. This unit is connected to processor unit through satellites. More than none transmission units may be connected to a centrally located receiver and processor unit. It cuts cost of the laser induced rainfall system and may cover larger region.
The transmitter could be a terawatt femtosecond Ti sapphire pulse laser; fundamental wavelength may be ~800nm; pulse energy ~400mJ, duration 100fs and repetition frequency of 10-100Hz. The laser pulse propagates with almost high peak intensity over a distance of ~500m. The transmitter unit should be mounted on a moving platform to cover large area as per demand. This nonlinear phenomenon is caused by the subtle interplay between self-focusing induced by optical Kerr effect and the defocusing by the self-generated plasma. It is essential to compute the power and wavelength of laser for bond breaking and ionization at the cloud height of 500m. The system is controlled by a Micro Controller remote unit having data acquisition and processing system, fast transient digitizer and computer controlled stepper motors. The laser beam energy is adjusted by the stepper motor. The system is operated by a MV power supply. Initially the beam will be of 15 cm arc and the beam expander vary the width of the beam to get significant amount of rain. A movable mirror directs the beam in the larger area of the atmosphere. It is also required to compute the cross-section of the beam for rainfall to cover a reasonably wider area.
The next element of the deep analytics is structure which should be analyzed from the perspective of organization structure and system architecture. The technological innovation related to the artificial rainfall and multi-agent resource sharing mechanism is suitable for a collaborative enterprise model. The system architecture is shown in figure at an abstract level. Let us also consider the structure of an information system to be used in allocation and sharing of water. The information system should monitor a set of entities such as various water bodies, rivers, canals, lakes and dams; demand of water in agriculture, industrial plants and domestic uses, supply of water, rainfall data, water level in rivers, lakes and storage systems, pollution levels and water sharing data (Reference: Table 2.1). It may be integrated with GIS. The information system is expected to support the decision making process associated with artificial rainfall i.e. what initiatives are essential to fulfill the demand-supply gap. The resource sharing system should be able to interact with various types of sensors and measuring instruments like water level indicator, inflow and outflow measuring instruments physically for real-time supply chain optimization in water resource management. The resource sharing mechanism may also require an intelligent negotiation support system (NSS) for multi-party negotiation in water sharing; it is basically a group decision support system; it permits collection of different views of the negotiating agents; defines the structure of the problem, generates alternatives for compromise and improves the quality and the acceptability of a negotiated agreement.
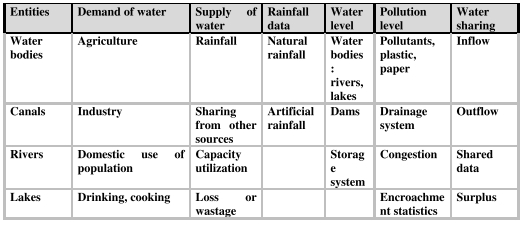
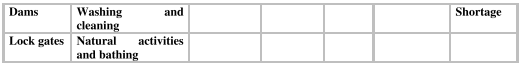
Table 2.1: Analytics for resource allocation and sharing





