Using Dither
Dithering is a method for reducing quantization errors in digital recordings. The theory behind this is that during low level passages, only a few bits are used to represent the signal, which leads to quantization errors and hence, distortion. For example, when “truncating bits”, as a result of moving from 24- to 16-bit resolution, quantization errors is added to an otherwise immaculate recording. By adding a special kind of noise at an extremely low level, these errors are minimized.
In Cubase VST, this is mainly relevant when you are mixing down to a new audio file, using the Export Audio Tracks function (see page 516). Since all internal audio processing is done at a very high resolution (32 bit float), mixing down to an audio file of lower resolution (typically 16 bits) would introduce the kind of quantization errors described above. Therefore:
P
When exporting to an audio file of low resolution, you should activate Dithering.
Basically, “low resolution” would mean 8, 16 or 24 bits, but in the case of Cubase VST/32, this only applies to 16 bit files. As described below, this is because the Apogee UV-22 dithering algorithm used in Cubase VST/32 always dithers to 16 bits.
You could also consider using dithering when mixing down to an external medium (such as a DAT recorder). As always, you should let your ears be the judge.
Activating Dither
Depending on which version of Cubase VST you are using, the available Dither functions differ:
• In the standard Cubase VST and Cubase VST Score, the function is simply called “Dither”. Dither is activated by clicking the Dither “ON” button in the VST Master Mixer (in the signal flow chart to the right of the Master Bus faders).
• Cubase VST/32 has an advanced dithering algorithm called “UV22”, developed by Apogee.
UV22 dithering is activated by clicking the “ON” button below the UV22 logotype in the VST Master Mixer.

 The Dither buttons in standard Cubase VST/Cubase VST Score (left) and Cubase VST/32 (right).
The Dither buttons in standard Cubase VST/Cubase VST Score (left) and Cubase VST/32 (right).
• For both versions, to make settings you need to open the control panel by clicking the Dither “EDIT” button.
From here on, the descriptions are specific to the respective dithering type.
Settings in the Dither Control Panel (Cubase VST and Score only)
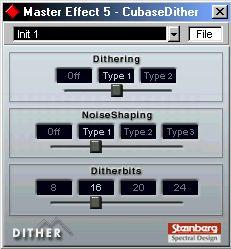 Dither is always applied post Master bus fader. The control panel comes up as “Master Effect 5" to indicate this special Master effect mode.
Dither is always applied post Master bus fader. The control panel comes up as “Master Effect 5" to indicate this special Master effect mode.
The following options can be set in the Dither Control Panel:
• Dithering Type
There are no hard and fast rules for the following options, it all depends on the type of material you are processing. We recommend that you experiment and let your ears be the final judge:
Option Description
Off No dithering is applied.
Type 1 Try this first, it is the most “all-round” type.
Type 2 This method emphasizes higher frequencies more than Type 1.
• Noise Shaping Options (Off, Type 1 - 3)
This parameter alters the character of the noise added when dithering. Again, there are no fixed general rules, but you may notice that the higher the number selected here, the more the noise is moved out of the ear’s most sensitive range, the midrange.
• Dither Bits
This is used to specify the intended bit resolution for the final result. Available options are 8, 16, 20 or 24 bit resolution.
Settings in the Apogee UV 22 Control Panel (Cubase VST/32 only)
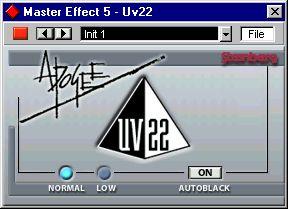 Dither is always applied post Master bus fader. The control panel comes up as “Master Effect 5" to indicate this special Master effect mode.
Dither is always applied post Master bus fader. The control panel comes up as “Master Effect 5" to indicate this special Master effect mode.
The following options can be set in the Apogee UV 22 Control Panel:
Option Description
Normal Try this first, it is the most “all-round” type.
Low This applies a lower level of dither noise.
Autoblack On When this is activated the dither noise is gated (muted) during silent passages in the material.
P
Apogee UV 22 always dithers to 16 bit resolution.







